High Voltage Hybrid Cars, Buses and Trucks 2021-2041高電圧ハイブリッド車両、バスとトラック 2021-2041年 Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) have seen a significant growth in sales over recent years and the HEV market is set to increase in 2020 despite the implications of COVID-19 on the global automo... もっと見る

※価格はデータリソースまでお問い合わせください。
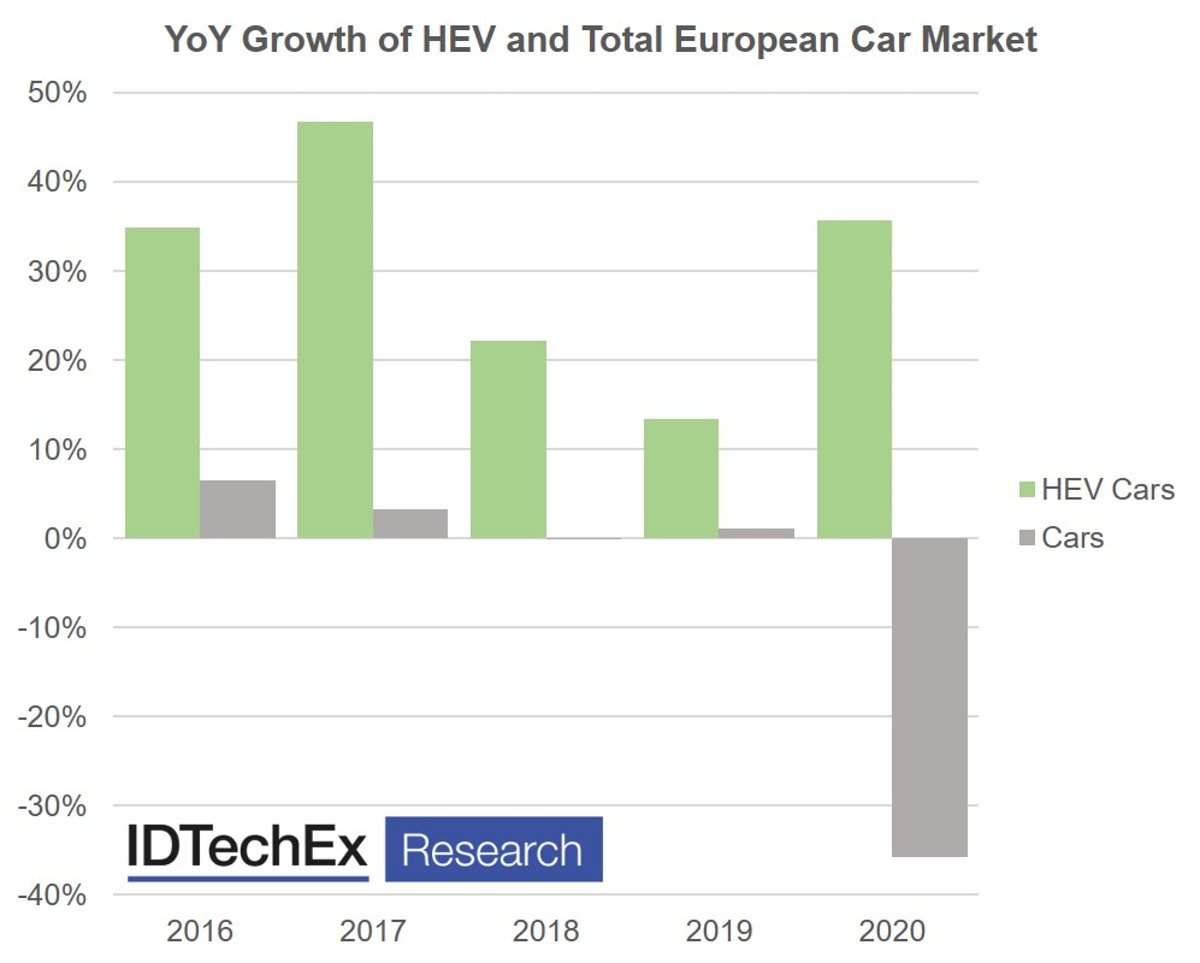
SummaryHybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) have seen a significant growth in sales over recent years and the HEV market is set to increase in 2020 despite the implications of COVID-19 on the global automotive industry. These HEVs or "self-charging hybrids" (hybrids which do not plug-in but have electric-only driving modes), provide for the consumer that wants reduced fuel consumption and CO2 emissions but isn't completely convinced by the proposition of plug-in vehicles. This could be due to the increased cost of battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs), or the potential lack of charging capabilities at their residence. Either way, the HEV presents a good opportunity in the short term for these consumers.
This report from IDTechEx gives a granular breakdown of the HEV market in Japan, Europe, the US, China and South Korea. Cars, buses, trucks and light commercial vehicles (LCVs) are detailed along with their battery and motor-generator technologies. The report is highly data-driven: an extensive HEV car model database of over 80 HEV models sold between 2015-2019 was created by IDTechEx to determine trends in historic sales, battery capacity, motor-generator power and number, market share and market value. Historic sales data for each of the vehicle categories provides unique insight into the future: the report provides detailed forecasts for sales, battery demand, motor-generator demand and market value out to 2041 split by key geographical regions. HEVs can also aid manufacturers: with CO2 emissions targets becoming stricter worldwide, sales of HEVs can serve to lower the overall CO2 output of a manufacturers' fleet and help to avoid the related fines. In fact, in Europe, the report finds several automotive manufacturers are not going to meet the emissions targets and will have to either purchase credits from other manufacturers or face large fines. The CO2 reduction benefits of HEVs are nowhere near that of BEV and PHEV drivetrains but the technology is more mature, making it a potential stop-gap to meet these targets in the short-term. Japan has historically been the strongest market for HEVs with the likes of Toyota, Honda and Nissan all playing significant roles. However, it is expected that Europe will overtake Japan in 2020, even if the majority of HEV sales still come from Japanese manufacturers. Whilst it appears that Europe will remain the largest HEV market for some time, it is an inherently limited one. Several European countries have set out plans or regulations to ban the sales of new ICE vehicles in the 2030s. Several have not made their stance clear on HEVs and PHEVs, but some have. The UK for example is aiming to have no vehicles with combustion engines of any form being sold from 2030. Given that the EU is such a strong market for HEVs, this could drive the trend worldwide. HEVs do not only have to contend with impending regulations, but also with competition from other drivetrain technologies. Of course, PHEVs present much better fuel consumption and CO2 emissions figures (at least under testing standards), but there is also a threat from the rise of 48V hybrid technology, for which some are promising 80% of HEV performance for 30% of the powertrain cost (see the IDTechEx report: 48V Full Hybrid, 48V Mild Hybrid, 48V BEV Cars: Markets, Technology Roadmap 2021-2041). All three could potentially be limited by future fossil fuel bans, but PHEVs are certainly looked upon more favourably and the 48V mild hybrids present an easier integration challenge to improve CO2 emissions and fuel economy quickly. There are several factors that could potentially cause a massive growth of the HEV market but also a rapid decline. This report from IDTechEx considers extensive historic data, analysing trends and looks forwards at the potential for HEVs to help meet emissions targets before the fossil fuel bans are enacted across various regions. Forecasts for 2021-2041 are given for HEV cars, buses and trucks across the various quantities listed below, allowing for a deep-dive into the HEV market now and for the future. Report Summary Market assessments:
Historic and Forecast lines: units, battery demand, motor-generator demand and market value (2015-2041):
Table of Contents
|