Off-Grid Charging For Electric Vehicles 2024-2034: Technologies, Benchmarking, Players and Forecasts電気自動車向けオフグリッド充電 2024-2034年:技術、ベンチマーク、プレーヤー、予測 この調査レポートでは、電気自動車向けオフグリッド充電のためのいくつかの技術オプションの評価とベンチマークを行っています。 主な掲載内容(目次より抜粋) ユーティリティ・... もっと見る
※ 調査会社の事情により、予告なしに価格が変更になる場合がございます。
Summary
この調査レポートでは、電気自動車向けオフグリッド充電のためのいくつかの技術オプションの評価とベンチマークを行っています。
主な掲載内容(目次より抜粋)
Report Summary
This report assesses and benchmarks several technology options for off-grid EV charging and provides in-depth market coverage and interviews of a range of players in this rapidly growing industry. As BEV uptake increases, utility grids are becoming increasingly strained, leading to growing concerns about the capacity of distribution networks being able to support the necessary roll-out of EV charging infrastructure. Additionally, the expansion of electrification in new sectors such as construction presents unique challenges and opportunities in charging requirements. To address these issues, grid-independent charging systems are being developed and deployed, and IDTechEx's report contains extensive coverage and analysis of technology and players.
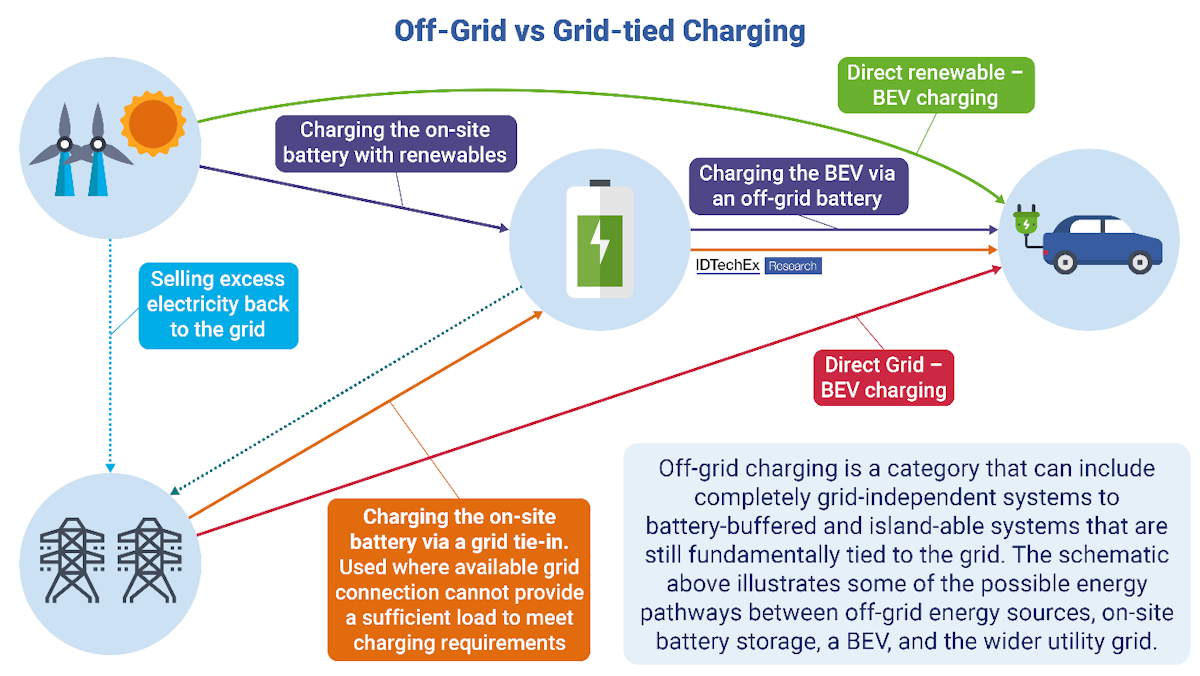
Off-grid: Battery and Renewables Integration
One of the key aspects of any renewables-based charging is dealing with the problem of intermittency (wind and solar in particular). This is usually done via integrating an on-site battery, which increases the energy capacity of the system and thus possible charging rates. This can be extended into hybrid systems, where energy can be distributed back to the grid in times of excess generation, or when the charging requirements increase the power that can be drawn from the grid.
Photovoltaic Canopies and Hydrogen Generators are the renewables of choice
A wide range of fully off-grid and hybrid solutions are emerging to the market, powered by a range of energy sources. Solar canopy chargers are currently the most mature market and offer 100% renewable electricity without any infrastructure required. Hydrogen fuel cell technology is increasingly prevalent in distributed generation and is seen by many advocates as a green alternative to polluting and carbon-intensive diesel generators. Hydrogen generators offer temporary and high-powered outputs, which IDTechEx believes offers strong value propositions to the growing numbers of electric construction vehicles.
Alternative Energy Sources - AWE, LNG and beyond
IDTechEx's report also covers a range of alternative energy sources, such as airborne wind energy (AWE), conventional wind, and fossil fuels. IDTechEx benchmarking assesses the relative strengths and weaknesses of each technology within this report, considering aspects such as power per unit area, OPEX, CAPEX, complexity of installation, stability of power and more. The results of this analysis are disseminated in this report.
End Use Sectors - Construction and Fleet
IDTechEx research indicates that fleet operators seeking to electrify their vehicles are facing increasing challenges in sourcing sufficient electrical power to fuel their operations. This problem is often exacerbated by the lack of available infrastructure in their depts - put simply, these locations were never built to require electricity to charge vehicles. Grid upgrades are also slow and prohibitively expensive, with the average wait time to get a grid connection in the US approaching 4 years. As net-zero targets get stricter and the push for electrification grows, infrastructure is expected to be required much quicker than the grid can be built out. In this context, off-grid charging presents itself as a strong candidate for supplying this power without having to resort to carbon-intensive diesel generators. Powering BEVs with diesel is not only inefficient but potentially damaging to the EV reputation as a cleaner alternative to ICEs. In most cases grid electricity will always be cheaper and more stable than on-site renewable generation, however hybridized integration of a range of energy sources can 'augment' the existing grid connection. A common example IDTechEx encountered in its research was fleet and public highway operators how had a limited grid connection but wished to enable faster and more outlets. A grid upgrade can take up to several years, but integration of hybrid charging systems can provide the necessary power boost, potentially on a temporary basis whilst improvement works are carried out. This has applications for mission critical fleets, who wish to be insulated from potential power outages. By charging from a combination of grid power, renewables charged batteries, and an emergency fuel-cell, energy security can be enhanced.
As construction goes electric diesel generators are phased out
IDTechEx identifies the electrification of the construction industry as a key opportunity for off-grid charging hardware. The larger and more powerful vehicles will require large quantities of electrical energy, and high-power outputs to charge quickly and minimize vehicle downtime. As construction sites are by their nature often in undeveloped areas, sourcing grid power is likely to be a challenge, especially as the temporary nature of these sites negates the value of building out grid capacity. In this context, hydrogen generator units offer a combination of high-power outputs, temporary installation and scalable amounts of fuel. Diesel generators also emit noise and particulate pollution (NOx), and it is expected that regulations, especially in urban areas will become tougher. IDTechEx therefore expects there to be a significant opportunity for off-grid charging to emerge as the choice solution for electric construction vehicles.
This report provides technical analysis and business intelligence about the emerging off-grid EV charging market. This includes:
A review of the context of off-grid EV charging, a ageing and strained utility grid
Assessment of the state of utility grids by key regions, including market players and key supply constraints. An assessment of the likely impacts of BEV uptake, as well as current and proposed grid load management strategies.
Grid component upgrade timelines, annual expenditure in grid growth by region.
Technical analysis and benchmarking of key off-grid technologies, solar hydrogen and wind
Player coverage including Beam Global, Paired Power, AFC Energy, GeoPura, GenCell, KitePower and many more.
In depth independent technical assessment of relative strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of the differing solutions. Considerations include installation size and complexity, CAPEX, OPEX, stability, green credentials and other parameters.
Granular 10-year forecasts by sector and region
In-depth and granular forecasts across various end-use sectors including construction, fleet operators, and public. Regional resolution includes key regions such as Europe (further breakdowns included), USA, China and RoW. Unit installations, market revenues, and hydrogen requirements in Mtpa over 10 years.
Table of Contents
|




.png)
.png)
