Autonomous Cars, Robotaxis & Sensors 2022-2042自律走行車両、ロボッタクシー、センサー 2022-2042年 この調査レポートは、自律走行車とロボッタクシー市場について詳細に調査・分析しています。 主な掲載内容(目次より抜粋) 全体概要と結論 はじめに規制と立法の進... もっと見る
※価格はデータリソースまでお問い合わせください。
Summary
この調査レポートは、自律走行車とロボッタクシー市場について詳細に調査・分析しています。
主な掲載内容(目次より抜粋)
Report Summary
In recent years, vast improvements to autonomous vehicle technologies such as radar, lidar, HD cameras and software have propelled robotaxis to the cusp of market-readiness. Autonomous trials from Waymo, Cruise, and others are now evolving into autonomous services, with legislative barriers clearing. New IDTechEx forecasts reveal how these services will come to dominate within 20 years, creating massive opportunities for the underlying sensors market, which grows at over 30% CAGR.
Autonomous Vehicles
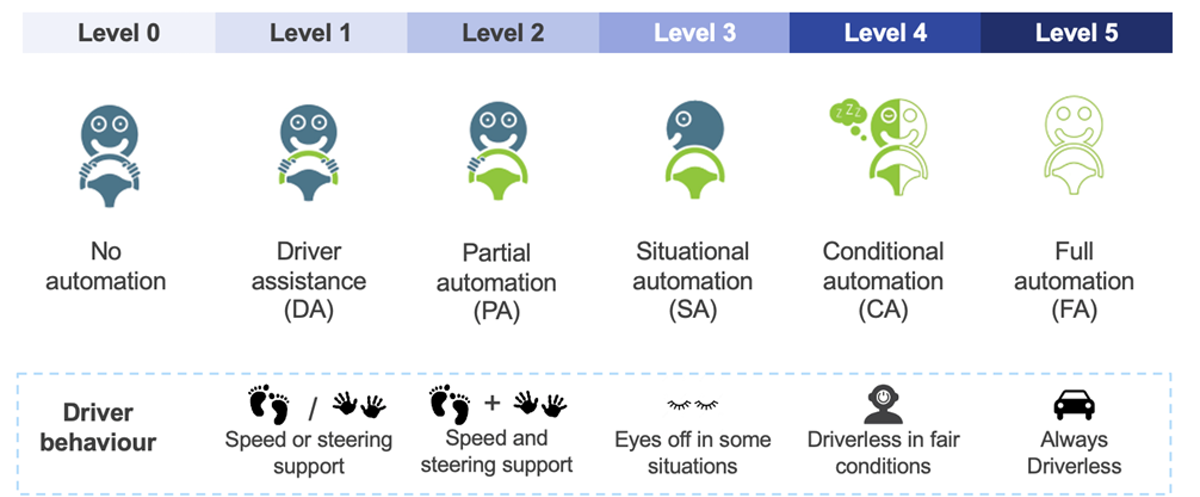
'Autonomous vehicle' (AV) is an umbrella term for the six levels as defined by the SAE. Today, most new cars are arriving with the option of level 2 functionality, and the industry is technically ready for level 3 once regulatory hurdles clear.
Some regions are even pushing for level 4 technology, but most activity here is still with autonomous mobility start-ups and in trial stages. Overall, the report finds autonomous vehicles will become a massively disruptive technology which will grow rapidly at a rate of up to 47% to transform the auto market over the next two decades.
SAE's six levels of autonomy. Source: SAE, IDTechEx
Generally, there are two pathways to full autonomy: incremental progression through the SAE levels, the path taken by established OEMs; and direct to level 4 with autonomous trialling (typically with retrofitted vehicles) with the aim to provide mobility-as-a-service (MaaS), the path taken by the start-ups. In both areas, the report finds significant growth and progression in Europe, the US and China.
Regulatory Hurdles Overcome
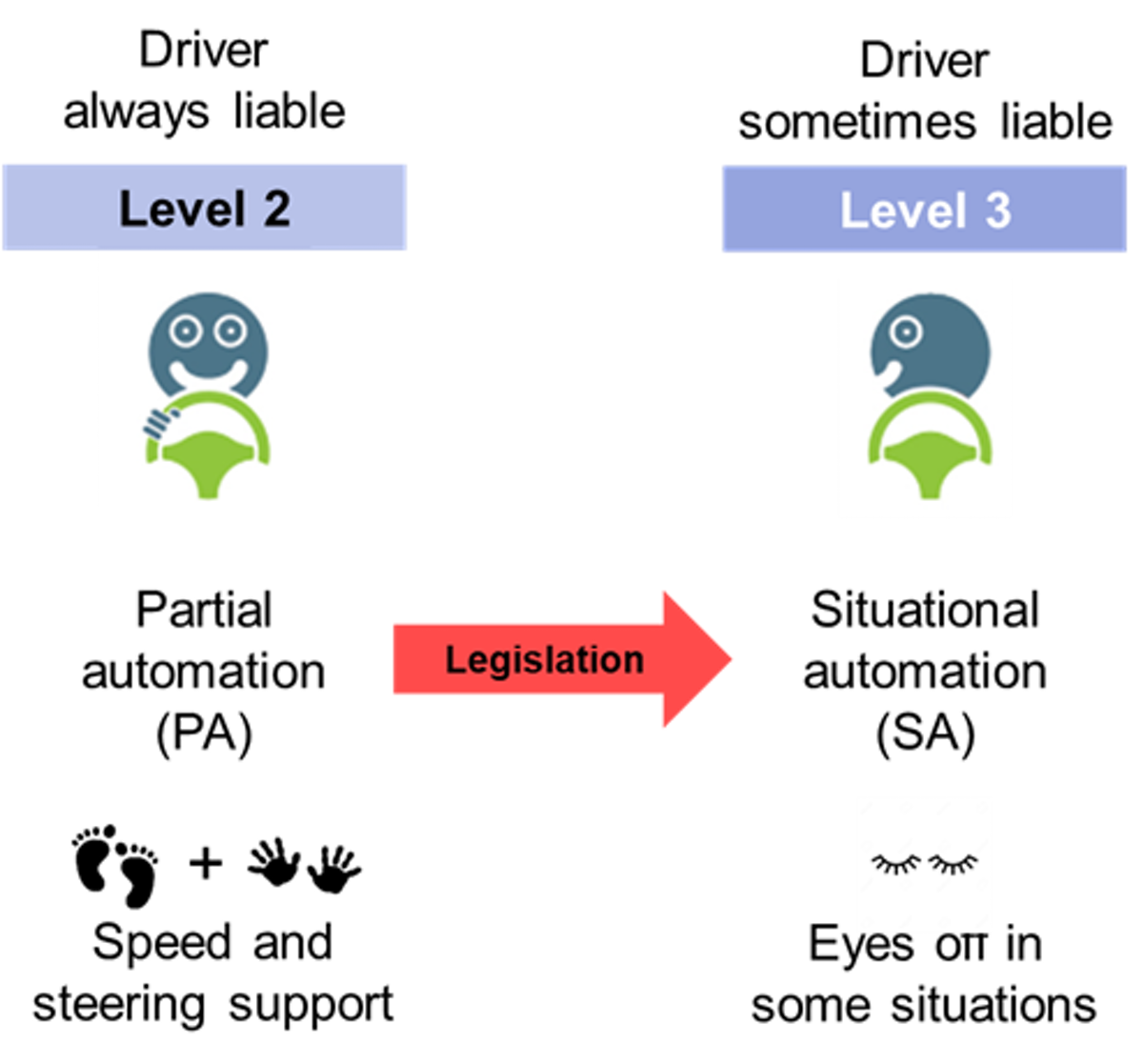
Level 3 technology has been ready since 2017, however automakers have not been able to release these autonomous features due to legislation, which has had unclear definitions about how the technology should work, and liability in the event of an accident.
Recently, regulations have started to improve, allowing some regions such as Japan, Germany and the UK to have level 3 vehicles on their roads by the end of 2021. IDTechEx expects significant adoption of level 3 and level 4 technology within the car market over the next 10-20 years, radicalising the way society travels and causing huge disruption to the auto sector's century old business models.
Source: IDTechEx
Market Leaders
Within this report, we analyse the strategies of OEMs and their attitudes towards autonomising their models, what features they are bringing and what sensor suites they are using, including solid state LiDAR, mechanically rotating LiDAR, radar, imaging radar, cameras, short wave infrared (SWIR) thermal cameras and more. Honda and Mercedes are the leaders here, with Honda releasing a level 3 vehicle into the Japanese market and Mercedes preparing a level 3 release in Autumn 2021. GM and Tesla are close behind with level 3 cars in waiting (technically ready but held back by regulations). In China Arcfox and Xpeng are pushing for level 3 to level 4 vehicles, but are again held back by regulations.
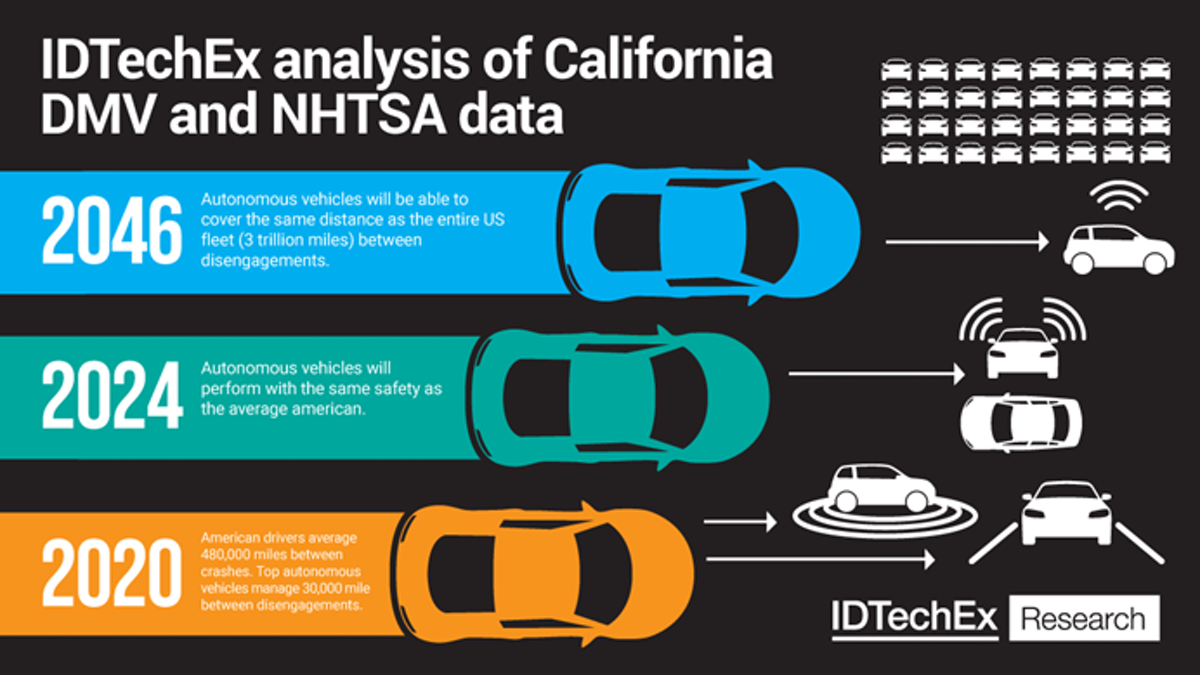
The leaders of the mobility start-ups such as Waymo, Cruise, Baidu and AutoX are well established, and their trials are progressively transforming into commercial services. From analysis of the top performing players since 2015, IDTechEx predicts that autonomous driving systems will be on par with human safety levels by the end of 2023.
Given the current state of trials and existing plans for further expansion from key players, IDTechEx believes 2023 will be the start of the AV revolution. IDTechEx expects that the trials will grow within their existing cities and then spread from city to city much in the same way as ride-hailing platforms (Uber, Lyft, Didi etc.) over the past decade. IDTechEx reports on the activity of the key autonomous players, their response to the COVID-19 crisis and their latest sensor suites.
Source: IDTechEx
Sensor Trends
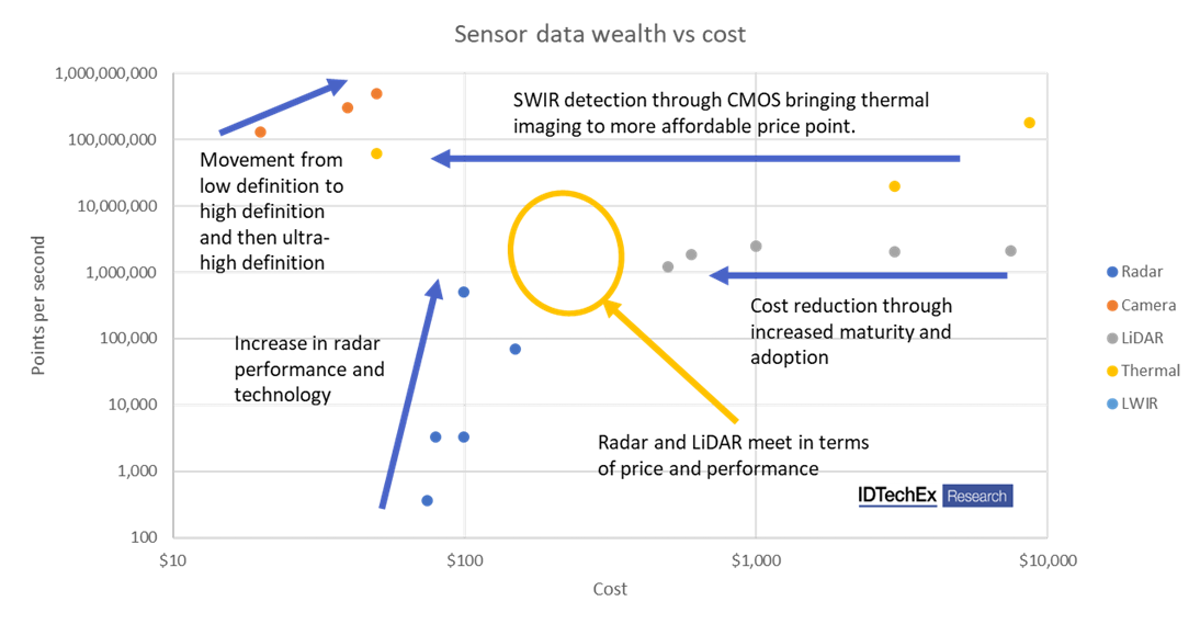
The report finds that autonomy will create massive opportunities in the automotive sensors industry. IDTechEx reports on the progress in cameras (including infrared and event-based detection), radar, LiDAR and supporting technologies such as connectivity and teleoperation. Within the key three sensors we see adoption of higher resolution cameras and higher frame rates, advancements in the performance and power of radar and significant cost reductions in LiDAR. Our analysis is based on primary information, with the report containing 8+ primary interviews from key players.
Source: IDTechEx
Key topics covered:
Table of Contents
|