協働ロボット2025-2045:技術、プレーヤー、市場Collaborative Robots 2025-2045: Technologies, Players, and Markets 協働ロボットは、物理的な柵なしに人間の隣で作業できるように設計された、軽量で動きの遅いロボットの一種で、その柔軟性と、人間を工場に呼び戻す取り組み、インダストリー5.0、メイド・イン・チャイナ2025... もっと見る

※ 調査会社の事情により、予告なしに価格が変更になる場合がございます。
サマリー
協働ロボットは、物理的な柵なしに人間の隣で作業できるように設計された、軽量で動きの遅いロボットの一種で、その柔軟性と、人間を工場に呼び戻す取り組み、インダストリー5.0、メイド・イン・チャイナ2025、そして二酸化炭素排出量の削減を目指す大手企業の多くの発表のおかげで、大きな勢いを得ている。
協働ロボット(コボット)は、低コスト、設置面積の小ささ、プログラミングの容易さ、柔軟性、消費電力の低さにより、中小企業(SME)にとって理想的な選択肢である。大企業が工場に人を呼び戻すことを目指す中、コボットの採用はますます進むと予想される。さらに、マシンビジョンや音声認識などのAIの進歩により、コボットの機能追加やソフトウェアの遠隔更新が可能になる。コボットがダッシュボード部品の組み立て、表面の研磨、溶接、ネジ締めなどに使用できる自動車産業などの伝統的な産業が、コボットの主な用途となっている。コボットはまた、食品・飲料、半導体・電池の品質検査、包装・パレタイジング、機械操作など、他の産業や作業にも使用できる。IDTechExの調査レポート「協働ロボット2025-2045:技術、プレーヤー、市場」は、自動車組立、表面研磨、ネジ締め、射出成形、PCプロセッサー検査、電話チップ検査、電話組立、ウェアラブルデバイス組立、PCB組立、包装、リチウムイオン電池産業などの用途と産業について深く掘り下げている。また、主要な実現技術、プレーヤー、市場について詳細な分析を行い、今後20年間のきめ細かな市場規模・数量予測を掲載しています。
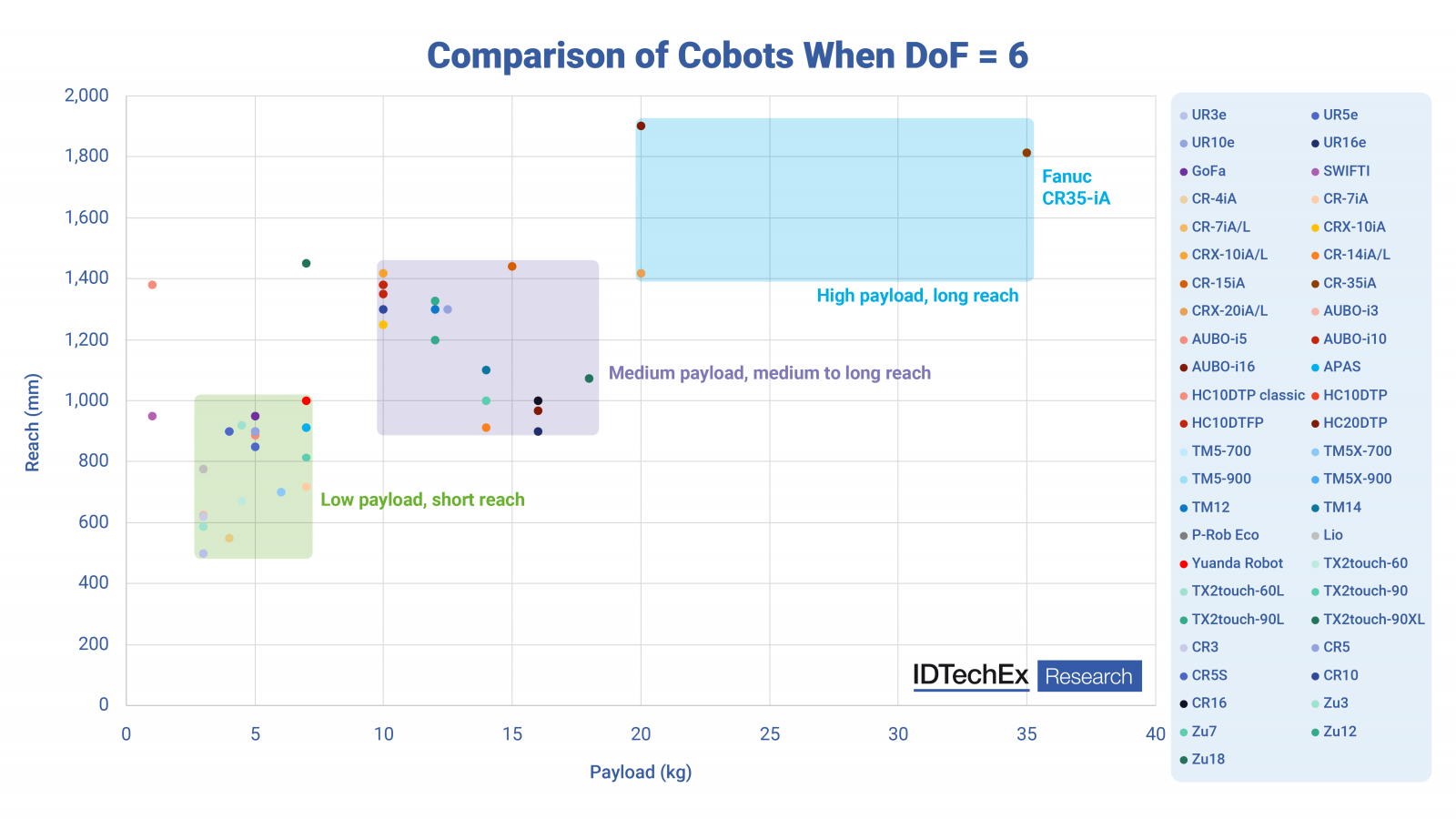
ペイロード、リーチ、再現性に基づいて、市販の6自由度コボットを詳細に分析。
出典:IDTechEx
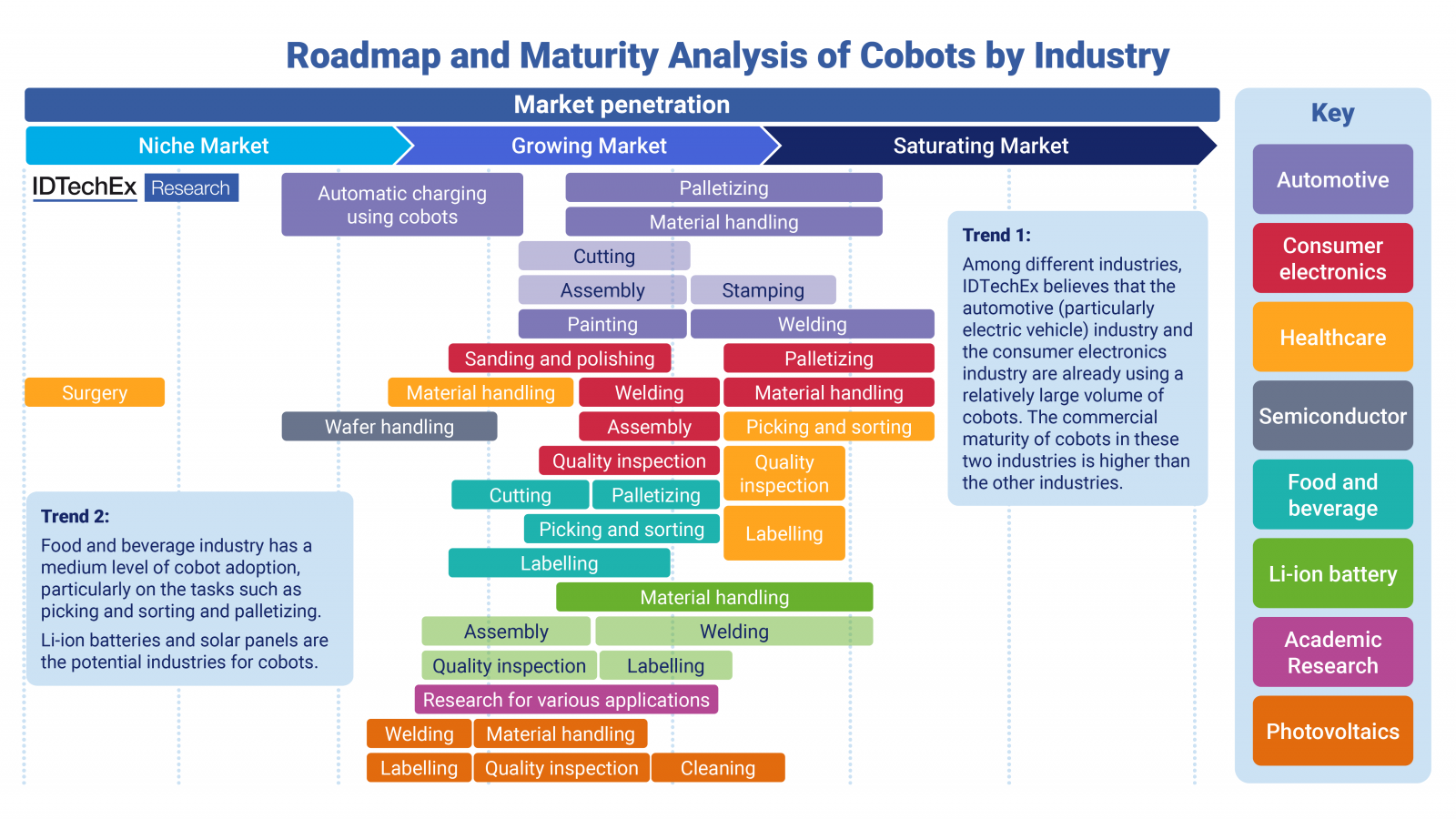
コボットは多くの産業で利用されている。これらの産業におけるコボットの技術と市場の準備レベルは異なっており、IDTechExはさまざまな産業とタスクにおけるコボットの成熟度をまとめている。
自動車産業はコボットの最も顕著な用途である。コボットは、自動車の組み立て(溶接、ダッシュボードの組み立てなど)、表面研磨、ネジ締めなどの複数の作業に使用できる。電気自動車の普及に伴い、既存の自動車製品ラインの多くが改造や再構築を必要としている。自動車OEMの悩みの一つは、産業用ロボットが1台でも故障すると、人間のオペレーターが点検のためにロボットの作業ゾーンに安全に入れるようにするため、生産ライン全体が停止してしまう危険性があることだ。このプロセスは、大きなダウンタイムコストにつながっている。例えば、フリーモント工場でテスラ・モデル3を生産するのにかかる時間は約90分なので、生産ラインが数時間停止すれば莫大な損失につながる。このような潜在的な問題を軽減するために、コボットは理想的なソリューションとなり得る。コボットは、重作業を行う産業用ロボットを完全に置き換えることはできないものの、人間のオペレーターと緊密に連携し、柔軟に作業することができるからだ。一方、大手自動車メーカー(アウディ、フォルクスワーゲンなど)は、人間とロボットの相互作用を改善することで生産の柔軟性を高めることを目指す「インテリジェント工場」計画を提案している。IDTechExは、自動車産業におけるコボットの市場規模は今後20年間で年平均成長率22%で成長すると予測している。
タスク別、産業別のコボット市場浸透度の分析。
出典:IDTechEx
自動車産業だけでなく、コボットは食品・飲料など他の産業でも可能性があり、多品種少量生産にコボットが使用され、柔軟性が向上する。2024年の現段階では、包装のほとんどはまだ手作業で行われている。食品・飲料産業は歴史的にコボットの主要ターゲット産業ではなかったが、IDTechExは今後20年間、より多くのコボットメーカーがロングテール戦略を採用し、食品・飲料産業への取り組みを強化し始めると見ている。大きな市場ポテンシャルがあるにもかかわらず、IDTechExは、これらの業界の企業の限られた予算、限られた技術力、投資回収時間に対する理解不足などの課題を目の当たりにしてきた。この課題を軽減するため、一部のコボットOEMは、ユーザーが最初に試して後で購入できるコボット・アズ・ア・サービス・モデルを提案している。詳細は「協働ロボット2025-2045:技術、プレーヤー、市場」レポートに記載されている。
本レポートでは、半導体産業やリチウムイオン電池リサイクル産業などの新興産業を含む、その他多くの産業も取り上げている。これらの産業はここ数年で大きな成長を遂げている。インフィニオンのクリーンルームにおけるKUKAのcobotのように、半導体クリーンルームでのcobot使用の成功例もあるが、IDTechExはいくつかのハードルを指摘している。例えば、コボットが半導体製造環境の厳しい清浄度要件を満たすようにするのは難しいかもしれない。また、現在のコボットは、半導体製造に必要な超精密作業に苦戦する可能性があり、さらなる技術的進歩が必要となる。半導体産業におけるコボットに関する課題と今後の動向は、「協働ロボット2025-2045:技術、プレーヤー、市場」レポートでご覧いただけます。これとは対照的に、リチウムイオン電池のリサイクル業界も、現段階では採用率は低いものの、コボット活用の可能性を見出している。使用済みバッテリーのリサイクルは重要な市場であり、生産されるバッテリー数の増加により大幅な成長が見込まれている。しかし、バッテリーの分解プロセスでは標準化が進んでいないため、現在のところ、この業界ではコボットの利用は限られている。
さらに、コボットの基本はセンサーやソフトウェアなどの技術にある。センサーは協働ロボットを実現する最も重要な技術の一つである。安全性のためにコボットに使用される最も典型的なセンサーはトルクセンサーで、センサー値の範囲があらかじめ設定されており、衝突が発生した場合、値が範囲を超えるとロボットの緊急停止がトリガーされる。しかし、IDTechExは、安全性を提供するための多くの新興センサー(触覚、近接など)に注目しているが、これまでのところ市場で広く採用されていない。
エンドエフェクタは、ロボットとそのタスクとのインタラクションを可能にするために設計されています。エンドエフェクタは、作動原理によって、機械部品と電気機械部品に分類されます。典型的なエンドエフェクターには、グリッパー、プロセスツール、センサーなどがあります。IDTechExは、コボットの採用が進むにつれてエンドエフェクター市場が拡大するとみている。ただし、異なるコボットがエンドエフェクターを共有できるため、エンドエフェクター市場はコボット市場よりも早期に飽和すると考えている。
過去のコボット市場規模。出典:IDTechEx
主要側面
技術動向とコボットプレーヤーの分析:
市場予測と分析:
Summary
この調査レポートは、自動車組立、表面研磨、ネジ締め、射出成形、PCプロセッサー検査、電話チップ検査、電話組立、ウェアラブルデバイス組立、PCB組立、包装、リチウムイオン電池産業などの用途と産業について詳細に調査・分析しています。
主な掲載内容(目次より抜粋)
Report Summary
Collaborative robots, a type of lightweight and slow-moving robot designed to work next to human operators without a physical fence, has gained significant momentum thanks to their flexibility and the initiatives of bringing humans back to factories, industry 5.0, made in China 2025, and many announcements from leading companies of reducing carbon footprint.
Collaborative robots (cobots) are ideal options for small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs) thanks to their low costs, small footprint, ease of programming, flexibility, and low power consumption. As the large companies aim to bring people back to their factories, cobots are expected to be increasingly adopted. Further, the advancement of AI, such as machine vision and voice recognition, enable additional functions and remote software updates of cobots. Traditional industries such as the automotive industry where cobots can be used for assembling dashboard components, polishing surfaces, welding, and screwing, have been the primary cobot applications. Cobots can also be used for other industries and tasks such as food and beverage, semiconductor and battery quality inspection, packaging and palletizing, and machine tending. IDTechEx's report on "Collaborative Robots 2025-2045: Technologies, Players, and Markets", takes a deep dive into the applications and industries including car assembly, surface polishing, screwing, injection molding, PC processor inspection, phone chip inspection, phone assembly, wearable device assembly, PCB assembly, packaging, and Li-ion battery industry. The report also conducts an in-depth analysis of the key enabling technologies, players, and markets with granular market size and volume forecast over the next 20 years.
A granular analysis of the commercially available 6 degrees of freedom cobots based on their payloads, reaches, and repeatability. Source: IDTechEx
Cobots have found usage across many industries. The technology and market readiness levels of cobots in these industries differ, and IDTechEx has summarized the level of maturity of cobots across different industries and tasks.
The automotive industry is the most prominent application of cobots. Cobots can be used for multiple tasks including car assembly (e.g., welding, assembling dashboards, etc.), surface polishing, and screwing. With the increasing popularity of electric vehicles, many existing car product lines need retrofitting or reconstruction. One of the pain points of automotive OEMs is that if one industrial robot malfunctions, the entire production line risks of getting shut down to ensure human operators can safely enter the robot working zone for inspection. This process leads to a significant downtime cost. For instance, it takes around 90 minutes to produce a Tesla model 3 at the Fremont factory, so if the production line is down for a few hours, then it will lead to a huge loss. To mitigate these potential issues, cobots can be the ideal solution as they can work closely and flexibly with human operators despite that they cannot fully replace industrial robots for heavy-duty tasks. Meanwhile, large automotive manufacturers (e.g., Audi, Volkswagen, etc.) have proposed "intelligent factories" plans where they aim to enhance the flexibility of their production by improving human-robot interaction. IDTechEx forecasts that the market size of cobots in the automotive industry will grow at a CAGR of 22% over the next 20 years.
Analysis of cobots market penetration by different tasks and industries. Source: IDTechEx
Further to the automotive industry, cobots also pose potential in other industries such as food and beverage where cobots are used for high-mix low-volume production for improved flexibility. At this stage in 2024, most of the packaging is still done manually. Although the food and beverage industry has historically not been the primary target industry for cobots, IDTechEx noticed that more cobot makers would start to use a long-tail strategy and make increasing efforts in the food and beverage industry for the next 20 years. Despite the significant market potential, IDTechEx has seen challenges such as limited budget from companies in these industries, limited technical capabilities and lack of understanding of the payback time. To mitigate this challenge, some cobot OEMs have proposed a cobot-as-a-service model where users can try first and buy later. More details are included in the "Collaborative Robots 2025-2045: Technologies, Players, and Markets" report.
The report also covers many other industries, including a few emerging ones such as the semiconductor industry and the Li-ion battery recycling industries. These industries have experienced significant growth over the past few years. Despite some successful examples of using cobots in semiconductor cleanrooms, such as KUKA's cobot in Infineon's cleanroom, IDTechEx has noted a few hurdles. For instance, it can be challenging to ensure that cobots meet stringent cleanliness requirements for semiconductor manufacturing environments. Current cobots may also struggle with ultra-precise tasks required in semiconductor production, necessitating further technological advancements. More challenges and future trends on cobots in the semiconductor industry can be found in the "Collaborative Robots 2025-2045: Technologies, Players, and Markets" report. Li-ion battery recycling industry, in contrast, has also seen potential of using cobots despite the low adoption rate at this stage. End-of-life battery recycling has been a significant market and is expected to grow substantially due to the increasing number of batteries being produced. However, cobots only has limited usage in this industry as of today because of the lack of standardization in battery disassembly process.
Further to the applications, the fundamentals of cobots lie in the technologies, such as sensors and software. Sensors are one of the most important enabling technologies for collaborative robots. The most typical sensors used in cobots for safety are torque sensors, where a range of sensor values are pre-set, and if a collision occurs, the values will exceed the range, which triggers the robot's emergency stop. However, IDTechEx has noticed a number of emerging sensors (e.g., tactile, proximity, etc.) to provide safety, but they have not been widely adopted in the markets so far.
End-effectors, also known as end-of-the-arm-tooling, are designed to enable robots to interact with their tasks. End-effectors can be classified as mechanical or electromechanical components depending on actuation principles. Typical end-effectors include grippers, process tools, and sensors. IDTechEx believes that the end-effector market will increase with the increasing adoption of cobots. However, since different cobots can share end-effectors, we think the end-effector market will saturate earlier than the cobot market.
Historic cobots market size. Source: IDTechEx
Key Aspects
Technology trends & cobot players analysis:
Market Forecasts & Analysis:
Table of Contents
ご注文は、お電話またはWEBから承ります。お見積もりの作成もお気軽にご相談ください。本レポートと同分野(ロボット)の最新刊レポート
IDTechEx社の ロボティクス - Robotics分野 での最新刊レポート
よくあるご質問IDTechEx社はどのような調査会社ですか?IDTechExはセンサ技術や3D印刷、電気自動車などの先端技術・材料市場を対象に広範かつ詳細な調査を行っています。データリソースはIDTechExの調査レポートおよび委託調査(個別調査)を取り扱う日... もっと見る 調査レポートの納品までの日数はどの程度ですか?在庫のあるものは速納となりますが、平均的には 3-4日と見て下さい。
注文の手続きはどのようになっていますか?1)お客様からの御問い合わせをいただきます。
お支払方法の方法はどのようになっていますか?納品と同時にデータリソース社よりお客様へ請求書(必要に応じて納品書も)を発送いたします。
データリソース社はどのような会社ですか?当社は、世界各国の主要調査会社・レポート出版社と提携し、世界各国の市場調査レポートや技術動向レポートなどを日本国内の企業・公官庁及び教育研究機関に提供しております。
|
|




.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)
