5G時代のRANオートメーション、SON、RIC、xApps、rApps:2024年2030年の機会、課題、戦略、予測RAN Automation, SON, RIC, xApps & rApps in the 5G Era: 2024 2030 Opportunities, Challenges, Strategies & Forecasts 概要 携帯電話インフラの中で最も高価で、技術的に複雑で、電力集約的な部分であるRAN(無線アクセス・ネットワーク)の自動化は、TCO(総所有コスト)の削減、ネットワーク品質の向上、収益創... もっと見る
日本語のページは自動翻訳を利用し作成しています。
サマリー
概要
携帯電話インフラの中で最も高価で、技術的に複雑で、電力集約的な部分であるRAN(無線アクセス・ネットワーク)の自動化は、TCO(総所有コスト)の削減、ネットワーク品質の向上、収益創出目標の達成を目指すモバイル事業者のデジタルトランスフォーメーション戦略の重要な側面である。AI(人工知能)やML(機械学習)と組み合わせることで、RAN自動化は、OpEx(営業費用)-収益比の削減、エネルギー消費の最小化、CO2(二酸化炭素)排出量の削減、回避可能なCapEx(設備投資)の延期、パフォーマンスの最適化、ユーザーエクスペリエンスの向上、新サービスの実現など、モバイルネットワークの経済性を大きく変革する可能性を秘めています。
RAN自動化市場の起源は、SON(Self-Organizing Network)技術が導入され、自己構成、自己最適化、自己回復によりセルラーネットワークの複雑性を軽減したLTE時代の始まりに遡る。ANR(自動隣接関係)などの組み込み型D-SON(分散型SON)機能がRAN製品の標準機能となっている一方で、ネットワーク全体のアクションのためにエッジノードから制御を抽象化するC-SON(集中型SON)ソリューションは、マルチベンダーの相互運用性、スケーラビリティ、遅延に関連する制約のため、世界の約800の国内移動通信事業者の3分の1未満しか採用されていません。
このような欠点に加え、携帯電話業界では、オープンインターフェース、共通情報モデル、仮想化、ソフトウェア駆動型ネットワーキングへの移行が進んでいるため、従来のD-SONやC-SONのアプローチから、標準ベースのコンポーネント、特にNear-RT(リアルタイム)およびNon-RT RIC(RANインテリジェントコントローラ)、SMO(サービス管理・オーケストレーション)フレームワーク、xApps(拡張アプリケーション)、rApps(RANアプリケーション)を使用したオープンRANオートメーションへの移行が進んでいます。
現在進行中のSONからRICへの移行に伴い、RAN自動化のユースケースも過去10年間で進化してきました。例えば、比較的基本的なMLB(Mobility Load Balancing)機能は、AI/ML主導の最適化アルゴリズムを利用して、無線リソースや周波数レイヤーのトラフィックを動的に管理・再分配することで、ネットワーク負荷やサービス利用のピークと谷間に効率的に適応する、より洗練されたポリシー誘導型トラフィックステアリング・アプリケーションへと変貌を遂げました。
5G時代には無線とセルサイトの密度が大幅に向上するため、エネルギー効率はRAN自動化の最も優先されるユースケースの1つとして浮上しています。先進的なモバイル事業者は、ネットワーク品質を低下させることなく、エネルギー消費、二酸化炭素排出量、運用コストを削減する持続可能性イニシアチブを推進しています。通信事業者コミュニティから大きな関心を集めているその他のユースケースには、ネットワークスライシングの実現、アプリケーションを考慮した最適化、異常検出などがあります。
ライブネットワークにおけるSONベースのRAN自動化のメリットはよく知られているが、RIC、SMO、x/rAppsのアプローチでは、さらに期待が高まっている。例えば、日本のブラウンフィールド事業者であるNTTドコモは、Open RANによる自動化によって、TCOを最大30%削減し、基地局の消費電力を最大50%削減できると見込んでいる。国内のライバルである楽天モバイルは、RICがホストするRAN自動化アプリケーションを使用して、ライブネットワークでセルあたり約17%の省エネをすでに達成していることは注目に値する。ラボでのトライアルが成功した後、このグリーンフィールド事業者は、より洗練されたAI/MLモデルを使って、節約率を25%まで高めることを目指している。
Open RANの自動化の取り組みは、過去数年間、フィールドトライアルの段階を越えて勢いを失っていたように見えたが、その後、いくつかの商業的な取り組みが登場し、Open RAN、目的別およびハイブリッドRAN環境全体で自動化された管理と最適化のためのSMO、Non-RT RICおよびrAppsに初期の焦点が当てられている。AT&Tは、エリクソンとの5年間の140億ドルのオープンRANインフラ契約の枠組みの中で、2つのレガシーC-SONシステムを置き換えるために、スウェーデンの大手通信会社のSMOとNon-RT RICソリューションを採用している。隣国のカナダでは、TelusもマルチベンダーのOpen RANの展開とともにSMOとRICプラットフォームの導入を開始し、RANフットプリントの最大50%を変革し、4G/5Gネットワークからファーウェイの機器を入れ替えました。
同様の取り組みは他の地域でも行われている。例えば、ヨーロッパでは、スイスコムがSMOとNon-RT RICプラットフォームを展開し、ブラウンフィールドのモバイルネットワークの将来性を高めるための幅広い取り組みの一環として、マルチテクノロジーのネットワーク管理と自動化機能を提供しています。オープンRANオートメーションは、ボーダフォン・グループの17万セルサイトのリフレッシュのためのグローバル入札の一部として導入される予定である。
新世代の独自SONベースRAN自動化ソリューションの展開も停滞していない。L4(Highly Autonomous Network:高度に自律的なネットワーク)運用の実現に向けて、China Mobileは最近、中国の河南省を皮切りに、階層型RAN自動化プラットフォームと関連するデジタル・ツイン・システムの導入を開始した。他の興味深い例としては、ソフトバンクが、日本全国のスタジアム、イベント会場、その他の戦略的な場所において、クラスタ全体のRAN最適化のための閉ループ自動化ソリューションを実装している。なお、日本の通信事業者は、将来的にRIC主催の集中型RAN最適化アプリケーションを採用する予定です。
さらに、ソフトバンク、ボーダフォン、ベル・カナダ、ベトテルなど、複数の携帯電話事業者の支援を受けて、RANベースバンドプラットフォーム内で、リアルタイムのインテリジェント制御と最適化のためのサードパーティ製アプリケーション(dApps(分散型アプリケーション)とも呼ばれる)を直接ホスティングするという考え方も普及し始めています。このアプローチに対抗するものとして、エリクソン、ノキア、ファーウェイ、その他の既存RANベンダーは、6G時代のAI/MLベースのエア・インターフェースという3GPPの長期ビジョンに沿って、AIとMLの機能をDU(分散ユニット)とCU(集中ユニット)製品に深く組み込むという段階的なアプローチでかなりの進歩を遂げている。
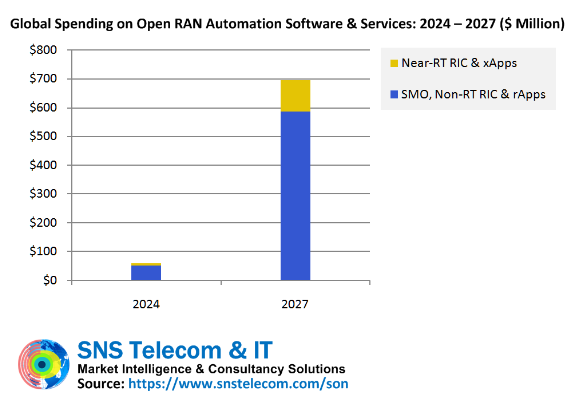
SNS Telecom & ITは、ブラウンフィールド事業者によるOpen RANインフラ展開の第2波に伴い、RIC、SMO、x/rAppsに対する世界の支出は2024年から2027年の間に年平均成長率125%以上で成長すると予測している。Open RANオートメーション市場は、SMO-to-Non-RT RICインターフェース、RICプラットフォーム間のアプリケーションポータビリティ、x/rApps間の競合緩和などの標準化ギャップや技術的課題が解決されるにつれて、2027年末までに最終的に年間投資額7億ドル近くを占めるようになる。オープンRANオートメーション、RANベンダーのSONソリューション、サードパーティのC-SONプラットフォーム、ベースバンド統合インテリジェントRANアプリケーション、RANプランニングおよび最適化ソフトウェア、テスト/測定ソリューションなど、広範なRANオートメーションソフトウェアおよびサービス市場は、同期間中に約8%のCAGRで成長する見込みです。
5G時代のRAN自動化、SON、RIC、xApps & rApps:2024 ?Opportunities, Challenges, Strategies & Forecasts」レポートは、バリューチェーン、市場促進要因、導入障壁、実現技術、機能分野、ユースケース、主要動向、将来ロードマップ、標準化、ケーススタディ、エコシステムプレーヤーのプロファイル、戦略など、RAN自動化市場の詳細な評価を掲載しています。また、2024年から2030年までのRANとエンドツーエンドのモバイルネットワーク自動化に関する世界と地域の市場規模予測も掲載している。予測は、3つのネットワーク領域、9つの機能領域、3つのアクセス技術、5つの地域市場をカバーしている。
本レポートには、関連するExcelデータシートが付属しており、本レポートに掲載されているすべての数値予測の定量データを網羅しています。
主な調査結果
本レポートの主な調査結果は以下の通りである:
SNS Telecom & ITは、ブラウンフィールド事業者によるOpen RANインフラ展開の第二波に伴い、RIC、SMO、x/rAppsに対する世界の支出は2024年から2027年の間に年平均成長率125%以上で成長すると予測している。Open RANオートメーション市場は、SMO-to-Non-RT RICインターフェイス、RICプラットフォーム間のアプリケーションポータビリティ、x/rApps間の競合緩和などの標準化ギャップや技術的課題が解決されるにつれて、2027年末までに最終的に年間投資額7億ドル近くを占めるようになる。
RAN 自動化ソフトウェアおよびサービス市場には、オープン RAN 自動化、RAN ベンダーの SON ソリューション、サードパーティの C-SON プラットフォーム、ベースバンド統合型インテリジェント RAN アプリケーション、RAN プランニングおよび最適化ソフトウェア、テスト/測定ソリューションなどが含まれ、同期間の年平均成長率は約 8%となる見込みです。
従来のD-SONおよびC-SONアプローチの欠点は、オープンインターフェース、共通情報モデル、仮想化、ソフトウェア駆動型ネットワーキングへのセルラー業界のシフトとともに、RANのプログラマビリティと自動化をより高いレベルで実現する標準ベースのコンポーネントを備えたOpen RANオートメーションへの移行を促しています。
オープン RAN オートメーションの動きは、アプリケーション開発者の多様なコミュニティからのイノベーションを刺激しています。SMO、Non-RT RIC、Near-RT RICの各製品を提供する十数社に加え、50社以上がxAppsやrAppsの開発に積極的に取り組んでいます。
モバイル事業者の中には、RAN自動化の専門知識をコモディティ化するために専門の事業部門を設立したところもある。NTTドコモのOREXブランドと楽天モバイルの姉妹会社である楽天シンフォニーは、その代表的な2つの有名なケースである。また、今後数年間は、ノースイースタン大学の zTouch Networks や TU Ilmenau の AiVader のように、商用グレードのオープン RAN オートメーションを提供する学術機関のスピンオフが増えると予想される。
SMOとRICのエコシステムは、ブロードコムによるVMwareの買収とHPEによるジュニパーネットワークスの買収計画によって、初期の統合の兆しを見せている。サードパーティのRAN自動化プラットフォームの商業的成功次第では、過去10年間のSONブームを彷彿とさせるM&A(合併・買収)の動きがさらに活発化すると予想される。
ライブネットワークにおけるSONベースのRAN自動化のメリットはよく知られていますが、RIC、SMO、x/rAppsのアプローチでは、さらに期待が高まります。例えば、日本のブラウンフィールド事業者であるNTTドコモは、Open RANによる自動化によって、TCOを最大30%削減し、基地局の消費電力を最大50%削減できると見込んでいる。
国内のライバルである楽天モバイルは、RICがホストするRAN自動化アプリケーションを使用して、ライブネットワークでセルあたり約17%の省エネをすでに達成していることは注目に値する。ラボでのトライアルが成功した後、このグリーンフィールド事業者は、より洗練されたAI/MLモデルを使って、節約率を25%まで高めることを目指している。
公共移動体通信事業者ネットワーク以外でも、垂直産業や民間無線セグメントでも関心が高まっている。米国防総省(DOD)は、商用および戦闘機の通信シナリオの両方で、オープンRANネットワークにおける広範なセキュリティ脅威を検出、分析、緩和する能力を強化するために、RICがホストするx/rAppsの可能性を積極的に模索している。他の例としては、台湾の電子機器メーカーであるInventec社が、スマート工場向けのプライベート5Gネットワークソリューションの一部として、屋内測位とトラフィックステアリング用のrAppsを組み込んでいる。
Open RANの自動化の取り組みは、過去2、3年の間、実地試験段階を越えて勢いを失っていたように見えたが、その後、いくつかの商業的な取り組みが登場し、Open RAN、専用RAN、ハイブリッドRAN環境全体で自動化された管理と最適化のためのSMO、Non-RT RIC、rAppsに初期の焦点が当てられている。
AT&Tは、エリクソンとの5年間の140億ドルのオープンRANインフラ契約の枠組みの中で、2つのレガシーC-SONシステムを置き換えるために、スウェーデンの大手通信会社のSMOとNon-RT RICソリューションを採用している。隣国のカナダでは、TelusもマルチベンダーのOpen RANの展開とともにSMOとRICプラットフォームの導入を開始し、RANフットプリントの最大50%を変革し、4G/5Gネットワークからファーウェイの機器を入れ替えました。
同様の取り組みは他の地域でも行われている。例えば、ヨーロッパでは、スイスコムがSMOとNon-RT RICプラットフォームを展開し、ブラウンフィールドのモバイルネットワークの将来性を高めるための幅広い取り組みの一環として、マルチテクノロジーのネットワーク管理と自動化機能を提供しています。オープンRANオートメーションは、ボーダフォン・グループの17万セルサイトのリフレッシュのためのグローバル入札の一部として導入される予定である。
新世代の独自SONベースRAN自動化ソリューションの展開も停滞していない。L4 自動化の実現に向けて、China Mobile は最近、中国の河南省を皮切りに、階層型 RAN 自動化プラットフォームと関連するデジタル・ツイン・システムの導入を開始しました。
他の興味深い例としては、ソフトバンクが、日本全国のスタジアム、イベント会場、その他の戦略的な場所で、クラスタ全体のRAN最適化のための閉ループ自動化ソリューションを実装しています。これは、従来のC-SONシステムの制御サイクルが15分であるのに対し、1~5分間隔でデータ収集とパラメータチューニングをサポートします。なお、日本の通信事業者は、将来的にRIC主催の集中型RAN最適化アプリケーションを採用する予定です。
さらに、ソフトバンク、ボーダフォン、ベル・カナダ、ベトテルを含む複数の携帯電話事業者の支援を受けて、RANベースバンドプラットフォーム内でリアルタイムインテリジェント制御および最適化のためのサードパーティアプリケーション(dAppsとも呼ばれる)を直接ホスティングするという考え方が普及し始めている。
このアプローチへの対抗策として、エリクソン、ノキア、ファーウェイ、その他の既存RANベンダーは、6G時代のAI/MLベースのエア・インターフェースという3GPPの長期ビジョンに沿って、AIやMLの機能をDUやCU製品に深く組み込むという段階的なアプローチでかなりの進歩を遂げています。
AI主導のRANパフォーマンスと効率の改善だけでなく、モバイル通信事業者、技術サプライヤー、その他の関係者は、資産利用を最大化するためにvRANとAIワークロードを同じ基盤インフラ上で共同ホストすることや、エッジAIサービスのプラットフォームとしてRANを活用することなど、AIとRANの融合によって可能になるTCOメリットと新たな収益機会にも照準を合わせている。
対象トピック
本レポートでは、以下のトピックを取り上げている:
RAN 自動化の紹介
バリューチェーンとエコシステム構造
市場促進要因と課題
RAN 自動化の機能領域
D-SON、C-SON、H-SON、Near-RT/Non-RT RIC、SMO、x/rApps、ベースバンド統合インテリジェント RAN アプリケーション、RAN プランニングおよび最適化ソフトウェア、テストおよび測定ソリューションなどの RAN 自動化テクノロジーとアーキテクチャ
70 以上の RAN 自動化ユースケースのレビュー、ANR、PCI、RACH の最適化から、高度なトラフィックステアリング、QoE ベースのリソース割り当て、省エネルギー、ネットワークスライシング、プライベート 5G の自動化、異常検知、動的 RAN セキュリティに至るまで、
70 を
超える
RAN
自動化ユースケースの
レビュー
SON から RIC への移行、クローズドループ自動化、インテントドリブン管理、運用 AI/ML、Gen AI など、インテリジェント RAN 実装の主要トレンド、data analytics and application awareness
Cross-domain mobile network automation enablers and application scenarios across the RAN, core and xHaul transport segments of cellular infrastructure
20件のプロダクショングレードRAN自動化導入の詳細なケーススタディと、従来のSONとOpen RAN自動化アプローチの両方をカバーする進行中のプロジェクトの検討
RAN自動化の今後のロードマップ
Standardization and collaborative initiatives
280社以上のエコシステム関係者のプロフィールと戦略、RAN インフラベンダー、SON、RIC、SMO プラットフォームプロバイダー、x/rApp 開発者、AI/ML テクノロジースペシャリスト、RAN プランニングおよび最適化ソフトウェアサプライヤー、テスト/測定ソリューションプロバイダーなど
RAN 自動化のバリューチェーン全体にわたる 10 社の独占インタビュー記録:AirHop Communications、Amdocs、Groundhog Technologies、Innovile、Net AI、Nokia、P.I. Works、Qualcomm、Rakuten Mobile、RIMEDO Labs
RAN自動化ソリューションプロバイダーおよびモバイル通信事業者への戦略的提言
2024年から2030年までの市場分析と予測
予測セグメンテーション
以下のサブマーケットとそのサブカテゴリーごとに市場予測を掲載しています:
モバイルネットワークオートメーションサブマーケット
RAN
モバイルコア
xHaul(フロントホール、ミッドホール&バックホール)トランスポート
RANオートメーション機能分野
SONベースのオートメーション
RANベンダーSONソリューション
サードパーティC-SONプラットフォーム
オープンRANオートメーション
非RT RIC & SMO
Near-RT RIC
rApps
xApps
ベースバンド統合インテリジェントRANアプリケーション
RANプランニング&最適化ソフトウェア
テスト&測定ソリューション
アクセス技術世代サブマーケット
LTE
5G NR
6G
地域市場
北米
アジア太平洋
欧州
中東&アフリカ
中南米
主な質問に対する回答
目次
Table of Contents
1 Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Executive Summary
1.2 Topics Covered
1.3 Forecast Segmentation
1.4 Key Questions Answered
1.5 Key Findings
1.6 Methodology
1.7 Target Audience
2 Chapter 2: An Overview of RAN Automation
2.1 What is RAN Automation?
2.1.1 Automating Repetitive Manual Tasks
2.1.2 RAN Analytics & Data-Driven Decision Making
2.1.3 AI (Artificial Intelligence) & ML (Machine Learning) Integration
2.1.4 SMO (Service Management & Orchestration) Frameworks
2.2 Levels of Automation in Intelligent RAN Implementations
2.2.1 L0 ? Manual Operation
2.2.2 L1 ? Assisted Management
2.2.3 L2 ? Partial Autonomous Network
2.2.4 L3 ? Conditional Autonomous Network
2.2.5 L4 ? Highly Autonomous Network
2.2.6 L5 ? Fully Autonomous Network
2.3 Functional Areas of RAN Automation
2.3.1 The SON (Self-Organizing Network) Concept
2.3.2 RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller), xApps & rApps
2.3.3 Native AI Capabilities in RAN Infrastructure
2.3.4 Automation-Assisted RAN Planning & Optimization
2.3.5 RAN Test & Measurement Solutions
2.4 RAN Automation Value Chain
2.4.1 Semiconductor & Enabling AI/ML Technology Specialists
2.4.2 RAN Infrastructure Vendors
2.4.3 SON, xApp/rApp & Automation Application Developers
2.4.4 RIC, SMO & OSS Platform Providers
2.4.5 RAN Planning & Optimization Software Suppliers
2.4.6 Test & Measurement Solution Providers
2.4.7 Wireless Service Providers
2.4.7.1 National Mobile Operators
2.4.7.2 Fixed-Line Service Providers
2.4.7.3 Private 5G Network Operators
2.4.7.4 Neutral Hosts
2.4.8 End Users
2.4.8.1 Consumers
2.4.8.2 Enterprises & Vertical Industries
2.5 Market Drivers
2.5.1 Growing Complexity of RAN in the 5G Era
2.5.2 Open RAN & vRAN (Virtualized RAN) Adoption
2.5.3 TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) Reduction
2.5.4 Energy Savings, Sustainability & Environmental Conservation
2.5.5 Popularity of Both Operational & Generative AI Technologies
2.5.6 Subscriber Experience & Network Performance Benefits
2.5.7 Network Slicing & New Revenue-Generating Opportunities
2.5.8 Proliferation of Shared Spectrum, Private 5G & Neutral Host Networks
2.6 Market Barriers
2.6.1 Service Provider Revenue Stagnation & Cost-Cutting Measures
2.6.2 Slow Pace of Brownfield RAN Reinvestment Cycles
2.6.3 Implementation-Related Technical Challenges
2.6.4 Standardization Gaps & Multi-Vendor Interoperability
2.6.5 Conflict Mitigation Between x/rApps
2.6.6 Dominance of Incumbent RAN Vendors
2.6.7 Conservatism & Trust in Automation
2.6.8 Network Security & Privacy Concerns
3 Chapter 3: RAN Automation Technology, Architecture & Use Cases
3.1 Traditional SON Solutions
3.1.1 Application Areas
3.1.1.1 Self-Configuration
3.1.1.2 Self-Optimization
3.1.1.3 Self-Healing
3.1.1.4 Self-Protection
3.1.1.5 Self-Learning
3.1.2 SON Architecture
3.1.2.1 D-SON (Distributed SON)
3.1.2.2 C-SON (Centralized SON)
3.1.2.3 H-SON (Hybrid SON)
3.2 Open Specifications-Based RIC, SMO, xApps & rApps
3.2.1 Architectural Elements
3.2.1.1 Near-RT (Real-Time) RIC
3.2.1.2 Non-RT RIC
3.2.1.3 SMO Framework
3.2.1.4 xApps (Extended Applications)
3.2.1.5 rApps (RAN Applications)
3.2.2 Open Interfaces
3.2.2.1 A1 Interface Between Non-RT RIC & Near-RT RIC
3.2.2.2 E2 Interface Between Near RT-RIC & RAN Nodes
3.2.2.3 O1 Interface for OAM (Operations, Administration & Maintenance)
3.2.2.4 O2 Interface for Cloud Infrastructure Management
3.2.2.5 R1 Interface for rApp Portability Across RIC Platforms
3.2.2.6 xApp APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
3.2.2.7 Potential Decoupling of the SMO & Non-RT RIC
3.2.2.8 Open Fronthaul M-Plane Interface
3.2.2.9 Y1 Interface for RAN Analytics Exposure
3.3 AI-Native RAN Infrastructure
3.3.1 AI/ML-Based Air Interface for 6G Networks
3.3.2 Microsecond-Level Intelligent RAN Control & Optimization
3.3.3 Synergies With the dApps (Distributed Applications) Concept
3.3.4 AI-RAN Workload Sharing & RAN as a Platform for Edge AI Services
3.4 RAN Planning & Optimization
3.4.1 RAN Planning & Optimization Software Platforms
3.4.2 Specialized Products for In-Building Wireless Network Design
3.4.3 Other Categories of RAN Operations Support & Optimization Tools
3.5 Test & Measurement Solutions
3.5.1 Testing of RIC Platforms & Other RAN Automation Products
3.5.2 Automation & AI/ML Features in Test & Measurement Solutions
3.6 Automation & Intelligence Beyond the RAN
3.6.1 Mobile Core Networks
3.6.2 xHaul (Fronthaul, Midhaul & Backhaul) Transport
3.6.3 Device-Driven Intelligence & Optimization
3.7 Network Automation Use Cases
3.7.1 Neighbor Relations, PCI & RACH Optimization
3.7.1.1 ANR (Automatic Neighbor Relations)
3.7.1.2 CNR (Centralized Neighbor Relations)
3.7.1.3 PCI (Physical Cell ID) Conflict Detection & Resolution
3.7.1.4 RACH (Random Access Channel)/RSI (Root Sequence Index) Optimization
3.7.2 Mobility & Handover Management
3.7.2.1 MRO/bMRO (Cell & Beam-Based Mobility Robustness Optimization)
3.7.2.2 QoS-Based Adaptive & Intelligent Handover Optimization
3.7.2.3 CHO (Conditional Handover) Management
3.7.2.4 DAPS (Dual Active Protocol Stack) Handover Management
3.7.2.5 Handover Management for V2X, UAV & Railway Communications
3.7.3 RAN Resource Optimization
3.7.3.1 CCO (Coverage & Capacity Optimization)
3.7.3.2 AI/ML-Assisted Dynamic Cell Shaping
3.7.3.3 MLB (Mobility Load Balancing)/LBO (Load Balancing Optimization)
3.7.3.4 Advanced Traffic Steering for Efficient Load Distribution
3.7.3.5 QoS & QoE-Based Dynamic Resource Allocation
3.7.3.6 Policy-Guided QoS/QoE Nudging
3.7.3.7 Application-Aware RAN Optimization
3.7.3.8 Special Event Management
3.7.3.9 Intelligent Control in RAN Sharing Arrangements
3.7.3.10 Dynamic Reallocation of Idle RAN Compute Resources
3.7.4 Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
3.7.4.1 Energy Savings in the RAN
3.7.4.2 Dynamic Transmit Power Adaptation
3.7.4.3 Carrier & Cell On/Off Switching
3.7.4.4 RF Channel Reconfiguration: Massive MIMO Muting
3.7.4.5 Advanced Sleep Mode Control in RUs (Radio Units)
3.7.4.6 DU/CU (Distributed & Centralized Unit) Pooling & Power Management
3.7.4.7 Carbon Footprint Awareness & Emission Control
3.7.4.8 RAN-Driven Optimization of UE Energy Consumption
3.7.5 Spectrum Management & Multi-RAT Connectivity
3.7.5.1 Frequency Layer Management
3.7.5.2 Sector Carrier Orchestration
3.7.5.3 CA (Carrier Aggregation) Optimization
3.7.5.4 MCIM/ICIM (Multi/Inter-Cell Interference Management)
3.7.5.5 Atmospheric Ducting Interference Mitigation
3.7.5.6 Shared & Unlicensed Spectrum Coordination
3.7.5.7 DSS (Dynamic Spectrum Sharing)
3.7.5.8 4G-5G DC (Dual Connectivity) Control
3.7.5.9 JCAS (Joint Communication & Sensing)
3.7.6 Network Healing & Protection
3.7.6.1 AD (Anomaly Detection) & Remediation
3.7.6.2 COD/COC (Cell Outage Detection & Compensation)
3.7.6.3 SCDR (Sleeping Cell Detection & Recovery)
3.7.6.4 RET (Remote Electrical Tilt) Adjustment in Disaster Scenarios
3.7.6.5 CPM (Congestion Prediction & Management)
3.7.6.6 RF Jamming Detection
3.7.6.7 Signaling Storm Protection
3.7.6.8 Closed Loop RAN Security
3.7.7 Massive MIMO, Beamforming & Lower-Layer Optimization
3.7.7.1 GoB (Grid-of-Beams) Beamforming Optimization
3.7.7.2 Non-GoB (Reciprocity-Based) Beamforming Optimization
3.7.7.3 AI/ML-Assisted Beam Selection & Management
3.7.7.4 Initial Access Optimization in Massive MIMO Systems
3.7.7.5 MU (Multi-User)-MIMO Pairing Enhancement
3.7.7.6 Massive MIMO Grouping Optimization
3.7.7.7 Channel Estimation, Interpolation & Equalization
3.7.7.8 Link Adaptation & Other L1 (PHY)/MAC Algorithms
3.7.8 Network Slicing, Private 5G, NTN & Vertical Applications
3.7.8.1 RAN Slice Resource Allocation Optimization
3.7.8.2 RAN Slice SLA (Service Level Agreement) Assurance
3.7.8.3 Multi-Vendor Slice Management
3.7.8.4 Private 5G & Neutral Host Network Automation
3.7.8.5 IIoT (Industrial IoT) & Enterprise RAN Customization
3.7.8.6 NTN (Non-Terrestrial Network) Resource Orchestration
3.7.9 Network Planning & Evolution
3.7.9.1 RF Design
3.7.9.2 Site Selection
3.7.9.3 Capacity Planning
3.7.9.4 Canary Release
3.7.9.5 Network Digital Twin
3.7.9.6 Legacy Network Shutdown
3.7.10 Automation & AI Enablement
3.7.10.1 Conflict Management & Governance
3.7.10.2 RAN Geolocation Intelligence
3.7.10.3 UE Positioning & Trajectory Prediction
3.7.10.4 KPI (Key Performance Indicator) Monitoring
3.7.10.5 MDT (Minimization of Drive Tests) & RAN Data Collection
3.7.10.6 Integration of Datasets External to the RAN
3.7.10.7 AI/ML-Enabled Network Insights & Diagnostics
3.7.10.8 Traffic Forecasting & QoS/QoE Prediction
3.7.11 Multi-Domain, Core & Transport-Related Use Cases
3.7.11.1 Automated Configuration & Testing
3.7.11.2 Dynamic Autoscaling of Network Resources
3.7.11.3 Service Assurance, Fault Management & Cybersecurity
3.7.11.4 AI/ML-Driven Intelligence for End-to-End Network Slicing
3.7.11.5 Core Network Automation & Intelligent Orchestration
3.7.11.6 NWDAF (Network Data Analytics Function) for Core Network Analytics
3.7.11.7 MDAF (Management Data Analytics Function) for Management Plane Analytics
3.7.11.8 SDN (Software-Defined Networking)-Based xHaul Transport Automation
3.7.11.9 Interference Management in Microwave & mmWave (Millimeter Wave) Transport Links
3.7.11.10 Interworking Between RAN SMO, NWDAF, MDAF & Transport Domain SDN Controllers
4 Chapter 4: Key Trends in Intelligent RAN Implementations
4.1 Transition From SON to Open RAN-Based RIC, SMO, xApps & rApps
4.1.1 AI/ML Integration From the Outset
4.1.2 Granular Insights & Faster Control Loops
4.1.3 Multi-Vendor Interoperability & Scalability
4.1.4 Diversified Ecosystem of RAN Application Developers
4.1.5 SDKs (Software Development Kits) for Accelerated Development
4.2 Moving Closer to Higher Levels of Automation
4.2.1 Building Confidence in Closed Loop Automation
4.2.2 Service-Centric Automated Network Optimization
4.2.3 Intent-Driven Network & Service Management
4.2.4 Long-Term Vision of Zero-Touch Operations
4.3 Operational AI & ML
4.3.1 Replacement of Classic Rule-Based Solutions With AI Algorithms
4.3.2 ML Models for Network Operations Automation
4.3.3 Supervised & Unsupervised Learning
4.3.4 RL (Reinforcement Learning)
4.3.5 Federated Learning
4.3.6 Deep Learning
4.4 Gen AI (Generative AI)
4.4.1 Differences From Conventional AI/ML
4.4.2 GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks)
4.4.3 VAEs (Variational Autoencoders)
4.4.4 Transformer Architecture
4.4.5 LLMs (Large Language Models)
4.4.6 Natural Language Interface for RAN Operations
4.5 Network Data Analytics
4.5.1 Descriptive Analytics
4.5.2 Diagnostic Analytics
4.5.3 Predictive Analytics
4.5.4 Prescriptive Analytics
4.6 Observability of Network Operations
4.6.1 Deeper Visibility Into RAN Telemetry
4.6.2 Integrating Supplementary Data Sources
4.6.3 End-to-End Network Observability Control
4.7 Cloud-Native & Software-Centric Networking
4.7.1 Cloud-Native Technologies
4.7.2 Microservices & SBA (Service-Based Architecture)
4.7.3 Network Virtualization & Containerization
4.7.4 SDN for Network Programmability
4.7.5 DevOps & CI/CD (Continuous Integration & Delivery)
4.8 Other Trends & Developments
4.8.1 RAN Densification & Multi-Layer Coordination
4.8.2 Plug & Play Small Cells in Industrial, Enterprise & Public Venues
4.8.3 RAN Automation for Private 5G Network Management
4.8.4 Support for Vertical Industry-Specific Use Cases
4.8.5 FWA (Fixed Wireless Access) Deployments
4.8.6 Shared & Unlicensed Spectrum
4.8.7 Network Slicing Enablement
4.8.8 AI-RAN & Edge Computing
4.8.9 Application Awareness
4.8.10 Dynamic Security
5 Chapter 5: Standardization & Collaborative Initiatives
5.1 3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project)
5.1.1 Releases 8-14: LTE SON Features
5.1.2 Release 15: 5G ANR, NWDAF & MDAF
5.1.3 Release 16: 5G SON, MDT & L2 Measurement Support
5.1.4 Release 17: Expansion of 5G Network Intelligence & Automation
5.1.5 Release 18: Laying the AI/ML Foundation for 5G Advanced Systems
5.1.6 Releases 19, 20, 21 & Beyond: Succession From 5G Advanced to AI-Native 6G Networks
5.2 AI-RAN Alliance
5.2.1 AI for RAN
5.2.2 AI & RAN
5.2.3 AI on RAN
5.3 ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute)
5.3.1 OCG AI (Operational Co-ordination Group on AI)
5.3.2 Specific ISGs (Industry Specification Groups) & TCs (Technical Committees)
5.3.2.1 ENI (Experiential Networked Intelligence) ISG
5.3.2.2 ZSM (Zero-Touch Network & Service Management) ISG
5.3.2.3 TC INT (TC on Core Network & Interoperability Testing)
5.3.2.4 TC SAI (TC on Securing Artificial Intelligence)
5.3.2.5 Other ISGs & TCs
5.4 GSMA (GSM Association)
5.4.1 Efforts Related to AI & Network Automation
5.5 GTAA (Global Telco AI Alliance)
5.5.1 Accelerating Telco AI Transformation
5.5.2 Multi-Lingual LLM for Telco Operations
5.6 IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
5.6.1 Standardization for Automated Network Management
5.7 ITU (International Telecommunication Union)
5.7.1 ITU-R (ITU Radiocommunication Sector)
5.7.1.1 Work Related to AI-Native Air Interface & RAN
5.7.2 ITU-T (ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector)
5.7.2.1 SG13 (Study Group 13): Future Networks & Emerging Technologies
5.7.2.2 FG-AN (Focus Group on Autonomous Networks)
5.7.2.3 FG-ML5G (Focus Group on ML for 5G & Future Networks)
5.8 Linux Foundation
5.8.1 ONAP (Open Network Automation Platform)
5.8.2 Other AI & Network Automation-Related Projects
5.9 NGMN Alliance
5.9.1 SON Definition & Recommendations
5.9.2 Network Automation & Autonomy Based on AI
5.9.3 Green Future Networks for Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
5.10 ONF (Open Networking Foundation)
5.10.1 SMaRT-5G (Sustainable Mobile & RAN Transformation 5G)
5.10.2 SD-RAN (Software-Defined RAN): Near-RT RIC & Exemplar xApps
5.10.3 RRAIL (RAN RIC & Applications Interoperability Lab)
5.11 O-RAN Alliance
5.11.1 RIC Architecture Specifications
5.11.2 xApp & rApp Use Cases
5.11.3 O-RAN SC (Software Community)
5.11.4 Testing & Integration Support
5.12 OSA (OpenAirInterface Software Alliance)
5.12.1 M5G (MOSAIC5G): Flexible RAN & Core Controllers
5.12.2 FlexRIC (Flexible RAN Intelligent Controller) & xApp SDK Framework
5.13 OSSii (Operations Support Systems Interoperability Initiative)
5.13.1 Enabling Multi-Vendor OSS Interoperability
5.14 SCF (Small Cell Forum)
5.14.1 Small Cell SON & RAN Orchestration
5.15 TIP (Telecom Infra Project)
5.15.1 OpenRAN Project Group
5.15.1.1 RIA (RAN Intelligence & Automation) Subgroup
5.15.1.2 ROMA (RAN Orchestration & Lifecycle Management Automation) Subgroup
5.15.2 TelcoAI Project Group
5.16 TM Forum
5.16.1 Addressing Higher-Level Aspects of Autonomous Networks
5.17 Other Initiatives & Academic Research
6 Chapter 6: RAN Automation Case Studies
6.1 AT&T
6.1.1 Vendor Selection
6.1.2 Deployment Review
6.1.3 Results & Future Plans
6.2 Bell Canada
6.2.1 Vendor Selection
6.2.2 Deployment Review
6.2.3 Results & Future Plans
6.3 Bharti Airtel
6.3.1 Vendor Selection
6.3.2 Deployment Review
6.3.3 Results & Future Plans
6.4 BT Group
6.4.1 Vendor Selection
6.4.2 Deployment Review
6.4.3 Results & Future Plans
6.5 DT (Deutsche Telekom)
6.5.1 Vendor Selection
6.5.2 Deployment Review
6.5.3 Results & Future Plans
6.6 Elisa
6.6.1 Vendor Selection
6.6.2 Deployment Review
6.6.3 Results & Future Plans
6.7 Globe Telecom
6.7.1 Vendor Selection
6.7.2 Deployment Review
6.7.3 Results & Future Plans
6.8 NTT DoCoMo
6.8.1 Vendor Selection
6.8.2 Deployment Review
6.8.3 Results & Future Plans
6.9 Ooredoo
6.9.1 Vendor Selection
6.9.2 Deployment Review
6.9.3 Results & Future Plans
6.10 Orange
6.10.1 Vendor Selection
6.10.2 Deployment Review
6.10.3 Results & Future Plans
6.11 Rakuten Mobile
6.11.1 Vendor Selection
6.11.2 Deployment Review
6.11.3 Results & Future Plans
6.12 Singtel
6.12.1 Vendor Selection
6.12.2 Deployment Review
6.12.3 Results & Future Plans
6.13 SK Telecom
6.13.1 Vendor Selection
6.13.2 Deployment Review
6.13.3 Results & Future Plans
6.14 STC (Saudi Telecom Company)
6.14.1 Vendor Selection
6.14.2 Deployment Review
6.14.3 Results & Future Plans
6.15 Telecom Argentina
6.15.1 Vendor Selection
6.15.2 Deployment Review
6.15.3 Results & Future Plans
6.16 Telefonica Group
6.16.1 Vendor Selection
6.16.2 Deployment Review
6.16.3 Results & Future Plans
6.17 TIM (Telecom Italia Mobile)
6.17.1 Vendor Selection
6.17.2 Deployment Review
6.17.3 Results & Future Plans
6.18 Turkcell
6.18.1 Vendor Selection
6.18.2 Deployment Review
6.18.3 Results & Future Plans
6.19 Verizon Communications
6.19.1 Vendor Selection
6.19.2 Deployment Review
6.19.3 Results & Future Plans
6.20 Vodafone Group
6.20.1 Vendor Selection
6.20.2 Deployment Review
6.20.3 Results & Future Plans
6.21 Other Recent Deployments & Ongoing Projects
6.21.1 1&1: Highly Automated Control of Europe's First Greenfield Open RAN Network
6.21.2 4iG Group: Closed Loop Network Management & Customer Experience Monitoring
6.21.3 America Movil: SON-Based RAN Automation for 5G Network Rollout & Optimization
6.21.4 Andorra Telecom: Doubling Throughput With Automated RF Interference Mitigation
6.21.5 Axiata Group: Autonomous Network Initiative for Streamlining Operations
6.21.6 Batelco: AI-Powered Energy Savings & Carbon Footprint Reduction
6.21.7 beCloud (Belarusian Cloud Technologies): AI-Enabled Network Management
6.21.8 Beeline Russia (VimpelCom): Transforming the Mobile Experience Using C-SON
6.21.9 BTC (Botswana Telecommunications Corporation): Nationwide Network Optimization
6.21.10 C Spire: SON-Enabled Automation of Regional Wireless Network
6.21.11 Cellfie Mobile: Intelligent RAN Monitoring & Management
6.21.12 CETIN Group: Multi-Domain Automated Network Optimization
6.21.13 China Mobile: Aiming for AI/ML-Assisted L4 Automation by 2025
6.21.14 China Telecom: Co-Governance of Shared 5G Network Infrastructure
6.21.15 China Unicom: CUBE-RAN Intelligent Open Platform
6.21.16 CK Hutchison: Accelerating the Journey Towards Fully Automated RAN Operations
6.21.17 DIGI Communications: Laying the Groundwork for Zero-Touch Automation
6.21.18 DISH Network Corporation: RIC-Based RAN Programmability & Intelligence
6.21.19 Djezzy: Harnessing C-SON for Automated RAN Optimization & Management
6.21.20 Etisalat Group (e&): AI/ML-Enabled Intelligent Network Management Platform
6.21.21 FET (Far EasTone Telecommunications): Advancing Sustainability Goals With ML-Driven RAN Automation
6.21.22 KDDI: Moving Towards RIC-Based Automation for Network Slicing Enablement
6.21.23 KPN: Replacing Labor-Intensive RAN Optimization Tools With SON-Based Automation
6.21.24 KT Corporation: Embracing Intelligent Control of RAN Resources & Operations
6.21.25 LG Uplus: Evaluating the RIC Approach for Vendor-Independent RAN Automation
6.21.26 Liberty Global: Building a Customer-First 5G Network Using Autonomous Optimization Decisions
6.21.27 LTT (Libya Telecom & Technology): Nationwide RAN Automation for Enhanced Network Quality
6.21.28 MASMOVIL: Improving Customer Experience During Peak Hours With ML-Assisted Optimization
6.21.29 MegaFon: Delivering an Exemplary Subscriber Experience Through SON Technology
6.21.30 MEO (Altice Portugal): Automated RAN Optimization & Service Assurance
6.21.31 MTN Group: Pioneering Autonomous Mobile Networks in Africa
6.21.32 MTS (Mobile TeleSystems): Self-Adjusting Intelligent Network
6.21.33 Odido: AI-Driven Cell Site Energy Management Solution
6.21.34 Reliance Jio Infocomm: Improving Customer Experience With C-SON
6.21.35 Rogers Communications: Cross-Domain Service Orchestration & Automation
6.21.36 Smart Communications (PLDT): Planning the SON-to-RIC Transition
6.21.37 Smartfren: Automating Heterogenous Network Management
6.21.38 SoftBank Group: Spearheading AI/ML-Driven Advancements in the RAN
6.21.39 Swisscom: Future-Proofing Brownfield Mobile Network With SMO & Non-RT RIC
6.21.40 TDC NET: Inching Towards Net Zero Goals With RAN Automation
6.21.41 Telia Company: Setting the Foundation for Zero-Touch Mobile Networks
6.21.42 Telkomsel: Autonomous Network Program for Operational Efficiency
6.21.43 Telstra: Advancing Mobile Network Automation Capabilities
6.21.44 Telus: SMO & RIC-Based RAN Network Intelligence Platform
6.21.45 TPG Telecom: Managing Peak Traffic Congestion With C-SON
6.21.46 Turk Telekom: Driving Efficiency Through Network Automation
6.21.47 Ucom (Armenia): AI Functionalities for Mobile Network Modernization
6.21.48 VEON: Leveraging C-SON to Enhance Network Performance
6.21.49 Viettel Group: AI/ML-Enabled Physical Layer Signal Processing
6.21.50 Zain Group: Targeting L4 Automation for Efficient 5G Network Operations
7 Chapter 7: Key Ecosystem Players
7.1 A10 Networks
7.2 A5G Networks
7.3 Aalyria
7.4 Aarna Networks
7.5 Abside Networks
7.6 Accedian
7.7 Accelleran
7.8 Accuver (InnoWireless)
7.9 Acentury
7.10 Actiontec Electronics
7.11 Adtran
7.12 Aglocell
7.13 AI-LINK
7.14 Aira Technologies
7.15 AirHop Communications
7.16 Airspan Networks
7.17 AiVader
7.18 Aliniant
7.19 Allot
7.20 Alpha Networks
7.21 Amazon/AWS (Amazon Web Services)
7.22 AMD (Advanced Micro Devices)
7.23 Amdocs
7.24 Anktion (Fujian) Technology
7.25 Anritsu
7.26 Antevia Networks
7.27 Arcadyan Technology Corporation (Compal Electronics)
7.28 Argela
7.29 Arm
7.30 ArrayComm (Chengdu ArrayComm Wireless Technologies)
7.31 Arrcus
7.32 Artemis Networks
7.33 Artiza Networks
7.34 Arukona
7.35 AsiaInfo Technologies
7.36 Askey Computer Corporation (ASUS ? ASUSTeK Computer)
7.37 ASOCS
7.38 Aspire Technology (NEC Corporation)
7.39 ASTRI (Hong Kong Applied Science and Technology Research Institute)
7.40 Ataya
7.41 ATDI
7.42 Atesio
7.43 Atrinet (ServiceNow)
7.44 Auray Technology (Auden Techno)
7.45 Aviat Networks
7.46 Azcom Technology
7.47 Baicells
7.48 Betacom
7.49 BLiNQ Networks (CCI ? Communication Components Inc.)
7.50 Blu Wireless
7.51 Booz Allen Hamilton
7.52 BravoCom
7.53 Broadcom
7.54 BTI Wireless
7.55 BubbleRAN
7.56 B-Yond/Reailize
7.57 C3Spectra
7.58 CableFree (Wireless Excellence)
7.59 Cambium Networks
7.60 Capgemini Engineering
7.61 CBNG (Cambridge Broadband Networks Group)
7.62 Celfinet (Cyient)
7.63 Celona
7.64 CelPlan Technologies
7.65 Ceragon Networks
7.66 CGI
7.67 Chengdu NTS
7.68 CICT ? China Information and Communication Technology Group (China Xinke Group)
7.69 Ciena Corporation
7.70 CIG (Cambridge Industries Group)
7.71 Cisco Systems
7.72 Clavister
7.73 Cohere Technologies
7.74 Comarch
7.75 Comba Telecom
7.76 CommAgility (E-Space)
7.77 CommScope
7.78 Compal Electronics
7.79 COMSovereign
7.80 Contela
7.81 Corning
7.82 Creanord
7.83 Cyient
7.84 DeepSig
7.85 Dell Technologies
7.86 DGS (Digital Global Systems)
7.87 Digis Squared
7.88 Digitata
7.89 D-Link Corporation
7.90 Druid Software
7.91 DZS
7.92 ECE (European Communications Engineering)
7.93 EDX Wireless
7.94 eino
7.95 Elisa Polystar
7.96 Encora
7.97 Equiendo
7.98 Ericsson
7.99 Errigal
7.100 ETRI (Electronics & Telecommunications Research Institute, South Korea)
7.101 EXFO
7.102 F5
7.103 Fairspectrum
7.104 Federated Wireless
7.105 Firecell
7.106 Flash Networks
7.107 Forsk
7.108 Fortinet
7.109 Foxconn (Hon Hai Technology Group)
7.110 Fraunhofer HHI (Heinrich Hertz Institute)
7.111 Fujitsu
7.112 FullRays (LDAS ? LocationDAS)
7.113 Future Connections
7.114 FYRA
7.115 G REIGNS (HTC Corporation)
7.116 Gemtek Technology
7.117 GENEViSiO (QNAP Systems)
7.118 Gigamon
7.119 GigaTera Communications (KMW)
7.120 GlobalLogic (Hitachi)
7.121 Globalstar
7.122 Google (Alphabet)
7.123 Groundhog Technologies
7.124 Guavus (Thales)
7.125 GXC (Formerly GenXComm)
7.126 HCLTech (HCL Technologies)
7.127 Helios (Fujian Helios Technologies)
7.128 HFR Networks
7.129 Highstreet Technologies
7.130 Hitachi
7.131 HPE (Hewlett Packard Enterprise)
7.132 HSC (Hughes Systique Corporation)
7.133 Huawei
7.134 IBM
7.135 iBwave Solutions
7.136 iConNext
7.137 Infinera
7.138 Infosys
7.139 Infovista
7.140 Inmanta
7.141 Innovile
7.142 InnoWireless
7.143 Intel Corporation
7.144 InterDigital
7.145 Intracom Telecom
7.146 Inventec Corporation
7.147 ISCO International
7.148 IS-Wireless
7.149 Itential
7.150 ITRI (Industrial Technology Research Institute, Taiwan)
7.151 JMA Wireless
7.152 JRC (Japan Radio Company)
7.153 Juniper Networks (HPE ? Hewlett Packard Enterprise)
7.154 Key Bridge Wireless
7.155 Keysight Technologies
7.156 Kleos
7.157 KMW
7.158 Kumu Networks
7.159 Lemko Corporation
7.160 Lenovo
7.161 Lime Microsystems
7.162 LIONS Technology
7.163 LITE-ON Technology Corporation
7.164 LitePoint (Teradyne)
7.165 LS telcom
7.166 LuxCarta
7.167 MantisNet
7.168 Marvell Technology
7.169 Mavenir
7.170 Maxar Technologies
7.171 Meta
7.172 MicroNova
7.173 Microsoft Corporation
7.174 MikroTik
7.175 MitraStar Technology (Unizyx Holding Corporation)
7.176 Mobileum
7.177 MosoLabs (Sercomm Corporation)
7.178 MYCOM OSI
7.179 Nash Technologies
7.180 NEC Corporation
7.181 Net AI
7.182 Netcracker Technology (NEC Corporation)
7.183 NETSCOUT Systems
7.184 Netsia (Argela)
7.185 Neutroon Technologies
7.186 New H3C Technologies (Tsinghua Unigroup)
7.187 New Postcom Equipment
7.188 Nextivity
7.189 Node-H
7.190 Nokia
7.191 Novowi
7.192 NuRAN Wireless
7.193 NVIDIA Corporation
7.194 NXP Semiconductors
7.195 Oceus Networks
7.196 Omnitele
7.197 OneLayer
7.198 Ookla
7.199 Opanga Networks
7.200 OREX (NTT DoCoMo)
7.201 P.I. Works
7.202 Palo Alto Networks
7.203 Parallel Wireless
7.204 Pente Networks
7.205 Phluido
7.206 Picocom
7.207 Pivotal Commware
7.208 Potevio (CETC ? China Electronics Technology Group Corporation)
7.209 QCT (Quanta Cloud Technology)
7.210 Qualcomm
7.211 Quanta Computer
7.212 Qucell Networks (InnoWireless)
7.213 RADCOM
7.214 Radisys (Reliance Industries)
7.215 Radware
7.216 Rakuten Symphony
7.217 Ranlytics
7.218 Ranplan Wireless
7.219 Rebaca Technologies
7.220 Red Hat (IBM)
7.221 RED Technologies
7.222 REPLY
7.223 RIMEDO Labs
7.224 Rivada Networks
7.225 Rohde & Schwarz
7.226 Ruijie Networks
7.227 RunEL
7.228 SageRAN (Guangzhou SageRAN Technology)
7.229 Samji Electronics
7.230 Samsung
7.231 Sandvine
7.232 Sercomm Corporation
7.233 ServiceNow
7.234 Shabodi
7.235 Signalwing
7.236 SIRADEL
7.237 Skyvera (TelcoDR)
7.238 SOLiD
7.239 Sooktha
7.240 Spectrum Effect
7.241 Spirent Communications
7.242 SRS (Software Radio Systems)
7.243 SSC (Shared Spectrum Company)
7.244 Star Solutions
7.245 Subex
7.246 Sunwave Communications
7.247 Supermicro (Super Micro Computer)
7.248 SynaXG Technologies
7.249 Systemics-PAB
7.250 T&W (Shenzhen Gongjin Electronics)
7.251 Tarana Wireless
7.252 TCS (Tata Consultancy Services)
7.253 Tech Mahindra
7.254 Tecore Networks
7.255 TECTWIN
7.256 Telrad Networks
7.257 TEOCO/Aircom
7.258 ThinkRF
7.259 TI (Texas Instruments)
7.260 TietoEVRY
7.261 Tropico (CPQD ? Center for Research and Development in Telecommunications, Brazil)
7.262 TTG International
7.263 Tupl
7.264 ULAK Communication
7.265 Vavitel (Shenzhen Vavitel Technology)
7.266 VHT (Viettel High Tech)
7.267 VIAVI Solutions
7.268 VMware (Broadcom)
7.269 VNL ? Vihaan Networks Limited (Shyam Group)
7.270 Wave Electronics
7.271 WDNA (Wireless DNA)
7.272 WIM Technologies
7.273 Wind River Systems
7.274 Wipro
7.275 Wiwynn (Wistron Corporation)
7.276 WNC (Wistron NeWeb Corporation)
7.277 Xingtera
7.278 ZaiNar
7.279 Z-Com
7.280 Zeetta Networks
7.281 Zinkworks
7.282 ZTE
7.283 zTouch Networks
7.284 Zyxel (Unizyx Holding Corporation)
8 Chapter 8: Market Sizing & Forecasts
8.1 Mobile Network Automation
8.2 Network Domain Submarkets
8.2.1 RAN Automation
8.2.2 Mobile Core Automation
8.2.3 xHaul Transport Automation
8.3 RAN Automation Functional Areas
8.3.1 SON-Based Automation
8.3.2 Open RAN Automation
8.3.3 Baseband-Integrated Intelligent RAN Applications
8.3.4 RAN Planning & Optimization Software
8.3.5 Test & Measurement Solutions
8.4 SON-Based Automation Submarkets
8.4.1 RAN Vendor SON Solutions
8.4.2 Third Party C-SON Platforms
8.5 Open RAN Automation Submarkets
8.5.1 Non-RT RIC & SMO
8.5.2 Near-RT RIC
8.5.3 rApps
8.5.4 xApps
8.6 Access Technology Generations
8.6.1 LTE
8.6.2 5G NR
8.6.3 6G
8.7 Regional Segmentation
8.7.1 North America
8.7.2 Asia Pacific
8.7.3 Europe
8.7.4 Middle East & Africa
8.7.5 Latin & Central America
9 Chapter 9: Conclusion & Strategic Recommendations
9.1 Why is the Market Poised to Grow?
9.2 Future Roadmap: 2024 ? 2030
9.2.1 2024 ? 2026: Production-Grade Deployments of SMO & RIC Platforms for Brownfield Networks
9.2.2 2027 ? 2029: Widespread Adoption of Open RAN Automation & Diverse RIC-Hosted Applications
9.2.3 2030 & Beyond: Towards AI-Native Air Interfaces & Zero-Touch 5G/6G Network Automation
9.3 Reviewing the Real-World Benefits & TCO Savings Potential of RAN Automation
9.4 Impact of Intelligent Automation on RAN Engineering Roles
9.5 Transition From SON to Open RAN Automation
9.6 Evolution of Use Cases & AI/ML Algorithms
9.7 Growing Focus on Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
9.8 Vertical Industries & Private Wireless Automation
9.9 Diversified Community of x/rApp Developers
9.10 Signs of Consolidation in the SMO & RIC Ecosystem
9.11 Which RAN Automation Platform & Application Vendors Are Leading the Market?
9.12 Prospects of Hosting Third Party Applications Within RAN Baseband Products
9.13 Paving the Path to an AI/ML-Based 6G Air Interface
9.14 Convergence of AI & RAN Infrastructure
9.15 Strategic Recommendations
9.15.1 RAN Automation Solution Providers
9.15.2 Mobile Operators
10 Chapter 10: Expert Opinion ? Interview Transcripts
10.1 AirHop Communications
10.2 Amdocs
10.3 Groundhog Technologies
10.4 Innovile
10.5 Net AI
10.6 Nokia
10.7 P.I. Works
10.8 Qualcomm
10.9 Rakuten Mobile
10.10 RIMEDO Labs
List of Companies Mentioned
The following companies and organizations have been reviewed, discussed or mentioned in the report:
1&1
3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project)
4iG Group
A10 Networks
A5G Networks
Aalyria
Aarna Networks
Abside Networks
Accedian
Accelleran
Accuver
Acentury
Actiontec Electronics
Adtran
Aglocell
AI-LINK
Aira Technologies
AI-RAN Alliance
Aircom
AirHop Communications
Airspan Networks
AiVader
Aliniant
Allot
Alpha Networks
Alphabet
Altice Portugal
Amazon
AMD (Advanced Micro Devices)
Amdocs
America Movil
Andorra Telecom
Anktion (Fujian) Technology
Anritsu
Antevia Networks
Arcadyan Technology Corporation
Argela
ARIB (Association of Radio Industries and Businesses, Japan)
Arm
ArrayComm (Chengdu ArrayComm Wireless Technologies)
Arrcus
Artemis Networks
Artiza Networks
Arukona
AsiaInfo Technologies
Askey Computer Corporation
ASOCS
Aspire Technology
ASTRI (Hong Kong Applied Science and Technology Research Institute)
ASUS (ASUSTeK Computer)
AT&T
Ataya
ATDI
Atesio
ATIS (Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions)
Atrinet
Auden Techno
Auray Technology
Aviat Networks
AWS (Amazon Web Services)
Axiata Group
Azcom Technology
Baicells
Batelco
beCloud (Belarusian Cloud Technologies)
Beeline Russia (VimpelCom)
Bell Canada
Betacom
Bharti Airtel
BLiNQ Networks
Blu Wireless
Booz Allen Hamilton
BravoCom
Broadcom
BT Group
BTC (Botswana Telecommunications Corporation)
BTI Wireless
BubbleRAN
B-Yond
C Spire
C3Spectra
CableFree (Wireless Excellence)
Cambium Networks
Capgemini Engineering
CBNG (Cambridge Broadband Networks Group)
CCI (Communication Components Inc.)
CCSA (China Communications Standards Association)
Celfinet
Cellfie Mobile
Celona
CelPlan Technologies
Ceragon Networks
CETC (China Electronics Technology Group Corporation)
CETIN Group
CGI
Chengdu NTS
China Mobile
China Telecom
China Unicom
CICT ? China Information and Communication Technology Group (China Xinke Group)
Ciena Corporation
CIG (Cambridge Industries Group)
Cisco Systems
CK Hutchison
Claro Colombia
Clavister
Cohere Technologies
Comarch
Comba Telecom
CommAgility
CommScope
Compal Electronics
COMSovereign
Contela
Corning
CPQD (Center for Research and Development in Telecommunications, Brazil)
Creanord
Cyient
Datang Telecom Technology & Industry Group
DeepSig
Dell Technologies
DGS (Digital Global Systems)
DIGI Communications
Digis Squared
Digitata
DISH Network Corporation
Djezzy
D-Link Corporation
Druid Software
DSA (Dynamic Spectrum Alliance)
DT (Deutsche Telekom)
DZS
ECE (European Communications Engineering)
EDX Wireless
EE
eino
Elisa
Elisa Polystar
Encora
Equiendo
Ericsson
Errigal
E-Space
Etisalat Group (e&)
ETRI (Electronics & Telecommunications Research Institute, South Korea)
ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute)
EXFO
F5
Fairspectrum
Federated Wireless
FET (Far EasTone Telecommunications)
FiberHome Technologies
Firecell
Flash Networks
Forsk
Fortinet
Foxconn (Hon Hai Technology Group)
Fraunhofer HHI (Heinrich Hertz Institute)
Fujitsu
FullRays (LDAS ? LocationDAS)
Future Connections
FYRA
G REIGNS
Gemtek Technology
GENEViSiO
Gigamon
GigaTera Communications
GlobalLogic
Globalstar
Globe Telecom
Google
Groundhog Technologies
GSMA (GSM Association)
GTAA (Global Telco AI Alliance)
Guavus
GXC (Formerly GenXComm)
HCLTech (HCL Technologies)
Helios (Fujian Helios Technologies)
HFR Networks
Highstreet Technologies
Hitachi
HPE (Hewlett Packard Enterprise)
HSC (Hughes Systique Corporation)
HTC Corporation
Huawei
Hutchison Drei Austria
IBM
iBwave Solutions
iConNext
IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
Infinera
Infosys
Infovista
Inmanta
Innovile
InnoWireless
Intel Corporation
InterDigital
Intracom Telecom
Inventec Corporation
ISCO International
IS-Wireless
Itential
ITRI (Industrial Technology Research Institute, Taiwan)
ITU (International Telecommunication Union)
JMA Wireless
JRC (Japan Radio Company)
Juniper Networks
KDDI
Key Bridge Wireless
Keysight Technologies
Kleos
KMW
KPN
KT Corporation
Kumu Networks
Kuzey K?br?s Turkcell
Kyivstar
Lemko Corporation
Lenovo
LG Uplus
Liberty Global
life:)/BeST (Belarusian Telecommunications Network)
lifecell Ukraine
Lime Microsystems
Linux Foundation
LIONS Technology
LITE-ON Technology Corporation
LitePoint
LS telcom
LTT (Libya Telecom & Technology)
LuxCarta
MantisNet
Marvell Technology
MASMOVIL
Mavenir
Maxar Technologies
MegaFon
MEO
Meta
MicroNova
Microsoft Corporation
MikroTik
MitraStar Technology
Mobileum
MosoLabs
MTN Group
MTS (Mobile TeleSystems)
MYCOM OSI
Nash Technologies
NEC Corporation
Net AI
Netcracker Technology
NETSCOUT Systems
Netsia
Neutroon Technologies
New H3C Technologies
New Postcom Equipment
Nextivity
NGMN Alliance
Node-H
Nokia
Northeastern University
Novowi
NTT DoCoMo
NuRAN Wireless
NVIDIA Corporation
NXP Semiconductors
NYCU (National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University)
Oceus Networks
Odido
Omnitele
OneLayer
ONF (Open Networking Foundation)
OnGo Alliance
Ookla
Ooredoo
Ooredoo Algeria
Ooredoo Tunisia
Opanga Networks
Optus
O-RAN Alliance
Orange
OREX
OSA (OpenAirInterface Software Alliance)
P.I. Works
Palo Alto Networks
Parallel Wireless
Pente Networks
Phluido
Picocom
Pivotal Commware
PLDT
Potevio
QCT (Quanta Cloud Technology)
QNAP Systems
Qualcomm
Quanta Computer
Qucell Networks
RADCOM
Radisys
Radware
Rakuten Mobile
Rakuten Symphony
Ranlytics
Ranplan Wireless
Reailize
Rebaca Technologies
Red Hat
RED Technologies
Reliance Industries
Reliance Jio Infocomm
REPLY
RIMEDO Labs
Rivada Networks
Rogers Communications
Rohde & Schwarz
Ruijie Networks
RunEL
SageRAN (Guangzhou SageRAN Technology)
Samji Electronics
Samsung
Sandvine
SCF (Small Cell Forum)
Sercomm Corporation
ServiceNow
Shabodi
Shyam Group
Signalwing
Singtel
SIRADEL
SK Telecom
Skyvera (TelcoDR)
Smart Communications
Smartfren
SoftBank Group
SOLiD
Sooktha
Spectrum Effect
Spirent Communications
SRS (Software Radio Systems)
SSC (Shared Spectrum Company)
Star Solutions
STC (Saudi Telecom Company)
Subex
Sunwave Communications
Supermicro (Super Micro Computer)
SUTD (Singapore University of Technology and Design)
Swisscom
SynaXG Technologies
Systemics-PAB
T&W (Shenzhen Gongjin Electronics)
Tarana Wireless
TCS (Tata Consultancy Services)
TDC NET
Tech Mahindra
Tecore Networks
TECTWIN
Telecom Argentina
Telefonica Germany
Telefonica Group
Telia Company
Telkomsel
Telrad Networks
Telstra
Telus
TEOCO
Teradyne
Texas A&M University
Thales
ThinkRF
TI (Texas Instruments)
TietoEVRY
TIM (Telecom Italia Mobile)
TIM Brasil
TIP (Telecom Infra Project)
TM Forum
TPG Telecom
Tropico
TSDSI (Telecommunications Standards Development Society, India)
Tsinghua Unigroup
TTA (Telecommunications Technology Association, South Korea)
TTC (Telecommunication Technology Committee, Japan)
TTG International
Tupl
Turk Telekom
Turkcell
U.S. DOD (Department of Defense)
U.S. NTIA (National Telecommunications and Information Administration)
Ucom (Armenia)
ULAK Communication
University of California San Diego
University of Lancaster
University of Malaga
Unizyx Holding Corporation
Vavitel (Shenzhen Vavitel Technology)
VEON
Verizon Communications
VHT (Viettel High Tech)
Vi (Vodafone Idea)
VIAVI Solutions
Viettel Group
Virgin Media O2
VMware
VNL (Vihaan Networks Limited)
Vodafone Germany
Vodafone Group
Vodafone Ireland
Vodafone Turkey
Wave Electronics
WDNA (Wireless DNA)
WIM Technologies
Wind River Systems
WInnForum (Wireless Innovation Forum)
Wipro
Wistron Corporation
Wiwynn
WNC (Wistron NeWeb Corporation)
Xingtera
Zain Group
Zain Saudi Arabia (Zain KSA)
ZaiNar
Z-Com
Zeetta Networks
Zinkworks
ZTE
zTouch Networks
Zyxel
Summary
Synopsis
Automation of the RAN (Radio Access Network) ? the most expensive, technically complex and power-intensive part of cellular infrastructure ? is a key aspect of mobile operators' digital transformation strategies aimed at reducing their TCO (Total Cost of Ownership), improving network quality and achieving revenue generation targets. In conjunction with AI (Artificial Intelligence) and ML (Machine Learning), RAN automation has the potential to significantly transform mobile network economics by reducing the OpEx (Operating Expenditure)-to-revenue ratio, minimizing energy consumption, lowering CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) emissions, deferring avoidable CapEx (Captial Expenditure), optimizing performance, improving user experience and enabling new services.
The RAN automation market traces its origins to the beginning of the LTE era when SON (Self-Organizing Network) technology was introduced to reduce cellular network complexity through self-configuration, self-optimization and self-healing. While embedded D-SON (Distributed SON) capabilities such as ANR (Automatic Neighbor Relations) have become a standard feature in RAN products, C-SON (Centralized SON) solutions that abstract control from edge nodes for network-wide actions have been adopted by less than a third of world's approximately 800 national mobile operators due to constraints associated with multi-vendor interoperability, scalability and latency.
These shortcomings, together with the cellular industry's shift towards open interfaces, common information models, virtualization and software-driven networking, are driving a transition from the traditional D-SON and C-SON approach to Open RAN automation with standards-based components ? specifically the Near-RT (Real-Time) and Non-RT RICs (RAN Intelligent Controllers), SMO (Service Management & Orchestration) framework, xApps (Extended Applications) and rApps (RAN Applications) ? that enable greater levels of RAN programmability and automation.
Along with the ongoing SON to RIC transition, RAN automation use cases have also evolved over the last decade. For example, relatively basic MLB (Mobility Load Balancing) capabilities have metamorphosed into more sophisticated policy-guided traffic steering applications that utilize AI/ML-driven optimization algorithms to efficiently adapt to peaks and troughs in network load and service usage by dynamically managing and redistributing traffic across radio resources and frequency layers.
Due to the much higher density of radios and cell sites in the 5G era, energy efficiency has emerged as one of the most prioritized use cases of RAN automation as forward-thinking mobile operators push ahead with sustainability initiatives to reduce energy consumption, carbon emissions and operating costs without degrading network quality. Some of the other use cases that have garnered considerable interest from the operator community include network slicing enablement, application-aware optimization and anomaly detection.
While the benefits of SON-based RAN automation in live networks are well-known, expectations are even higher with the RIC, SMO and x/rApps approach. For example, Japanese brownfield operator NTT DoCoMo expects to lower its TCO by up to 30% and decrease power consumption at base stations by as much as 50% using Open RAN automation. It is worth highlighting that domestic rival Rakuten Mobile has already achieved approximately 17% energy savings per cell in its live network using RIC-hosted RAN automation applications. Following successful lab trials, the greenfield operator aims to increase savings to 25% with more sophisticated AI/ML models.
Although Open RAN automation efforts seemingly lost momentum beyond the field trial phase for the past couple of years, several commercial engagements have emerged since then, with much of the initial focus on the SMO, Non-RT RIC and rApps for automated management and optimization across Open RAN, purpose-built and hybrid RAN environments. Within the framework of its five-year $14 Billion Open RAN infrastructure contract with Ericsson, AT&T is adopting the Swedish telecommunications giant's SMO and Non-RT RIC solution to replace two legacy C-SON systems. In neighboring Canada, Telus has also initiated the implementation of an SMO and RIC platform along with its multi-vendor Open RAN deployment to transform up to 50% of its RAN footprint and swap out Huawei equipment from its 4G/5G network.
Similar efforts are also underway in other regions. For example, in Europe, Swisscom is deploying an SMO and Non-RT RIC platform to provide multi-technology network management and automation capabilities as part of a wider effort to future-proof its brownfield mobile network, while Deutsche Telekom is progressing with plans to develop its own vendor-independent SMO framework. Open RAN automation is also expected to be introduced as part of Vodafone Group's global tender for refreshing 170,000 cell sites.
Deployments of newer generations of proprietary SON-based RAN automation solutions have not stalled either. In its pursuit of achieving L4 (Highly Autonomous Network) operations, China Mobile has recently initiated the implementation of a hierarchical RAN automation platform and an associated digital twin system, starting with China's Henan province. Among other interesting examples, SoftBank is implementing a closed loop automation solution for cluster-wide RAN optimization in stadiums, event venues, and other strategic locations across Japan, which supports data collection and parameter tuning in 1-5 minute intervals as opposed to the 15-minute control cycle of traditional C-SON systems. It should be noted that the Japanese operator eventually plans to adopt RIC-hosted centralized RAN optimization applications in the future.
In addition, with the support of several mobile operators, including SoftBank, Vodafone, Bell Canada and Viettel, the idea of hosting third party applications for real-time intelligent control and optimization ? also referred to as dApps (Distributed Applications) ? directly within RAN baseband platforms is beginning to gain traction. As a counterbalance to this approach, Ericsson, Nokia, Huawei and other established RAN vendors are making considerable progress with a stepwise approach towards embedding AI and ML functionalities deeper into their DU (Distributed Unit) and CU (Centralized Unit) products in line with the 3GPP's long-term vision of an AI/ML-based air interface in the 6G era.
SNS Telecom & IT estimates that global spending on RIC, SMO and x/rApps will grow at a CAGR of more than 125% between 2024 and 2027 alongside the second wave of Open RAN infrastructure rollouts by brownfield operators. The Open RAN automation market will eventually account for nearly $700 Million in annual investments by the end of 2027 as standardization gaps and technical challenges in terms of the SMO-to-Non-RT RIC interface, application portability across RIC platforms and conflict mitigation between x/rApps are ironed out. The wider RAN automation software and services market ? which includes Open RAN automation, RAN vendor SON solutions, third party C-SON platforms, baseband-integrated intelligent RAN applications, RAN planning and optimization software, and test/measurement solutions ? is expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 8% during the same period.
The “RAN Automation, SON, RIC, xApps & rApps in the 5G Era: 2024 ? 2030 ? Opportunities, Challenges, Strategies & Forecasts” report presents an in-depth assessment of the RAN automation market, including the value chain, market drivers, barriers to uptake, enabling technologies, functional areas, use cases, key trends, future roadmap, standardization, case studies, ecosystem player profiles and strategies. The report also provides global and regional market size forecasts for RAN and end-to-end mobile network automation from 2024 to 2030. The forecasts cover three network domains, nine functional areas, three access technologies and five regional markets.
The report comes with an associated Excel datasheet suite covering quantitative data from all numeric forecasts presented in the report.
Key Findings
The report has the following key findings:
SNS Telecom & IT estimates that global spending on RIC, SMO and x/rApps will grow at a CAGR of more than 125% between 2024 and 2027 alongside the second wave of Open RAN infrastructure rollouts by brownfield operators. The Open RAN automation market will eventually account for nearly $700 Million in annual investments by the end of 2027 as standardization gaps and technical challenges in terms of the SMO-to-Non-RT RIC interface, application portability across RIC platforms and conflict mitigation between x/rApps are ironed out.
The wider market for RAN automation software and services ? which includes Open RAN automation, RAN vendor SON solutions, third party C-SON platforms, baseband-integrated intelligent RAN applications, RAN planning and optimization software, and test/measurement solutions ? is expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 8% during the same period.
The shortcomings of the traditional D-SON and C-SON approach, together with the cellular industry's shift towards open interfaces, common information models, virtualization and software-driven networking, are driving a transition to Open RAN automation with standards-based components that enable greater levels of RAN programmability and automation.
The Open RAN automation movement is stimulating innovation from a diversified community of application developers. In addition to well over a dozen providers of SMO, Non-RT RIC and Near-RT RIC products, more than 50 companies are actively engaged in the development of xApps and rApps.
Some mobile operators have established dedicated business units to commoditize their RAN automation expertise. NTT DoCoMo's OREX brand and Rakuten Mobile's sister company Rakuten Symphony are two well-known cases in point. In the coming years, we also expect to see more spinoffs of academic institutes with commercial-grade Open RAN automation offerings, such as Northeastern University's zTouch Networks and TU Ilmenau's AiVader.
The SMO and RIC ecosystem is exhibiting early signs of consolidation with Broadcom's takeover of VMware and HPE's planned acquisition of Juniper Networks, although both deals have much wider ranging implications for the AI infrastructure and networking industries. Depending on the commercial success of third party RAN automation platforms, we anticipate seeing further M&A (Mergers & Acquisition) activity reminiscent of the SON boom in the previous decade.
While the benefits of SON-based RAN automation in live networks are well-known, expectations are even higher with the RIC, SMO and x/rApps approach. For example, Japanese brownfield operator NTT DoCoMo expects to lower its TCO by up to 30% and decrease power consumption at base stations by as much as 50% using Open RAN automation.
It is worth highlighting that domestic rival Rakuten Mobile has already achieved approximately 17% energy savings per cell in its live network using RIC-hosted RAN automation applications. Following successful lab trials, the greenfield operator aims to increase savings to 25% with more sophisticated AI/ML models.
Outside of public mobile operator networks, interest is also growing in vertical industries and the private wireless segment. The U.S. DOD (Department of Defense) is actively exploring the potential of RIC-hosted x/rApps to enhance the ability to detect, analyze, and mitigate a wide range of security threats in Open RAN networks for both commercial and warfighter communication scenarios. Among other examples, Taiwanese electronics manufacturer Inventec has incorporated rApps for indoor positioning and traffic steering as part of its private 5G network solution for smart factories.
Although Open RAN automation efforts seemingly lost momentum beyond the field trial phase for the past couple of years, several commercial engagements have emerged since then, with much of the initial focus on the SMO, Non-RT RIC and rApps for automated management and optimization across Open RAN, purpose-built and hybrid RAN environments.
Within the framework of its five-year $14 Billion Open RAN infrastructure contract with Ericsson, AT&T is adopting the Swedish telecommunications giant's SMO and Non-RT RIC solution to replace two legacy C-SON systems. In neighboring Canada, Telus has also initiated the implementation of an SMO and RIC platform along with its multi-vendor Open RAN deployment to transform up to 50% of its RAN footprint and swap out Huawei equipment from its 4G/5G network.
Similar efforts are also underway in other regions. For example, in Europe, Swisscom is deploying an SMO and Non-RT RIC platform to provide multi-technology network management and automation capabilities as part of a wider effort to future-proof its brownfield mobile network, while Deutsche Telekom is progressing with plans to develop its own vendor-independent SMO framework. Open RAN automation is also expected to be introduced as part of Vodafone Group's global tender for refreshing 170,000 cell sites.
Deployments of newer generations of proprietary SON-based RAN automation solutions have not stalled either. In its pursuit of achieving L4 automation, China Mobile has recently initiated the implementation of a hierarchical RAN automation platform and an associated digital twin system, starting with China's Henan province.
Among other interesting examples, SoftBank is implementing a closed loop automation solution for cluster-wide RAN optimization in stadiums, event venues, and other strategic locations across Japan, which supports data collection and parameter tuning in 1-5 minute intervals as opposed to the 15-minute control cycle of traditional C-SON systems. It should be noted that the Japanese operator eventually plans to adopt RIC-hosted centralized RAN optimization applications in the future.
In addition, with the support of several mobile operators, including SoftBank, Vodafone, Bell Canada and Viettel, the idea of hosting third party applications for real-time intelligent control and optimization ? also referred to as dApps ? directly within RAN baseband platforms is beginning to gain traction.
As a counterbalance to this approach, Ericsson, Nokia, Huawei and other established RAN vendors are making considerable progress with a stepwise approach towards embedding AI and ML functionalities deeper into their DU and CU products in line with the 3GPP's long-term vision of an AI/ML-based air interface in the 6G era.
Beyond AI-driven RAN performance and efficiency improvements, mobile operators, technology suppliers and other stakeholders are also setting their sights on TCO benefits and new revenue opportunities enabled by the convergence of AI and RAN, including co-hosting vRAN and AI workloads on the same underlying infrastructure to maximize asset utilization and leveraging the RAN as a platform for edge AI services.
Topics Covered
The report covers the following topics:
Introduction to RAN automation
Value chain and ecosystem structure
Market drivers and challenges
Functional areas of RAN automation
RAN automation technology and architecture, including D-SON, C-SON, H-SON, Near-RT/Non-RT RICs, SMO, x/rApps, baseband-integrated intelligent RAN applications, RAN planning and optimization software, and test & measurement solutions
Review of over 70 RAN automation use cases, ranging from ANR, PCI and RACH optimization to advanced traffic steering, QoE-based resource allocation, energy savings, network slicing, private 5G automation, anomaly detection and dynamic RAN security
Key trends in intelligent RAN implementations, including the SON-to-RIC transition, closed loop automation, intent-driven management, operational AI/ML, Gen AI, data analytics and application awareness
Cross-domain mobile network automation enablers and application scenarios across the RAN, core and xHaul transport segments of cellular infrastructure
Detailed case studies of 20 production-grade RAN automation deployments and examination of ongoing projects covering both traditional SON and Open RAN automation approaches
Future roadmap of RAN automation
Standardization and collaborative initiatives
Profiles and strategies of more than 280 ecosystem players, including RAN infrastructure vendors, SON, RIC and SMO platform providers, x/rApp developers, AI/ML technology specialists, RAN planning and optimization software suppliers, and test/measurement solution providers
Exclusive interview transcripts from 10 companies across the RAN automation value chain: AirHop Communications, Amdocs, Groundhog Technologies, Innovile, Net AI, Nokia, P.I. Works, Qualcomm, Rakuten Mobile and RIMEDO Labs
Strategic recommendations for RAN automation solution providers and mobile operators
Market analysis and forecasts from 2024 to 2030
Forecast Segmentation
Market forecasts are provided for each of the following submarkets and their subcategories:
Mobile Network Automation Submarkets
RAN
Mobile Core
xHaul (Fronthaul, Midhaul & Backhaul) Transport
RAN Automation Functional Areas
SON-Based Automation
RAN Vendor SON Solutions
Third Party C-SON Platforms
Open RAN Automation
Non-RT RIC & SMO
Near-RT RIC
rApps
xApps
Baseband-Integrated Intelligent RAN Applications
RAN Planning & Optimization Software
Test & Measurement Solutions
Access Technology Generation Submarkets
LTE
5G NR
6G
Regional Markets
North America
Asia Pacific
Europe
Middle East & Africa
Latin & Central America
Key Questions Answered
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
1 Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Executive Summary
1.2 Topics Covered
1.3 Forecast Segmentation
1.4 Key Questions Answered
1.5 Key Findings
1.6 Methodology
1.7 Target Audience
2 Chapter 2: An Overview of RAN Automation
2.1 What is RAN Automation?
2.1.1 Automating Repetitive Manual Tasks
2.1.2 RAN Analytics & Data-Driven Decision Making
2.1.3 AI (Artificial Intelligence) & ML (Machine Learning) Integration
2.1.4 SMO (Service Management & Orchestration) Frameworks
2.2 Levels of Automation in Intelligent RAN Implementations
2.2.1 L0 ? Manual Operation
2.2.2 L1 ? Assisted Management
2.2.3 L2 ? Partial Autonomous Network
2.2.4 L3 ? Conditional Autonomous Network
2.2.5 L4 ? Highly Autonomous Network
2.2.6 L5 ? Fully Autonomous Network
2.3 Functional Areas of RAN Automation
2.3.1 The SON (Self-Organizing Network) Concept
2.3.2 RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller), xApps & rApps
2.3.3 Native AI Capabilities in RAN Infrastructure
2.3.4 Automation-Assisted RAN Planning & Optimization
2.3.5 RAN Test & Measurement Solutions
2.4 RAN Automation Value Chain
2.4.1 Semiconductor & Enabling AI/ML Technology Specialists
2.4.2 RAN Infrastructure Vendors
2.4.3 SON, xApp/rApp & Automation Application Developers
2.4.4 RIC, SMO & OSS Platform Providers
2.4.5 RAN Planning & Optimization Software Suppliers
2.4.6 Test & Measurement Solution Providers
2.4.7 Wireless Service Providers
2.4.7.1 National Mobile Operators
2.4.7.2 Fixed-Line Service Providers
2.4.7.3 Private 5G Network Operators
2.4.7.4 Neutral Hosts
2.4.8 End Users
2.4.8.1 Consumers
2.4.8.2 Enterprises & Vertical Industries
2.5 Market Drivers
2.5.1 Growing Complexity of RAN in the 5G Era
2.5.2 Open RAN & vRAN (Virtualized RAN) Adoption
2.5.3 TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) Reduction
2.5.4 Energy Savings, Sustainability & Environmental Conservation
2.5.5 Popularity of Both Operational & Generative AI Technologies
2.5.6 Subscriber Experience & Network Performance Benefits
2.5.7 Network Slicing & New Revenue-Generating Opportunities
2.5.8 Proliferation of Shared Spectrum, Private 5G & Neutral Host Networks
2.6 Market Barriers
2.6.1 Service Provider Revenue Stagnation & Cost-Cutting Measures
2.6.2 Slow Pace of Brownfield RAN Reinvestment Cycles
2.6.3 Implementation-Related Technical Challenges
2.6.4 Standardization Gaps & Multi-Vendor Interoperability
2.6.5 Conflict Mitigation Between x/rApps
2.6.6 Dominance of Incumbent RAN Vendors
2.6.7 Conservatism & Trust in Automation
2.6.8 Network Security & Privacy Concerns
3 Chapter 3: RAN Automation Technology, Architecture & Use Cases
3.1 Traditional SON Solutions
3.1.1 Application Areas
3.1.1.1 Self-Configuration
3.1.1.2 Self-Optimization
3.1.1.3 Self-Healing
3.1.1.4 Self-Protection
3.1.1.5 Self-Learning
3.1.2 SON Architecture
3.1.2.1 D-SON (Distributed SON)
3.1.2.2 C-SON (Centralized SON)
3.1.2.3 H-SON (Hybrid SON)
3.2 Open Specifications-Based RIC, SMO, xApps & rApps
3.2.1 Architectural Elements
3.2.1.1 Near-RT (Real-Time) RIC
3.2.1.2 Non-RT RIC
3.2.1.3 SMO Framework
3.2.1.4 xApps (Extended Applications)
3.2.1.5 rApps (RAN Applications)
3.2.2 Open Interfaces
3.2.2.1 A1 Interface Between Non-RT RIC & Near-RT RIC
3.2.2.2 E2 Interface Between Near RT-RIC & RAN Nodes
3.2.2.3 O1 Interface for OAM (Operations, Administration & Maintenance)
3.2.2.4 O2 Interface for Cloud Infrastructure Management
3.2.2.5 R1 Interface for rApp Portability Across RIC Platforms
3.2.2.6 xApp APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
3.2.2.7 Potential Decoupling of the SMO & Non-RT RIC
3.2.2.8 Open Fronthaul M-Plane Interface
3.2.2.9 Y1 Interface for RAN Analytics Exposure
3.3 AI-Native RAN Infrastructure
3.3.1 AI/ML-Based Air Interface for 6G Networks
3.3.2 Microsecond-Level Intelligent RAN Control & Optimization
3.3.3 Synergies With the dApps (Distributed Applications) Concept
3.3.4 AI-RAN Workload Sharing & RAN as a Platform for Edge AI Services
3.4 RAN Planning & Optimization
3.4.1 RAN Planning & Optimization Software Platforms
3.4.2 Specialized Products for In-Building Wireless Network Design
3.4.3 Other Categories of RAN Operations Support & Optimization Tools
3.5 Test & Measurement Solutions
3.5.1 Testing of RIC Platforms & Other RAN Automation Products
3.5.2 Automation & AI/ML Features in Test & Measurement Solutions
3.6 Automation & Intelligence Beyond the RAN
3.6.1 Mobile Core Networks
3.6.2 xHaul (Fronthaul, Midhaul & Backhaul) Transport
3.6.3 Device-Driven Intelligence & Optimization
3.7 Network Automation Use Cases
3.7.1 Neighbor Relations, PCI & RACH Optimization
3.7.1.1 ANR (Automatic Neighbor Relations)
3.7.1.2 CNR (Centralized Neighbor Relations)
3.7.1.3 PCI (Physical Cell ID) Conflict Detection & Resolution
3.7.1.4 RACH (Random Access Channel)/RSI (Root Sequence Index) Optimization
3.7.2 Mobility & Handover Management
3.7.2.1 MRO/bMRO (Cell & Beam-Based Mobility Robustness Optimization)
3.7.2.2 QoS-Based Adaptive & Intelligent Handover Optimization
3.7.2.3 CHO (Conditional Handover) Management
3.7.2.4 DAPS (Dual Active Protocol Stack) Handover Management
3.7.2.5 Handover Management for V2X, UAV & Railway Communications
3.7.3 RAN Resource Optimization
3.7.3.1 CCO (Coverage & Capacity Optimization)
3.7.3.2 AI/ML-Assisted Dynamic Cell Shaping
3.7.3.3 MLB (Mobility Load Balancing)/LBO (Load Balancing Optimization)
3.7.3.4 Advanced Traffic Steering for Efficient Load Distribution
3.7.3.5 QoS & QoE-Based Dynamic Resource Allocation
3.7.3.6 Policy-Guided QoS/QoE Nudging
3.7.3.7 Application-Aware RAN Optimization
3.7.3.8 Special Event Management
3.7.3.9 Intelligent Control in RAN Sharing Arrangements
3.7.3.10 Dynamic Reallocation of Idle RAN Compute Resources
3.7.4 Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
3.7.4.1 Energy Savings in the RAN
3.7.4.2 Dynamic Transmit Power Adaptation
3.7.4.3 Carrier & Cell On/Off Switching
3.7.4.4 RF Channel Reconfiguration: Massive MIMO Muting
3.7.4.5 Advanced Sleep Mode Control in RUs (Radio Units)
3.7.4.6 DU/CU (Distributed & Centralized Unit) Pooling & Power Management
3.7.4.7 Carbon Footprint Awareness & Emission Control
3.7.4.8 RAN-Driven Optimization of UE Energy Consumption
3.7.5 Spectrum Management & Multi-RAT Connectivity
3.7.5.1 Frequency Layer Management
3.7.5.2 Sector Carrier Orchestration
3.7.5.3 CA (Carrier Aggregation) Optimization
3.7.5.4 MCIM/ICIM (Multi/Inter-Cell Interference Management)
3.7.5.5 Atmospheric Ducting Interference Mitigation
3.7.5.6 Shared & Unlicensed Spectrum Coordination
3.7.5.7 DSS (Dynamic Spectrum Sharing)
3.7.5.8 4G-5G DC (Dual Connectivity) Control
3.7.5.9 JCAS (Joint Communication & Sensing)
3.7.6 Network Healing & Protection
3.7.6.1 AD (Anomaly Detection) & Remediation
3.7.6.2 COD/COC (Cell Outage Detection & Compensation)
3.7.6.3 SCDR (Sleeping Cell Detection & Recovery)
3.7.6.4 RET (Remote Electrical Tilt) Adjustment in Disaster Scenarios
3.7.6.5 CPM (Congestion Prediction & Management)
3.7.6.6 RF Jamming Detection
3.7.6.7 Signaling Storm Protection
3.7.6.8 Closed Loop RAN Security
3.7.7 Massive MIMO, Beamforming & Lower-Layer Optimization
3.7.7.1 GoB (Grid-of-Beams) Beamforming Optimization
3.7.7.2 Non-GoB (Reciprocity-Based) Beamforming Optimization
3.7.7.3 AI/ML-Assisted Beam Selection & Management
3.7.7.4 Initial Access Optimization in Massive MIMO Systems
3.7.7.5 MU (Multi-User)-MIMO Pairing Enhancement
3.7.7.6 Massive MIMO Grouping Optimization
3.7.7.7 Channel Estimation, Interpolation & Equalization
3.7.7.8 Link Adaptation & Other L1 (PHY)/MAC Algorithms
3.7.8 Network Slicing, Private 5G, NTN & Vertical Applications
3.7.8.1 RAN Slice Resource Allocation Optimization
3.7.8.2 RAN Slice SLA (Service Level Agreement) Assurance
3.7.8.3 Multi-Vendor Slice Management
3.7.8.4 Private 5G & Neutral Host Network Automation
3.7.8.5 IIoT (Industrial IoT) & Enterprise RAN Customization
3.7.8.6 NTN (Non-Terrestrial Network) Resource Orchestration
3.7.9 Network Planning & Evolution
3.7.9.1 RF Design
3.7.9.2 Site Selection
3.7.9.3 Capacity Planning
3.7.9.4 Canary Release
3.7.9.5 Network Digital Twin
3.7.9.6 Legacy Network Shutdown
3.7.10 Automation & AI Enablement
3.7.10.1 Conflict Management & Governance
3.7.10.2 RAN Geolocation Intelligence
3.7.10.3 UE Positioning & Trajectory Prediction
3.7.10.4 KPI (Key Performance Indicator) Monitoring
3.7.10.5 MDT (Minimization of Drive Tests) & RAN Data Collection
3.7.10.6 Integration of Datasets External to the RAN
3.7.10.7 AI/ML-Enabled Network Insights & Diagnostics
3.7.10.8 Traffic Forecasting & QoS/QoE Prediction
3.7.11 Multi-Domain, Core & Transport-Related Use Cases
3.7.11.1 Automated Configuration & Testing
3.7.11.2 Dynamic Autoscaling of Network Resources
3.7.11.3 Service Assurance, Fault Management & Cybersecurity
3.7.11.4 AI/ML-Driven Intelligence for End-to-End Network Slicing
3.7.11.5 Core Network Automation & Intelligent Orchestration
3.7.11.6 NWDAF (Network Data Analytics Function) for Core Network Analytics
3.7.11.7 MDAF (Management Data Analytics Function) for Management Plane Analytics
3.7.11.8 SDN (Software-Defined Networking)-Based xHaul Transport Automation
3.7.11.9 Interference Management in Microwave & mmWave (Millimeter Wave) Transport Links
3.7.11.10 Interworking Between RAN SMO, NWDAF, MDAF & Transport Domain SDN Controllers
4 Chapter 4: Key Trends in Intelligent RAN Implementations
4.1 Transition From SON to Open RAN-Based RIC, SMO, xApps & rApps
4.1.1 AI/ML Integration From the Outset
4.1.2 Granular Insights & Faster Control Loops
4.1.3 Multi-Vendor Interoperability & Scalability
4.1.4 Diversified Ecosystem of RAN Application Developers
4.1.5 SDKs (Software Development Kits) for Accelerated Development
4.2 Moving Closer to Higher Levels of Automation
4.2.1 Building Confidence in Closed Loop Automation
4.2.2 Service-Centric Automated Network Optimization
4.2.3 Intent-Driven Network & Service Management
4.2.4 Long-Term Vision of Zero-Touch Operations
4.3 Operational AI & ML
4.3.1 Replacement of Classic Rule-Based Solutions With AI Algorithms
4.3.2 ML Models for Network Operations Automation
4.3.3 Supervised & Unsupervised Learning
4.3.4 RL (Reinforcement Learning)
4.3.5 Federated Learning
4.3.6 Deep Learning
4.4 Gen AI (Generative AI)
4.4.1 Differences From Conventional AI/ML
4.4.2 GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks)
4.4.3 VAEs (Variational Autoencoders)
4.4.4 Transformer Architecture
4.4.5 LLMs (Large Language Models)
4.4.6 Natural Language Interface for RAN Operations
4.5 Network Data Analytics
4.5.1 Descriptive Analytics
4.5.2 Diagnostic Analytics
4.5.3 Predictive Analytics
4.5.4 Prescriptive Analytics
4.6 Observability of Network Operations
4.6.1 Deeper Visibility Into RAN Telemetry
4.6.2 Integrating Supplementary Data Sources
4.6.3 End-to-End Network Observability Control
4.7 Cloud-Native & Software-Centric Networking
4.7.1 Cloud-Native Technologies
4.7.2 Microservices & SBA (Service-Based Architecture)
4.7.3 Network Virtualization & Containerization
4.7.4 SDN for Network Programmability
4.7.5 DevOps & CI/CD (Continuous Integration & Delivery)
4.8 Other Trends & Developments
4.8.1 RAN Densification & Multi-Layer Coordination
4.8.2 Plug & Play Small Cells in Industrial, Enterprise & Public Venues
4.8.3 RAN Automation for Private 5G Network Management
4.8.4 Support for Vertical Industry-Specific Use Cases
4.8.5 FWA (Fixed Wireless Access) Deployments
4.8.6 Shared & Unlicensed Spectrum
4.8.7 Network Slicing Enablement
4.8.8 AI-RAN & Edge Computing
4.8.9 Application Awareness
4.8.10 Dynamic Security
5 Chapter 5: Standardization & Collaborative Initiatives
5.1 3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project)
5.1.1 Releases 8-14: LTE SON Features
5.1.2 Release 15: 5G ANR, NWDAF & MDAF
5.1.3 Release 16: 5G SON, MDT & L2 Measurement Support
5.1.4 Release 17: Expansion of 5G Network Intelligence & Automation
5.1.5 Release 18: Laying the AI/ML Foundation for 5G Advanced Systems
5.1.6 Releases 19, 20, 21 & Beyond: Succession From 5G Advanced to AI-Native 6G Networks
5.2 AI-RAN Alliance
5.2.1 AI for RAN
5.2.2 AI & RAN
5.2.3 AI on RAN
5.3 ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute)
5.3.1 OCG AI (Operational Co-ordination Group on AI)
5.3.2 Specific ISGs (Industry Specification Groups) & TCs (Technical Committees)
5.3.2.1 ENI (Experiential Networked Intelligence) ISG
5.3.2.2 ZSM (Zero-Touch Network & Service Management) ISG
5.3.2.3 TC INT (TC on Core Network & Interoperability Testing)
5.3.2.4 TC SAI (TC on Securing Artificial Intelligence)
5.3.2.5 Other ISGs & TCs
5.4 GSMA (GSM Association)
5.4.1 Efforts Related to AI & Network Automation
5.5 GTAA (Global Telco AI Alliance)
5.5.1 Accelerating Telco AI Transformation
5.5.2 Multi-Lingual LLM for Telco Operations
5.6 IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
5.6.1 Standardization for Automated Network Management
5.7 ITU (International Telecommunication Union)
5.7.1 ITU-R (ITU Radiocommunication Sector)
5.7.1.1 Work Related to AI-Native Air Interface & RAN
5.7.2 ITU-T (ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector)
5.7.2.1 SG13 (Study Group 13): Future Networks & Emerging Technologies
5.7.2.2 FG-AN (Focus Group on Autonomous Networks)
5.7.2.3 FG-ML5G (Focus Group on ML for 5G & Future Networks)
5.8 Linux Foundation
5.8.1 ONAP (Open Network Automation Platform)
5.8.2 Other AI & Network Automation-Related Projects
5.9 NGMN Alliance
5.9.1 SON Definition & Recommendations
5.9.2 Network Automation & Autonomy Based on AI
5.9.3 Green Future Networks for Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
5.10 ONF (Open Networking Foundation)
5.10.1 SMaRT-5G (Sustainable Mobile & RAN Transformation 5G)
5.10.2 SD-RAN (Software-Defined RAN): Near-RT RIC & Exemplar xApps
5.10.3 RRAIL (RAN RIC & Applications Interoperability Lab)
5.11 O-RAN Alliance
5.11.1 RIC Architecture Specifications
5.11.2 xApp & rApp Use Cases
5.11.3 O-RAN SC (Software Community)
5.11.4 Testing & Integration Support
5.12 OSA (OpenAirInterface Software Alliance)
5.12.1 M5G (MOSAIC5G): Flexible RAN & Core Controllers
5.12.2 FlexRIC (Flexible RAN Intelligent Controller) & xApp SDK Framework
5.13 OSSii (Operations Support Systems Interoperability Initiative)
5.13.1 Enabling Multi-Vendor OSS Interoperability
5.14 SCF (Small Cell Forum)
5.14.1 Small Cell SON & RAN Orchestration
5.15 TIP (Telecom Infra Project)
5.15.1 OpenRAN Project Group
5.15.1.1 RIA (RAN Intelligence & Automation) Subgroup
5.15.1.2 ROMA (RAN Orchestration & Lifecycle Management Automation) Subgroup
5.15.2 TelcoAI Project Group
5.16 TM Forum
5.16.1 Addressing Higher-Level Aspects of Autonomous Networks
5.17 Other Initiatives & Academic Research
6 Chapter 6: RAN Automation Case Studies
6.1 AT&T
6.1.1 Vendor Selection
6.1.2 Deployment Review
6.1.3 Results & Future Plans
6.2 Bell Canada
6.2.1 Vendor Selection
6.2.2 Deployment Review
6.2.3 Results & Future Plans
6.3 Bharti Airtel
6.3.1 Vendor Selection
6.3.2 Deployment Review
6.3.3 Results & Future Plans
6.4 BT Group
6.4.1 Vendor Selection
6.4.2 Deployment Review
6.4.3 Results & Future Plans
6.5 DT (Deutsche Telekom)
6.5.1 Vendor Selection
6.5.2 Deployment Review
6.5.3 Results & Future Plans
6.6 Elisa
6.6.1 Vendor Selection
6.6.2 Deployment Review
6.6.3 Results & Future Plans
6.7 Globe Telecom
6.7.1 Vendor Selection
6.7.2 Deployment Review
6.7.3 Results & Future Plans
6.8 NTT DoCoMo
6.8.1 Vendor Selection
6.8.2 Deployment Review
6.8.3 Results & Future Plans
6.9 Ooredoo
6.9.1 Vendor Selection
6.9.2 Deployment Review
6.9.3 Results & Future Plans
6.10 Orange
6.10.1 Vendor Selection
6.10.2 Deployment Review
6.10.3 Results & Future Plans
6.11 Rakuten Mobile
6.11.1 Vendor Selection
6.11.2 Deployment Review
6.11.3 Results & Future Plans
6.12 Singtel
6.12.1 Vendor Selection
6.12.2 Deployment Review
6.12.3 Results & Future Plans
6.13 SK Telecom
6.13.1 Vendor Selection
6.13.2 Deployment Review
6.13.3 Results & Future Plans
6.14 STC (Saudi Telecom Company)
6.14.1 Vendor Selection
6.14.2 Deployment Review
6.14.3 Results & Future Plans
6.15 Telecom Argentina
6.15.1 Vendor Selection
6.15.2 Deployment Review
6.15.3 Results & Future Plans
6.16 Telefonica Group
6.16.1 Vendor Selection
6.16.2 Deployment Review
6.16.3 Results & Future Plans
6.17 TIM (Telecom Italia Mobile)
6.17.1 Vendor Selection
6.17.2 Deployment Review
6.17.3 Results & Future Plans
6.18 Turkcell
6.18.1 Vendor Selection
6.18.2 Deployment Review
6.18.3 Results & Future Plans
6.19 Verizon Communications
6.19.1 Vendor Selection
6.19.2 Deployment Review
6.19.3 Results & Future Plans
6.20 Vodafone Group
6.20.1 Vendor Selection
6.20.2 Deployment Review
6.20.3 Results & Future Plans
6.21 Other Recent Deployments & Ongoing Projects
6.21.1 1&1: Highly Automated Control of Europe's First Greenfield Open RAN Network
6.21.2 4iG Group: Closed Loop Network Management & Customer Experience Monitoring
6.21.3 America Movil: SON-Based RAN Automation for 5G Network Rollout & Optimization
6.21.4 Andorra Telecom: Doubling Throughput With Automated RF Interference Mitigation
6.21.5 Axiata Group: Autonomous Network Initiative for Streamlining Operations
6.21.6 Batelco: AI-Powered Energy Savings & Carbon Footprint Reduction
6.21.7 beCloud (Belarusian Cloud Technologies): AI-Enabled Network Management
6.21.8 Beeline Russia (VimpelCom): Transforming the Mobile Experience Using C-SON
6.21.9 BTC (Botswana Telecommunications Corporation): Nationwide Network Optimization
6.21.10 C Spire: SON-Enabled Automation of Regional Wireless Network
6.21.11 Cellfie Mobile: Intelligent RAN Monitoring & Management
6.21.12 CETIN Group: Multi-Domain Automated Network Optimization
6.21.13 China Mobile: Aiming for AI/ML-Assisted L4 Automation by 2025
6.21.14 China Telecom: Co-Governance of Shared 5G Network Infrastructure
6.21.15 China Unicom: CUBE-RAN Intelligent Open Platform
6.21.16 CK Hutchison: Accelerating the Journey Towards Fully Automated RAN Operations
6.21.17 DIGI Communications: Laying the Groundwork for Zero-Touch Automation
6.21.18 DISH Network Corporation: RIC-Based RAN Programmability & Intelligence
6.21.19 Djezzy: Harnessing C-SON for Automated RAN Optimization & Management
6.21.20 Etisalat Group (e&): AI/ML-Enabled Intelligent Network Management Platform
6.21.21 FET (Far EasTone Telecommunications): Advancing Sustainability Goals With ML-Driven RAN Automation
6.21.22 KDDI: Moving Towards RIC-Based Automation for Network Slicing Enablement
6.21.23 KPN: Replacing Labor-Intensive RAN Optimization Tools With SON-Based Automation
6.21.24 KT Corporation: Embracing Intelligent Control of RAN Resources & Operations
6.21.25 LG Uplus: Evaluating the RIC Approach for Vendor-Independent RAN Automation
6.21.26 Liberty Global: Building a Customer-First 5G Network Using Autonomous Optimization Decisions
6.21.27 LTT (Libya Telecom & Technology): Nationwide RAN Automation for Enhanced Network Quality
6.21.28 MASMOVIL: Improving Customer Experience During Peak Hours With ML-Assisted Optimization
6.21.29 MegaFon: Delivering an Exemplary Subscriber Experience Through SON Technology
6.21.30 MEO (Altice Portugal): Automated RAN Optimization & Service Assurance
6.21.31 MTN Group: Pioneering Autonomous Mobile Networks in Africa
6.21.32 MTS (Mobile TeleSystems): Self-Adjusting Intelligent Network
6.21.33 Odido: AI-Driven Cell Site Energy Management Solution
6.21.34 Reliance Jio Infocomm: Improving Customer Experience With C-SON
6.21.35 Rogers Communications: Cross-Domain Service Orchestration & Automation
6.21.36 Smart Communications (PLDT): Planning the SON-to-RIC Transition
6.21.37 Smartfren: Automating Heterogenous Network Management
6.21.38 SoftBank Group: Spearheading AI/ML-Driven Advancements in the RAN
6.21.39 Swisscom: Future-Proofing Brownfield Mobile Network With SMO & Non-RT RIC
6.21.40 TDC NET: Inching Towards Net Zero Goals With RAN Automation
6.21.41 Telia Company: Setting the Foundation for Zero-Touch Mobile Networks
6.21.42 Telkomsel: Autonomous Network Program for Operational Efficiency
6.21.43 Telstra: Advancing Mobile Network Automation Capabilities
6.21.44 Telus: SMO & RIC-Based RAN Network Intelligence Platform
6.21.45 TPG Telecom: Managing Peak Traffic Congestion With C-SON
6.21.46 Turk Telekom: Driving Efficiency Through Network Automation
6.21.47 Ucom (Armenia): AI Functionalities for Mobile Network Modernization
6.21.48 VEON: Leveraging C-SON to Enhance Network Performance
6.21.49 Viettel Group: AI/ML-Enabled Physical Layer Signal Processing
6.21.50 Zain Group: Targeting L4 Automation for Efficient 5G Network Operations
7 Chapter 7: Key Ecosystem Players
7.1 A10 Networks
7.2 A5G Networks
7.3 Aalyria
7.4 Aarna Networks
7.5 Abside Networks
7.6 Accedian
7.7 Accelleran
7.8 Accuver (InnoWireless)
7.9 Acentury
7.10 Actiontec Electronics
7.11 Adtran
7.12 Aglocell
7.13 AI-LINK
7.14 Aira Technologies
7.15 AirHop Communications
7.16 Airspan Networks
7.17 AiVader
7.18 Aliniant
7.19 Allot
7.20 Alpha Networks
7.21 Amazon/AWS (Amazon Web Services)
7.22 AMD (Advanced Micro Devices)
7.23 Amdocs
7.24 Anktion (Fujian) Technology
7.25 Anritsu
7.26 Antevia Networks
7.27 Arcadyan Technology Corporation (Compal Electronics)
7.28 Argela
7.29 Arm
7.30 ArrayComm (Chengdu ArrayComm Wireless Technologies)
7.31 Arrcus
7.32 Artemis Networks
7.33 Artiza Networks
7.34 Arukona
7.35 AsiaInfo Technologies
7.36 Askey Computer Corporation (ASUS ? ASUSTeK Computer)
7.37 ASOCS
7.38 Aspire Technology (NEC Corporation)
7.39 ASTRI (Hong Kong Applied Science and Technology Research Institute)
7.40 Ataya
7.41 ATDI
7.42 Atesio
7.43 Atrinet (ServiceNow)
7.44 Auray Technology (Auden Techno)
7.45 Aviat Networks
7.46 Azcom Technology
7.47 Baicells
7.48 Betacom
7.49 BLiNQ Networks (CCI ? Communication Components Inc.)
7.50 Blu Wireless
7.51 Booz Allen Hamilton
7.52 BravoCom
7.53 Broadcom
7.54 BTI Wireless
7.55 BubbleRAN
7.56 B-Yond/Reailize
7.57 C3Spectra
7.58 CableFree (Wireless Excellence)
7.59 Cambium Networks
7.60 Capgemini Engineering
7.61 CBNG (Cambridge Broadband Networks Group)
7.62 Celfinet (Cyient)
7.63 Celona
7.64 CelPlan Technologies
7.65 Ceragon Networks
7.66 CGI
7.67 Chengdu NTS
7.68 CICT ? China Information and Communication Technology Group (China Xinke Group)
7.69 Ciena Corporation
7.70 CIG (Cambridge Industries Group)
7.71 Cisco Systems
7.72 Clavister
7.73 Cohere Technologies
7.74 Comarch
7.75 Comba Telecom
7.76 CommAgility (E-Space)
7.77 CommScope
7.78 Compal Electronics
7.79 COMSovereign
7.80 Contela
7.81 Corning
7.82 Creanord
7.83 Cyient
7.84 DeepSig
7.85 Dell Technologies
7.86 DGS (Digital Global Systems)
7.87 Digis Squared
7.88 Digitata
7.89 D-Link Corporation
7.90 Druid Software
7.91 DZS
7.92 ECE (European Communications Engineering)
7.93 EDX Wireless
7.94 eino
7.95 Elisa Polystar
7.96 Encora
7.97 Equiendo
7.98 Ericsson
7.99 Errigal
7.100 ETRI (Electronics & Telecommunications Research Institute, South Korea)
7.101 EXFO
7.102 F5
7.103 Fairspectrum
7.104 Federated Wireless
7.105 Firecell
7.106 Flash Networks
7.107 Forsk
7.108 Fortinet
7.109 Foxconn (Hon Hai Technology Group)
7.110 Fraunhofer HHI (Heinrich Hertz Institute)
7.111 Fujitsu
7.112 FullRays (LDAS ? LocationDAS)
7.113 Future Connections
7.114 FYRA
7.115 G REIGNS (HTC Corporation)
7.116 Gemtek Technology
7.117 GENEViSiO (QNAP Systems)
7.118 Gigamon
7.119 GigaTera Communications (KMW)
7.120 GlobalLogic (Hitachi)
7.121 Globalstar
7.122 Google (Alphabet)
7.123 Groundhog Technologies
7.124 Guavus (Thales)
7.125 GXC (Formerly GenXComm)
7.126 HCLTech (HCL Technologies)
7.127 Helios (Fujian Helios Technologies)
7.128 HFR Networks
7.129 Highstreet Technologies
7.130 Hitachi
7.131 HPE (Hewlett Packard Enterprise)
7.132 HSC (Hughes Systique Corporation)
7.133 Huawei
7.134 IBM
7.135 iBwave Solutions
7.136 iConNext
7.137 Infinera
7.138 Infosys
7.139 Infovista
7.140 Inmanta
7.141 Innovile
7.142 InnoWireless
7.143 Intel Corporation
7.144 InterDigital
7.145 Intracom Telecom
7.146 Inventec Corporation
7.147 ISCO International
7.148 IS-Wireless
7.149 Itential
7.150 ITRI (Industrial Technology Research Institute, Taiwan)
7.151 JMA Wireless
7.152 JRC (Japan Radio Company)
7.153 Juniper Networks (HPE ? Hewlett Packard Enterprise)
7.154 Key Bridge Wireless
7.155 Keysight Technologies
7.156 Kleos
7.157 KMW
7.158 Kumu Networks
7.159 Lemko Corporation
7.160 Lenovo
7.161 Lime Microsystems
7.162 LIONS Technology
7.163 LITE-ON Technology Corporation
7.164 LitePoint (Teradyne)
7.165 LS telcom
7.166 LuxCarta
7.167 MantisNet
7.168 Marvell Technology
7.169 Mavenir
7.170 Maxar Technologies
7.171 Meta
7.172 MicroNova
7.173 Microsoft Corporation
7.174 MikroTik
7.175 MitraStar Technology (Unizyx Holding Corporation)
7.176 Mobileum
7.177 MosoLabs (Sercomm Corporation)
7.178 MYCOM OSI
7.179 Nash Technologies
7.180 NEC Corporation
7.181 Net AI
7.182 Netcracker Technology (NEC Corporation)
7.183 NETSCOUT Systems
7.184 Netsia (Argela)
7.185 Neutroon Technologies
7.186 New H3C Technologies (Tsinghua Unigroup)
7.187 New Postcom Equipment
7.188 Nextivity
7.189 Node-H
7.190 Nokia
7.191 Novowi
7.192 NuRAN Wireless
7.193 NVIDIA Corporation
7.194 NXP Semiconductors
7.195 Oceus Networks
7.196 Omnitele
7.197 OneLayer
7.198 Ookla
7.199 Opanga Networks
7.200 OREX (NTT DoCoMo)
7.201 P.I. Works
7.202 Palo Alto Networks
7.203 Parallel Wireless
7.204 Pente Networks
7.205 Phluido
7.206 Picocom
7.207 Pivotal Commware
7.208 Potevio (CETC ? China Electronics Technology Group Corporation)
7.209 QCT (Quanta Cloud Technology)
7.210 Qualcomm
7.211 Quanta Computer
7.212 Qucell Networks (InnoWireless)
7.213 RADCOM
7.214 Radisys (Reliance Industries)
7.215 Radware
7.216 Rakuten Symphony
7.217 Ranlytics
7.218 Ranplan Wireless
7.219 Rebaca Technologies
7.220 Red Hat (IBM)
7.221 RED Technologies
7.222 REPLY
7.223 RIMEDO Labs
7.224 Rivada Networks
7.225 Rohde & Schwarz
7.226 Ruijie Networks
7.227 RunEL
7.228 SageRAN (Guangzhou SageRAN Technology)
7.229 Samji Electronics
7.230 Samsung
7.231 Sandvine
7.232 Sercomm Corporation
7.233 ServiceNow
7.234 Shabodi
7.235 Signalwing
7.236 SIRADEL
7.237 Skyvera (TelcoDR)
7.238 SOLiD
7.239 Sooktha
7.240 Spectrum Effect
7.241 Spirent Communications
7.242 SRS (Software Radio Systems)
7.243 SSC (Shared Spectrum Company)
7.244 Star Solutions
7.245 Subex
7.246 Sunwave Communications
7.247 Supermicro (Super Micro Computer)
7.248 SynaXG Technologies
7.249 Systemics-PAB
7.250 T&W (Shenzhen Gongjin Electronics)
7.251 Tarana Wireless
7.252 TCS (Tata Consultancy Services)
7.253 Tech Mahindra
7.254 Tecore Networks
7.255 TECTWIN
7.256 Telrad Networks
7.257 TEOCO/Aircom
7.258 ThinkRF
7.259 TI (Texas Instruments)
7.260 TietoEVRY
7.261 Tropico (CPQD ? Center for Research and Development in Telecommunications, Brazil)
7.262 TTG International
7.263 Tupl
7.264 ULAK Communication
7.265 Vavitel (Shenzhen Vavitel Technology)
7.266 VHT (Viettel High Tech)
7.267 VIAVI Solutions
7.268 VMware (Broadcom)
7.269 VNL ? Vihaan Networks Limited (Shyam Group)
7.270 Wave Electronics
7.271 WDNA (Wireless DNA)
7.272 WIM Technologies
7.273 Wind River Systems
7.274 Wipro
7.275 Wiwynn (Wistron Corporation)
7.276 WNC (Wistron NeWeb Corporation)
7.277 Xingtera
7.278 ZaiNar
7.279 Z-Com
7.280 Zeetta Networks
7.281 Zinkworks
7.282 ZTE
7.283 zTouch Networks
7.284 Zyxel (Unizyx Holding Corporation)
8 Chapter 8: Market Sizing & Forecasts
8.1 Mobile Network Automation
8.2 Network Domain Submarkets
8.2.1 RAN Automation
8.2.2 Mobile Core Automation
8.2.3 xHaul Transport Automation
8.3 RAN Automation Functional Areas
8.3.1 SON-Based Automation
8.3.2 Open RAN Automation
8.3.3 Baseband-Integrated Intelligent RAN Applications
8.3.4 RAN Planning & Optimization Software
8.3.5 Test & Measurement Solutions
8.4 SON-Based Automation Submarkets
8.4.1 RAN Vendor SON Solutions
8.4.2 Third Party C-SON Platforms
8.5 Open RAN Automation Submarkets
8.5.1 Non-RT RIC & SMO
8.5.2 Near-RT RIC
8.5.3 rApps
8.5.4 xApps
8.6 Access Technology Generations
8.6.1 LTE
8.6.2 5G NR
8.6.3 6G
8.7 Regional Segmentation
8.7.1 North America
8.7.2 Asia Pacific
8.7.3 Europe
8.7.4 Middle East & Africa
8.7.5 Latin & Central America
9 Chapter 9: Conclusion & Strategic Recommendations
9.1 Why is the Market Poised to Grow?
9.2 Future Roadmap: 2024 ? 2030
9.2.1 2024 ? 2026: Production-Grade Deployments of SMO & RIC Platforms for Brownfield Networks
9.2.2 2027 ? 2029: Widespread Adoption of Open RAN Automation & Diverse RIC-Hosted Applications
9.2.3 2030 & Beyond: Towards AI-Native Air Interfaces & Zero-Touch 5G/6G Network Automation
9.3 Reviewing the Real-World Benefits & TCO Savings Potential of RAN Automation
9.4 Impact of Intelligent Automation on RAN Engineering Roles
9.5 Transition From SON to Open RAN Automation
9.6 Evolution of Use Cases & AI/ML Algorithms
9.7 Growing Focus on Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
9.8 Vertical Industries & Private Wireless Automation
9.9 Diversified Community of x/rApp Developers
9.10 Signs of Consolidation in the SMO & RIC Ecosystem
9.11 Which RAN Automation Platform & Application Vendors Are Leading the Market?
9.12 Prospects of Hosting Third Party Applications Within RAN Baseband Products
9.13 Paving the Path to an AI/ML-Based 6G Air Interface
9.14 Convergence of AI & RAN Infrastructure
9.15 Strategic Recommendations
9.15.1 RAN Automation Solution Providers
9.15.2 Mobile Operators
10 Chapter 10: Expert Opinion ? Interview Transcripts
10.1 AirHop Communications
10.2 Amdocs
10.3 Groundhog Technologies
10.4 Innovile
10.5 Net AI
10.6 Nokia
10.7 P.I. Works
10.8 Qualcomm
10.9 Rakuten Mobile
10.10 RIMEDO Labs
List of Companies Mentioned
The following companies and organizations have been reviewed, discussed or mentioned in the report:
1&1
3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project)
4iG Group
A10 Networks
A5G Networks
Aalyria
Aarna Networks
Abside Networks
Accedian
Accelleran
Accuver
Acentury
Actiontec Electronics
Adtran
Aglocell
AI-LINK
Aira Technologies
AI-RAN Alliance
Aircom
AirHop Communications
Airspan Networks
AiVader
Aliniant
Allot
Alpha Networks
Alphabet
Altice Portugal
Amazon
AMD (Advanced Micro Devices)
Amdocs
America Movil
Andorra Telecom
Anktion (Fujian) Technology
Anritsu
Antevia Networks
Arcadyan Technology Corporation
Argela
ARIB (Association of Radio Industries and Businesses, Japan)
Arm
ArrayComm (Chengdu ArrayComm Wireless Technologies)
Arrcus
Artemis Networks
Artiza Networks
Arukona
AsiaInfo Technologies
Askey Computer Corporation
ASOCS
Aspire Technology
ASTRI (Hong Kong Applied Science and Technology Research Institute)
ASUS (ASUSTeK Computer)
AT&T
Ataya
ATDI
Atesio
ATIS (Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions)
Atrinet
Auden Techno
Auray Technology
Aviat Networks
AWS (Amazon Web Services)
Axiata Group
Azcom Technology
Baicells
Batelco
beCloud (Belarusian Cloud Technologies)
Beeline Russia (VimpelCom)
Bell Canada
Betacom
Bharti Airtel
BLiNQ Networks
Blu Wireless
Booz Allen Hamilton
BravoCom
Broadcom
BT Group
BTC (Botswana Telecommunications Corporation)
BTI Wireless
BubbleRAN
B-Yond
C Spire
C3Spectra
CableFree (Wireless Excellence)
Cambium Networks
Capgemini Engineering
CBNG (Cambridge Broadband Networks Group)
CCI (Communication Components Inc.)
CCSA (China Communications Standards Association)
Celfinet
Cellfie Mobile
Celona
CelPlan Technologies
Ceragon Networks
CETC (China Electronics Technology Group Corporation)
CETIN Group
CGI
Chengdu NTS
China Mobile
China Telecom
China Unicom
CICT ? China Information and Communication Technology Group (China Xinke Group)
Ciena Corporation
CIG (Cambridge Industries Group)
Cisco Systems
CK Hutchison
Claro Colombia
Clavister
Cohere Technologies
Comarch
Comba Telecom
CommAgility
CommScope
Compal Electronics
COMSovereign
Contela
Corning
CPQD (Center for Research and Development in Telecommunications, Brazil)
Creanord
Cyient
Datang Telecom Technology & Industry Group
DeepSig
Dell Technologies
DGS (Digital Global Systems)
DIGI Communications
Digis Squared
Digitata
DISH Network Corporation
Djezzy
D-Link Corporation
Druid Software
DSA (Dynamic Spectrum Alliance)
DT (Deutsche Telekom)
DZS
ECE (European Communications Engineering)
EDX Wireless
EE
eino
Elisa
Elisa Polystar
Encora
Equiendo
Ericsson
Errigal
E-Space
Etisalat Group (e&)
ETRI (Electronics & Telecommunications Research Institute, South Korea)
ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute)
EXFO
F5
Fairspectrum
Federated Wireless
FET (Far EasTone Telecommunications)
FiberHome Technologies
Firecell
Flash Networks
Forsk
Fortinet
Foxconn (Hon Hai Technology Group)
Fraunhofer HHI (Heinrich Hertz Institute)
Fujitsu
FullRays (LDAS ? LocationDAS)
Future Connections
FYRA
G REIGNS
Gemtek Technology
GENEViSiO
Gigamon
GigaTera Communications
GlobalLogic
Globalstar
Globe Telecom
Google
Groundhog Technologies
GSMA (GSM Association)
GTAA (Global Telco AI Alliance)
Guavus
GXC (Formerly GenXComm)
HCLTech (HCL Technologies)
Helios (Fujian Helios Technologies)
HFR Networks
Highstreet Technologies
Hitachi
HPE (Hewlett Packard Enterprise)
HSC (Hughes Systique Corporation)
HTC Corporation
Huawei
Hutchison Drei Austria
IBM
iBwave Solutions
iConNext
IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
Infinera
Infosys
Infovista
Inmanta
Innovile
InnoWireless
Intel Corporation
InterDigital
Intracom Telecom
Inventec Corporation
ISCO International
IS-Wireless
Itential
ITRI (Industrial Technology Research Institute, Taiwan)
ITU (International Telecommunication Union)
JMA Wireless
JRC (Japan Radio Company)
Juniper Networks
KDDI
Key Bridge Wireless
Keysight Technologies
Kleos
KMW
KPN
KT Corporation
Kumu Networks
Kuzey K?br?s Turkcell
Kyivstar
Lemko Corporation
Lenovo
LG Uplus
Liberty Global
life:)/BeST (Belarusian Telecommunications Network)
lifecell Ukraine
Lime Microsystems
Linux Foundation
LIONS Technology
LITE-ON Technology Corporation
LitePoint
LS telcom
LTT (Libya Telecom & Technology)
LuxCarta
MantisNet
Marvell Technology
MASMOVIL
Mavenir
Maxar Technologies
MegaFon
MEO
Meta
MicroNova
Microsoft Corporation
MikroTik
MitraStar Technology
Mobileum
MosoLabs
MTN Group
MTS (Mobile TeleSystems)
MYCOM OSI
Nash Technologies
NEC Corporation
Net AI
Netcracker Technology
NETSCOUT Systems
Netsia
Neutroon Technologies
New H3C Technologies
New Postcom Equipment
Nextivity
NGMN Alliance
Node-H
Nokia
Northeastern University
Novowi
NTT DoCoMo
NuRAN Wireless
NVIDIA Corporation
NXP Semiconductors
NYCU (National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University)
Oceus Networks
Odido
Omnitele
OneLayer
ONF (Open Networking Foundation)
OnGo Alliance
Ookla
Ooredoo
Ooredoo Algeria
Ooredoo Tunisia
Opanga Networks
Optus
O-RAN Alliance
Orange
OREX
OSA (OpenAirInterface Software Alliance)
P.I. Works
Palo Alto Networks
Parallel Wireless
Pente Networks
Phluido
Picocom
Pivotal Commware
PLDT
Potevio
QCT (Quanta Cloud Technology)
QNAP Systems
Qualcomm
Quanta Computer
Qucell Networks
RADCOM
Radisys
Radware
Rakuten Mobile
Rakuten Symphony
Ranlytics
Ranplan Wireless
Reailize
Rebaca Technologies
Red Hat
RED Technologies
Reliance Industries
Reliance Jio Infocomm
REPLY
RIMEDO Labs
Rivada Networks
Rogers Communications
Rohde & Schwarz
Ruijie Networks
RunEL
SageRAN (Guangzhou SageRAN Technology)
Samji Electronics
Samsung
Sandvine
SCF (Small Cell Forum)
Sercomm Corporation
ServiceNow
Shabodi
Shyam Group
Signalwing
Singtel
SIRADEL
SK Telecom
Skyvera (TelcoDR)
Smart Communications
Smartfren
SoftBank Group
SOLiD
Sooktha
Spectrum Effect
Spirent Communications
SRS (Software Radio Systems)
SSC (Shared Spectrum Company)
Star Solutions
STC (Saudi Telecom Company)
Subex
Sunwave Communications
Supermicro (Super Micro Computer)
SUTD (Singapore University of Technology and Design)
Swisscom
SynaXG Technologies
Systemics-PAB
T&W (Shenzhen Gongjin Electronics)
Tarana Wireless
TCS (Tata Consultancy Services)
TDC NET
Tech Mahindra
Tecore Networks
TECTWIN
Telecom Argentina
Telefonica Germany
Telefonica Group
Telia Company
Telkomsel
Telrad Networks
Telstra
Telus
TEOCO
Teradyne
Texas A&M University
Thales
ThinkRF
TI (Texas Instruments)
TietoEVRY
TIM (Telecom Italia Mobile)
TIM Brasil
TIP (Telecom Infra Project)
TM Forum
TPG Telecom
Tropico
TSDSI (Telecommunications Standards Development Society, India)
Tsinghua Unigroup
TTA (Telecommunications Technology Association, South Korea)
TTC (Telecommunication Technology Committee, Japan)
TTG International
Tupl
Turk Telekom
Turkcell
U.S. DOD (Department of Defense)
U.S. NTIA (National Telecommunications and Information Administration)
Ucom (Armenia)
ULAK Communication
University of California San Diego
University of Lancaster
University of Malaga
Unizyx Holding Corporation
Vavitel (Shenzhen Vavitel Technology)
VEON
Verizon Communications
VHT (Viettel High Tech)
Vi (Vodafone Idea)
VIAVI Solutions
Viettel Group
Virgin Media O2
VMware
VNL (Vihaan Networks Limited)
Vodafone Germany
Vodafone Group
Vodafone Ireland
Vodafone Turkey
Wave Electronics
WDNA (Wireless DNA)
WIM Technologies
Wind River Systems
WInnForum (Wireless Innovation Forum)
Wipro
Wistron Corporation
Wiwynn
WNC (Wistron NeWeb Corporation)
Xingtera
Zain Group
Zain Saudi Arabia (Zain KSA)
ZaiNar
Z-Com
Zeetta Networks
Zinkworks
ZTE
zTouch Networks
Zyxel
ご注文は、お電話またはWEBから承ります。お見積もりの作成もお気軽にご相談ください。本レポートと同分野の最新刊レポート
SNS Telecom & IT社の調査レポート分野での最新刊レポート
本レポートと同じKEY WORD()の最新刊レポート
よくあるご質問SNS Telecom & IT社はどのような調査会社ですか?SNSテレコム&IT (SNS Telecom & IT)はドバイに拠点をおき、通信技術やモバイル機器に関する継続的な非常に詳細なデータを提供しています。無線ネットワークインフラやビッグデータ、M2M... もっと見る 調査レポートの納品までの日数はどの程度ですか?在庫のあるものは速納となりますが、平均的には 3-4日と見て下さい。
注文の手続きはどのようになっていますか?1)お客様からの御問い合わせをいただきます。
お支払方法の方法はどのようになっていますか?納品と同時にデータリソース社よりお客様へ請求書(必要に応じて納品書も)を発送いたします。
データリソース社はどのような会社ですか?当社は、世界各国の主要調査会社・レポート出版社と提携し、世界各国の市場調査レポートや技術動向レポートなどを日本国内の企業・公官庁及び教育研究機関に提供しております。
|
詳細検索
2025/04/17 10:26 143.53 円 163.57 円 192.38 円 |