E-Textiles and Smart Clothing Markets 2023-2033: Technologies, Players, and ApplicationsEテキスタイルとスマート衣類の市場2023-2033年:技術、プレーヤー、アプリケーション この調査レポートでは、10年以上にわたるリサーチと200社以上の企業データベースをもとに、e-テキスタイル産業について詳細に調査・分析しています。 主な掲載内容(目次より抜粋) ... もっと見る
※ 調査会社の事情により、予告なしに価格が変更になる場合がございます。
Summary
この調査レポートでは、10年以上にわたるリサーチと200社以上の企業データベースをもとに、e-テキスタイル産業について詳細に調査・分析しています。
主な掲載内容(目次より抜粋)
Report Summary
Electronic textiles (e-textiles) involves the integration of electronics with textiles to form "smart" textile products. Research compiled over 10 years and a database of over 200 companies in the sector have been used to inform this report on the e-textiles industry. With coverage of each major product type, primary applications and markets, and forecasts up to 2033 based on several years of historic data, this is a comprehensive study of this technology.
An increasingly digitalized world and greater demands for connectivity has led towards a clear trend of miniaturization of electronic devices - enabling greater integration into our daily lives. This miniaturization has enabled the integration of electronics into textiles and clothing to form e-textiles. E-textiles exist as part of a wider ecosystem of connected wearable devices, which includes smartwatches, activity trackers, and electronic skin patches, to name a few. Yet despite such a diverse set of form factors among such wearable devices, one key trend is common - namely, a demand for increasingly discrete devices. This demand can be particularly well-fulfilled by e-textiles, where the electronics can be integrated with clothing itself - this is potentially one of the most seamless forms of electronics integration for wearable devices.
This report aims to contextualize the narrative around the e-textiles industry; the concept and core features of the e-textiles technology movement has been around for decades, with increasing commercial focus in the last 30 years. Some e-textile products such as heated blankets and heated clothing have developed throughout this time to become significant commercial markets selling millions of products each year. However, the variety of products is extremely broad; from clothing to bed linen and industrial fabrics, new products are appearing throughout a variety of verticals as this technology area is increasingly explored. This report covers the entire e-textiles value chain, from the manufacturing through yarns or conductive inks, to the components such as the sensors used today.
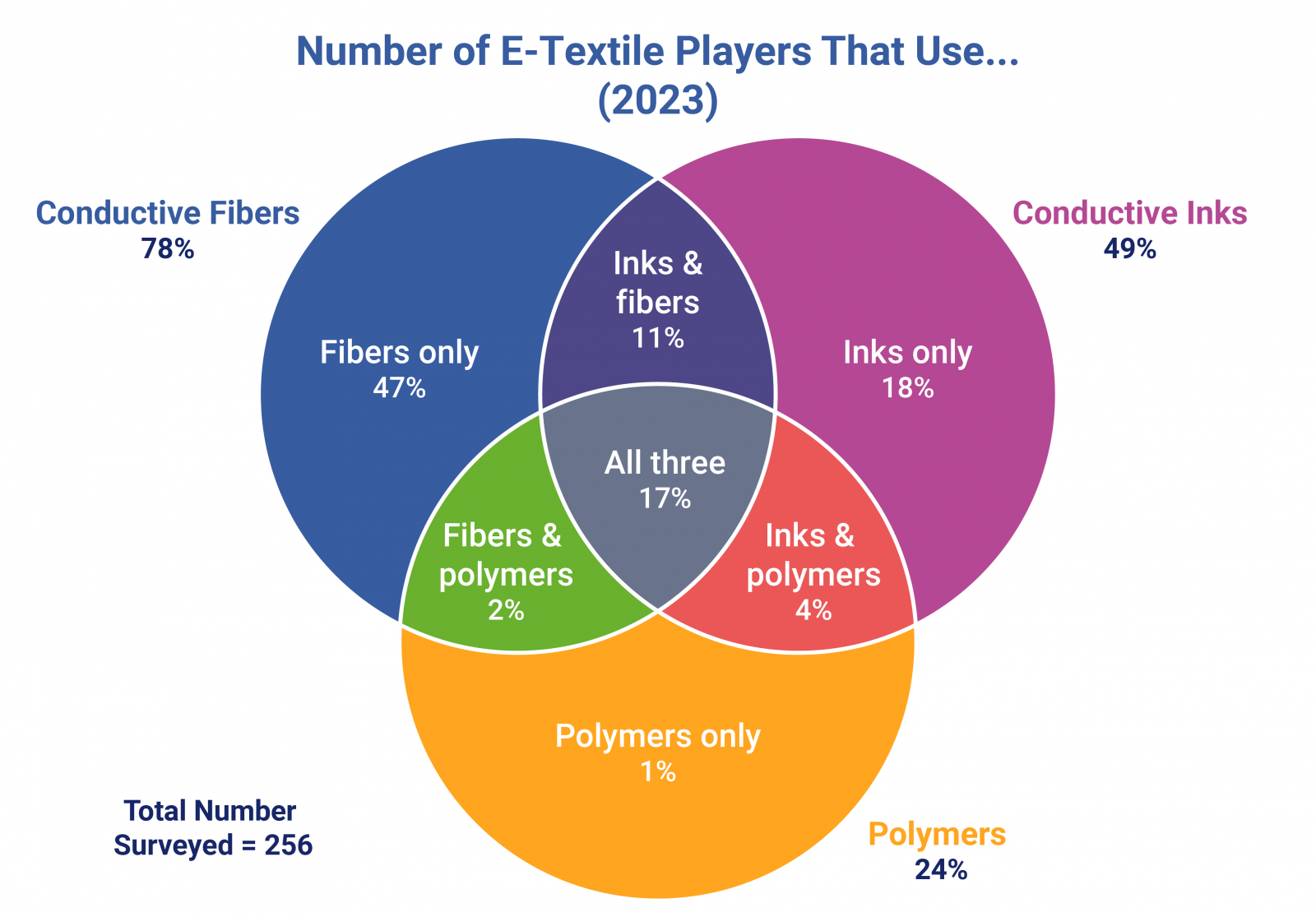
A breakdown of the preferred material choice in e-textile manufacturing across 256 players. Image source: E-Textiles and Smart Clothing Markets 2023-2033: Technologies, Players, and Applications
There remains a gulf in commercial maturity for different products within e-textiles. For example, heated clothing has a mature value chain with established manufacturing practices and products being sold around the world under hundreds of different brands. Other areas such as the integration of biometric monitoring are still being developed. Challenges around reliability, equipment suitability, materials availability and overhead costs have previously been prohibitive to commercial development of many different product types. However, thanks to significant investments and partnerships, some of these barriers are being lowered, with more players able to make more advanced e-textile products at less prohibitive prices. These developments improve the chances that emerging e-textile products have against incumbent options in each of the markets they target - this report goes through such recent developments.
Translating new technologies being developed for e-textiles through to successful commercial products requires targeted development which focuses on the specific needs across different target markets. The report describes efforts across a series of market sectors (such as medical & healthcare, sports & fitness, PPE & other workwear, etc), as well as other specific product types or groups that span different potential application areas (such as animal wearables, automotive interiors, motion capture, haptic suits and assistive clothing). This report covers the use and potential of e-textiles in many such applications in detail.
With continuous parallel research across the emerging technology ecosystem, including reports on conductive inks, stretchable electronics, wearable technology, printed electronics, printed and flexible sensors, the Internet of Things, healthcare & life sciences, and many more, IDTechEx has leveraged a broad network and experience across the team of expert analysts for this research. IDTechEx has also hosted many prominent industry events covering e-textile technology. The result of these efforts enables this report to be a comprehensive characterisation of the e-textiles industry today, and an excellent resource for any player involved in or actively investigating this space.
This report provides the following information.
Technology analysis:
Market analysis and forecast:
Table of Contents
|