COVID-19 DiagnosticsCOVID-19診断:技術、企業、動向 このレポートはCOVID-19に対しての世界の対応を調査し、100以上の商用デバイスのベンチマークと、技術動向とバイオテックの革新の深い考察を掲載しています。 Report Details COVID-19 is ... もっと見る
※価格はデータリソースまでお問い合わせください。
SummaryこのレポートはCOVID-19に対しての世界の対応を調査し、100以上の商用デバイスのベンチマークと、技術動向とバイオテックの革新の深い考察を掲載しています。 Report Details
COVID-19 is an infectious disease caused by SARS-CoV-2. The outbreak of COVID-19 started in Dec. 2019 with the first case reported in China. The World Health Organization (WHO) recognised the outbreak of COVID-19 as a pandemic on 11 March 2020. By April 2020, there are over 2 million confirmed cases and have brought the economies of many countries to a halt.
Diagnostic testing is possibly the only efficient way to know the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 in time and space, enabling policymakers and healthcare workers to track and mitigate the outbreak of COVID-19. The WHO has appealed for global mass testing. The demand for COVID-19 testing is estimated to be over 600 million tests including 120 million genetic tests and over 500 million rapid tests.
The need for universal and massive testing across the population has led to a race for technology innovations for COVID-19 diagnostics. This report surveys the technology landscape, with an in-depth analysis of the technology innovations that are enabling a quick access to COVID-19 diagnosis in response to the global pandemic.
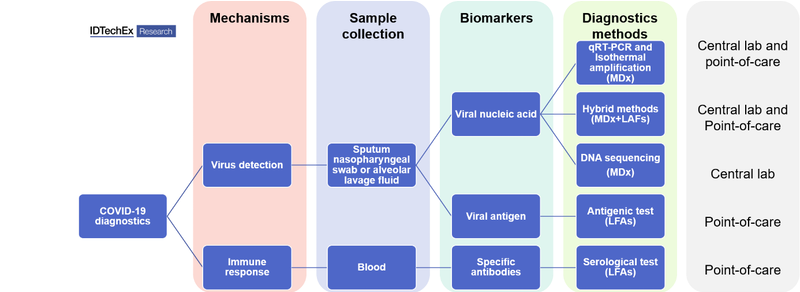
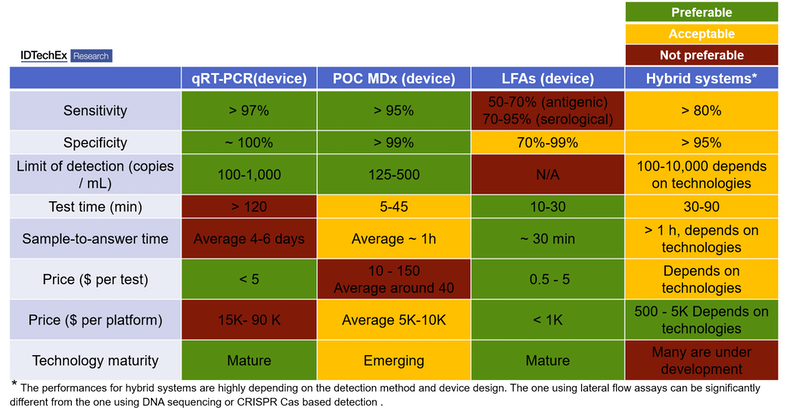
Molecules derived from the virus—nucleic acids like RNA or DNA, or proteins—form the basis of diagnostics as well as being essential for developing new therapies and vaccines. Depending on the target biomarkers, the diagnostic methods can be separated into two categories: genetic testing (detecting the viral genome) and serological & antigenic testing (detecting antibodies and viral antigens, respectively). From the technological perspective, molecular diagnostics (MDx) and lateral flow assays (LAFs) dominate COVID-19 diagnostics. The gold standard used across clinical laboratories is quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR, MDx), which requires a central lab setting. Such qRT-PCR testing lasts for more than 2 hour and the sample shipment cost up to several days. With the demand for quicker tests at community settings, the market is moving into point-of-care (POC) devices, including POC MDx and POC LFAs.
All molecular diagnostics tests detecting viral genomes share three common steps: sample collection from Nasopharyngeal swab and extraction of viral RNA, amplification of the analyte and read-out. The amplification step is performed reliably by RT-PCR, however alternatives that do not require expensive and bulky equipment exist, i.e. isothermal amplification. This approach, although less sensitive than PCR, allows for a quicker amplification step at a constant temperature.
The read-out of the amplified signal is normally achieved through fluorescence probes in the sample and detectors in qRT-PCR devices. Many companies have resorted to lateral flow assays and alternative read-out methods that require proprietary detection equipment. These "hybrid systems" benefit from the high specificity and sensitivity of MDx and the speed and low cost of LFAs.
This report identifies key innovations and technology trends currently being developed in the diagnostics ecosystem that will enable quick and sensitive diagnosis of COVID-19 at point-of-care settings:
Apart from genetic testing, antigenic tests and serological tests, so-called ¨rapid tests¨, are also becoming central tools in the fight against the pandemic. Both types of immunoassays rely on antibody-antigen recognition. Antigen tests are able to detect the presence of viral proteins in the blood All molecular diagnostics tests detecting viral genomes share three common steps: sample collection from Nasopharyngeal swab and extraction of viral RNA, amplification of the analyte and read-out. The amplification step is performed reliably by RT-PCR, however alternatives that do not require expensive and bulky equipment exist, i.e. isothermal amplification. This approach, although less sensitive than PCR, allows for a quicker amplification step at a constant temperature.
The read-out of the amplified signal is normally achieved through fluorescence probes in the sample and detectors in qRT-PCR devices. Many companies have resorted to lateral flow assays and alternative read-out methods that require proprietary detection equipment. These "hybrid systems" benefit from the high specificity and sensitivity of MDx and the speed and low cost of LFAs.
This report identifies key innovations and technology trends currently being developed in the diagnostics ecosystem that will enable quick and sensitive diagnosis of COVID-19 at point-of-care settings:
Apart from the effort from biotech, multiple software companies have developed algorithms to identify signs of COVID-19-related pneumonia in patient scans. CT imaging is an effective way of detecting abnormalities indicative of COVID-19, and image recognition AI algorithms have the potential to detect these abnormalities faster and more efficiently than radiologists.
In this report, we benchmarked more than 100 commercial devices across various technologies, providing a deep insight into the technology trends and biotech innovations surrounding the COVID-19 global response. Some of the companies mentioned in the report:
Table of ContentsTable of Contents
|