チェックすべき定置型蓄電池技術の可能性:重量エネルギー貯蔵、高圧空気エネルギー貯蔵、液体空気エネルギー貯蔵、熱エネルギー貯蔵などの新しいフロントオブメータ向け技術。予測2020-2030年、技術、市場と企業Potential Stationary Energy Storage Technologies to Monitor このレポートはエネルギー貯蔵の新しい技術に注目し、出力MWや貯蔵時間について言及しています。 Report Details Introduction to mechanical energy storage: ... もっと見る
出版社
IDTechEx
アイディーテックエックス 出版年月
2020年9月1日
価格
お問い合わせください
ライセンス・価格情報/注文方法はこちら 納期
お問合わせください
ページ数
120
言語
英語
※価格はデータリソースまでお問い合わせください。
サマリー
このレポートはエネルギー貯蔵の新しい技術に注目し、出力MWや貯蔵時間について言及しています。
Report Details
Introduction to mechanical energy storage:
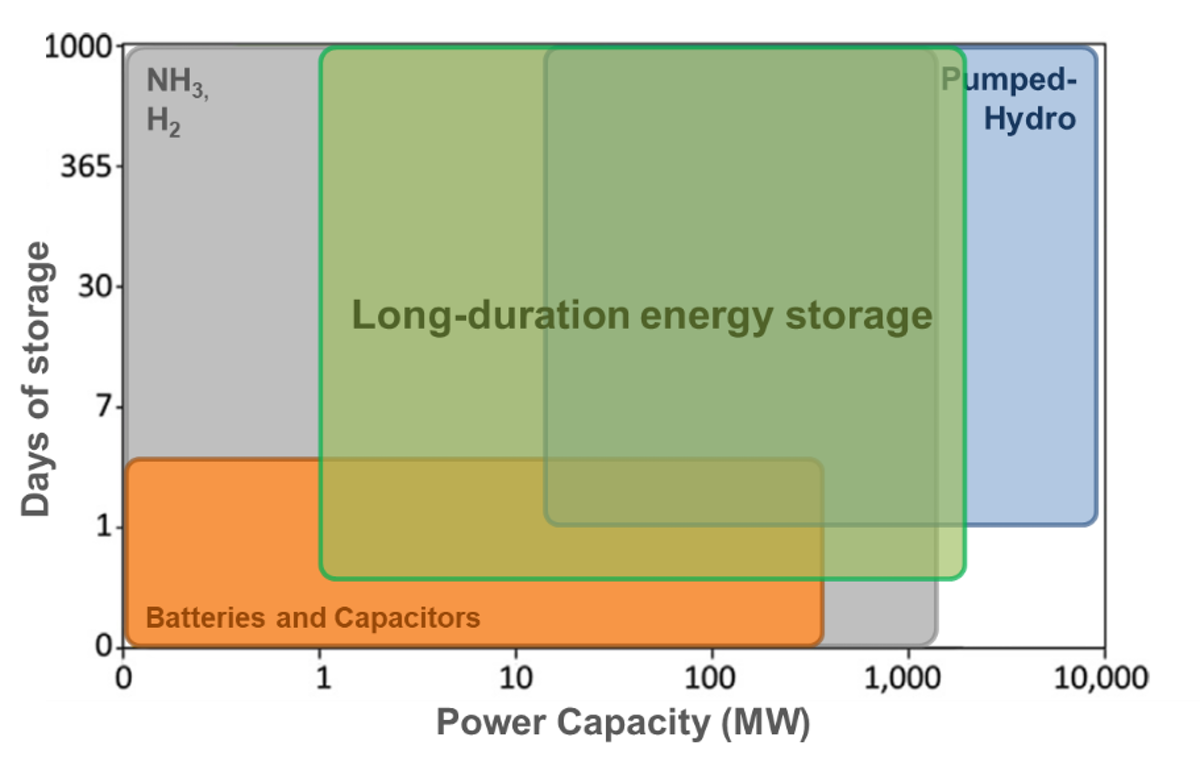
When talking about energy storage it is now common to think about Li-ion batteries, due to their success in the automotive sector, portable electronic devices, and stationary applications. In the last few years Li-ion batteries started to be constantly adopted in stationary energy storage with a power output of few kWs up to MWs scale. Although a powerful device, their application can hardly cover the entire range of power and energy demanded by the electricity grid. If one end is dominated by Li-ion batteries, on the other end, pumped hydro energy storage is the reference system to deliver large power output, and store large amounts of energy able to generate electricity for days. Pumped hydro energy storage was the first large power plant built to generate electricity, and still nowadays is the reference technology for large power output.
Between these two main technologies, a number of new technologies with a power output of tens of MWs are currently approaching the market. In the new report released: "Potential Stationary Energy Storage to Monitor", IDTechEx investigated this new group of technologies aiming to address MWs of power output and long storage time.
The technologies defined as mechanical energy storage include different types of technologies, all of them characterised by a large power output from MW size, and a simple mechanical working principles. Among them:
Power and storage capacity comparison of different technologies
These technologies are based on simple mechanical working principles, which allow them to employ well known components, like pumps, ventilators, cranes, and do not employ dangerous materials. A simple working principle implies high round-trip efficiencies, in most cases close to 80%. Finally, differently from electrochemical systems, mechanical energy storage systems are not affected by self-discharge, allowing them to store electricity for an indefinite amount of time.
Large amounts of energy, similarly to mechanical energy storage systems, could also be stored by hydrogen and ammonia. Storing electricity as chemical energy implies the adoption of other technologies like fuel cells, which strongly affect the overall efficiency of the system.
The growing interest in the renewable energies, driven by the necessity to decarbonise the electricity market, is leading to a growing adoption of energy storage devices. While renewable electricity sources allow us to reduce polluting emissions, their variable nature requires extra systems to adjust the timing of energy production and energy consumption. In addition, the adoption of renewable energies is leading to an upgrade of the electricity grid, shifting the power grid from a centralised model, to decentralised energy production. Therefore, the role of energy storage is constantly growing, and with it the technologies involved.
Report content:
Due to growing interest in energy storage devices, in particular for grid application, IDTechEx releases the new report titled: "Potential Stationary Energy Storage to Monitor", introducing an emerging group of technologies.
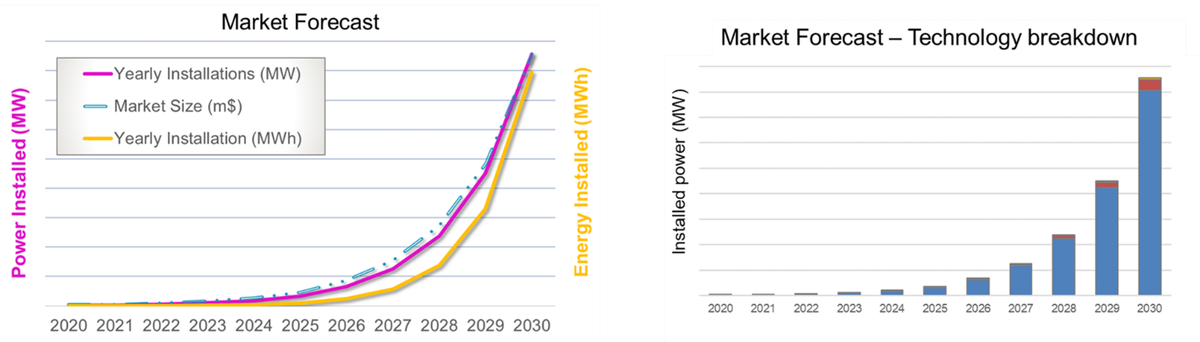
The report begins with an introduction about the electricity grid, explaining the role of energy storage systems, and the market these devices can address. In the following chapters, the different mechanical energy storage technologies are investigated. For each technology the working principle is initially explained, followed by an analysis of the main companies involved, showing the main advantages and disadvantages of the systems analysed. Moreover, the executive summary provides the reader with a comparison of the different technologies, showing the different TRL (technology readiness level) and MRL (manufacturing readiness level) of the technologies analysed in the report. A comparison of mechanical energy storage with Li-ion batteries and redox flow batteries allows the reader to appreciate the differences between these technologies. In conclusion, a market forecast for the period 2020-2030, in terms of installed power, energy and market size is provided, together with the technology breakdown.
Market forecast, and market forecast breakdown - IDTechEx Source
目次Table of Contents
Summary
このレポートはエネルギー貯蔵の新しい技術に注目し、出力MWや貯蔵時間について言及しています。
Report Details
Introduction to mechanical energy storage:
When talking about energy storage it is now common to think about Li-ion batteries, due to their success in the automotive sector, portable electronic devices, and stationary applications. In the last few years Li-ion batteries started to be constantly adopted in stationary energy storage with a power output of few kWs up to MWs scale. Although a powerful device, their application can hardly cover the entire range of power and energy demanded by the electricity grid. If one end is dominated by Li-ion batteries, on the other end, pumped hydro energy storage is the reference system to deliver large power output, and store large amounts of energy able to generate electricity for days. Pumped hydro energy storage was the first large power plant built to generate electricity, and still nowadays is the reference technology for large power output.
Between these two main technologies, a number of new technologies with a power output of tens of MWs are currently approaching the market. In the new report released: "Potential Stationary Energy Storage to Monitor", IDTechEx investigated this new group of technologies aiming to address MWs of power output and long storage time.
The technologies defined as mechanical energy storage include different types of technologies, all of them characterised by a large power output from MW size, and a simple mechanical working principles. Among them:
Power and storage capacity comparison of different technologies
These technologies are based on simple mechanical working principles, which allow them to employ well known components, like pumps, ventilators, cranes, and do not employ dangerous materials. A simple working principle implies high round-trip efficiencies, in most cases close to 80%. Finally, differently from electrochemical systems, mechanical energy storage systems are not affected by self-discharge, allowing them to store electricity for an indefinite amount of time.
Large amounts of energy, similarly to mechanical energy storage systems, could also be stored by hydrogen and ammonia. Storing electricity as chemical energy implies the adoption of other technologies like fuel cells, which strongly affect the overall efficiency of the system.
The growing interest in the renewable energies, driven by the necessity to decarbonise the electricity market, is leading to a growing adoption of energy storage devices. While renewable electricity sources allow us to reduce polluting emissions, their variable nature requires extra systems to adjust the timing of energy production and energy consumption. In addition, the adoption of renewable energies is leading to an upgrade of the electricity grid, shifting the power grid from a centralised model, to decentralised energy production. Therefore, the role of energy storage is constantly growing, and with it the technologies involved.
Report content:
Due to growing interest in energy storage devices, in particular for grid application, IDTechEx releases the new report titled: "Potential Stationary Energy Storage to Monitor", introducing an emerging group of technologies.
The report begins with an introduction about the electricity grid, explaining the role of energy storage systems, and the market these devices can address. In the following chapters, the different mechanical energy storage technologies are investigated. For each technology the working principle is initially explained, followed by an analysis of the main companies involved, showing the main advantages and disadvantages of the systems analysed. Moreover, the executive summary provides the reader with a comparison of the different technologies, showing the different TRL (technology readiness level) and MRL (manufacturing readiness level) of the technologies analysed in the report. A comparison of mechanical energy storage with Li-ion batteries and redox flow batteries allows the reader to appreciate the differences between these technologies. In conclusion, a market forecast for the period 2020-2030, in terms of installed power, energy and market size is provided, together with the technology breakdown.
Market forecast, and market forecast breakdown - IDTechEx Source
Table of ContentsTable of Contents
ご注文は、お電話またはWEBから承ります。お見積もりの作成もお気軽にご相談ください。本レポートと同分野(太陽光)の最新刊レポートIDTechEx社の エネルギー、電池 - Energy, Batteries分野 での最新刊レポート
よくあるご質問IDTechEx社はどのような調査会社ですか?IDTechExはセンサ技術や3D印刷、電気自動車などの先端技術・材料市場を対象に広範かつ詳細な調査を行っています。データリソースはIDTechExの調査レポートおよび委託調査(個別調査)を取り扱う日... もっと見る 調査レポートの納品までの日数はどの程度ですか?在庫のあるものは速納となりますが、平均的には 3-4日と見て下さい。
注文の手続きはどのようになっていますか?1)お客様からの御問い合わせをいただきます。
お支払方法の方法はどのようになっていますか?納品と同時にデータリソース社よりお客様へ請求書(必要に応じて納品書も)を発送いたします。
データリソース社はどのような会社ですか?当社は、世界各国の主要調査会社・レポート出版社と提携し、世界各国の市場調査レポートや技術動向レポートなどを日本国内の企業・公官庁及び教育研究機関に提供しております。
|
|