ヘリウム市場2025-2035年:用途、代替品、再生利用Helium Market 2025-2035: Applications, Alternatives, and Reclamation ヘリウムは有限の資源であり、医療用画像処理、バッテリーの熱管理システム、航空宇宙工学、化学・製薬、半導体製造、光ファイバー、素粒子物理学、科学用気球など、さまざまな産業で重要な役割を果たしていま... もっと見る

※ 調査会社の事情により、予告なしに価格が変更になる場合がございます。
サマリー
ヘリウムは有限の資源であり、医療用画像処理、バッテリーの熱管理システム、航空宇宙工学、化学・製薬、半導体製造、光ファイバー、素粒子物理学、科学用気球など、さまざまな産業で重要な役割を果たしています。ヘリウムの高い熱伝導性、化学的不活性、極低温特性は、場合によっては利用可能な代替物質が限られている、あるいは利用できないヘリウムの用途に独自に適している。ヘリウムは、エネルギー転換(電気自動車やバッテリーなど)、デジタル変革(エレクトロニクス、AI、通信など)、宇宙探査において重要な役割を果たすため、EUやカナダなどの政府機関によって重要鉱物に分類されている。その重要性にもかかわらず、生産の多様化や地政学的緊張の欠如により、ヘリウム市場は慢性的な供給不足と価格変動の影響を受けやすいことで有名である。
IDTechExのレポートでは、ヘリウム生産の見通し、主要産業におけるヘリウムの役割、ヘリウム代替品の入手可能性と実行可能性、ヘリウム再生技術について批判的に評価しています。市場予測は、主要用途別に区分した年間ヘリウム需要と、地域別の年間生産能力で行っている。
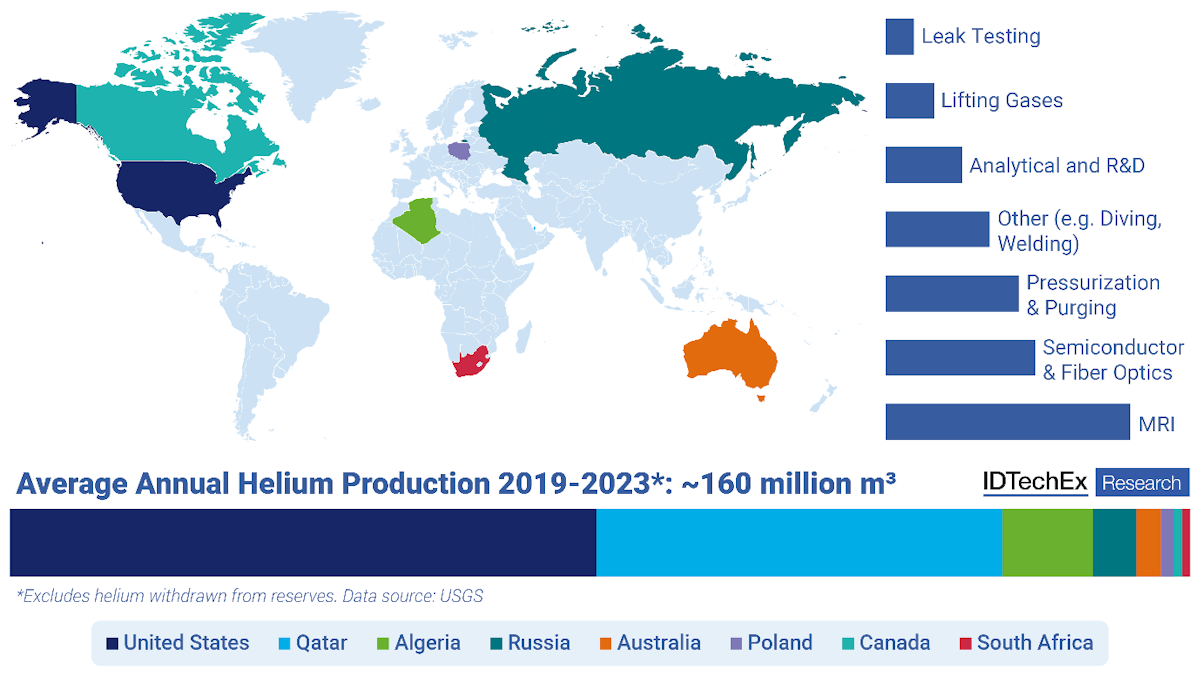
図1:ヘリウムの主な生産源と用途。出典 IDTechEx
製造業におけるヘリウム
ヘリウムはその冷却性と不活性特性により、製造工程で広く使用されている。半導体製造時の熱管理、光ファイバー製造に不可欠であり、HVAC機器、燃料タンク、バッテリーパック、航空宇宙部品などの部品のリークテストなど、品質管理プロセスにとって極めて重要なコンポーネントである。また、電気部品や自動車部品など数多くの部品を製造する溶接工程でも重要な役割を担っている。特に、半導体製造プロセスの微細化(AI、自律走行車などに不可欠)は、半導体産業のヘリウムへの依存度を高めることになり、現在のところ代替手段はない。
本レポートでは、これらの産業が慢性的なヘリウム供給の課題にどのように対処しているかを批判的に検証する。Telstar社やRosendahl Nextrom社などの再生技術メーカーなど、主要企業へのインタビューを通じて、ヘリウムの節約(再生技術への投資など)や、可能な限りのヘリウム代替品の採用に関する動向や市場活動を明らかにしている。
極低温物質としてのヘリウム
通常の沸点が4.2Kであるヘリウムは、絶対零度(0K)に近い温度で唯一の液体である。そのため、医療や化学産業におけるMRIやNMR装置、大型ハドロン衝突型加速器のような粒子加速器、一部の核融合炉のような超伝導装置の運転に不可欠である。量子コンピューティングでは、初期化、操作、読み出しの一連の動作において、10mKから4Kの冷却が必要とされる量子ビットがいくつかある。mK(1mK=0.001K)の温度に到達するためには、現在、クライオスタット内でヘリウムを使用することが不可欠である。
ここ数十年、ヘリウムの最終用途としてはMRIスキャナーが主流であった。しかし、ハードウェア設計(密閉型フォーライフ設計など)、ソフトウェア(AI、ディープラーニングなど)、材料開発(メタマテリアル、高温超伝導体など)の改善により、ヘリウムの必要量を削減するサクセスストーリーが到来しつつある。本レポートでは、MRI、NMR、量子コンピューティングなど、ヘリウム需要の新たなトレンドを牽引する技術進歩を批判的に分析する。
航空宇宙産業におけるヘリウム
ヘリウムは航空宇宙産業の様々な場面で重要な役割を果たしています。ヘリウムは不活性ガスとして、水素システムのパージ、地上および飛行流体システムの加圧、部品のリークテスト、精密溶接時のシールドガスとして使用される。また、部品を冷却するための極低温ガスとしても使用される。過去5年間で、軌道打ち上げの頻度は急増し、商業的な事業体は業界の拡大にとってますます重要となっている。この成長はヘリウムの重要な役割を強調し、この分野での不可欠な資源としての地位をさらに強固なものにしている。IDTechExのレポートでは、航空宇宙セクターにおけるヘリウムの需要予測を詳述した10年予測を提供している。
ヘリウム生産の動向
カタールとロシアがヘリウムの生産能力を増強する見込みであるため、ヘリウムの生産能力は増加すると予想されるが、地政学的緊張を考慮すると、将来にわたってヘリウム供給に支障がないことを必ずしも保証するものではない。
炭化水素以外のガスに含まれる地質埋蔵量から、一次ヘリウム/グリーンヘリウムを探鉱する独立系の小規模プレーヤーが増えている。とはいえ、中長期的な生産能力の見通しを明らかにするには、広範なデータと検証が必要である。これらのプロジェクトは、坑井現場や地元の処理施設でヘリウムをアップグレード・精製するために、膜やPSA技術などの低コストの分離システムを活用している。UGSやGeneronなどのヘリウム分離技術プロバイダーから得た洞察に基づき、本レポートはヘリウム分離・精製技術の利点と課題を包括的に比較する。
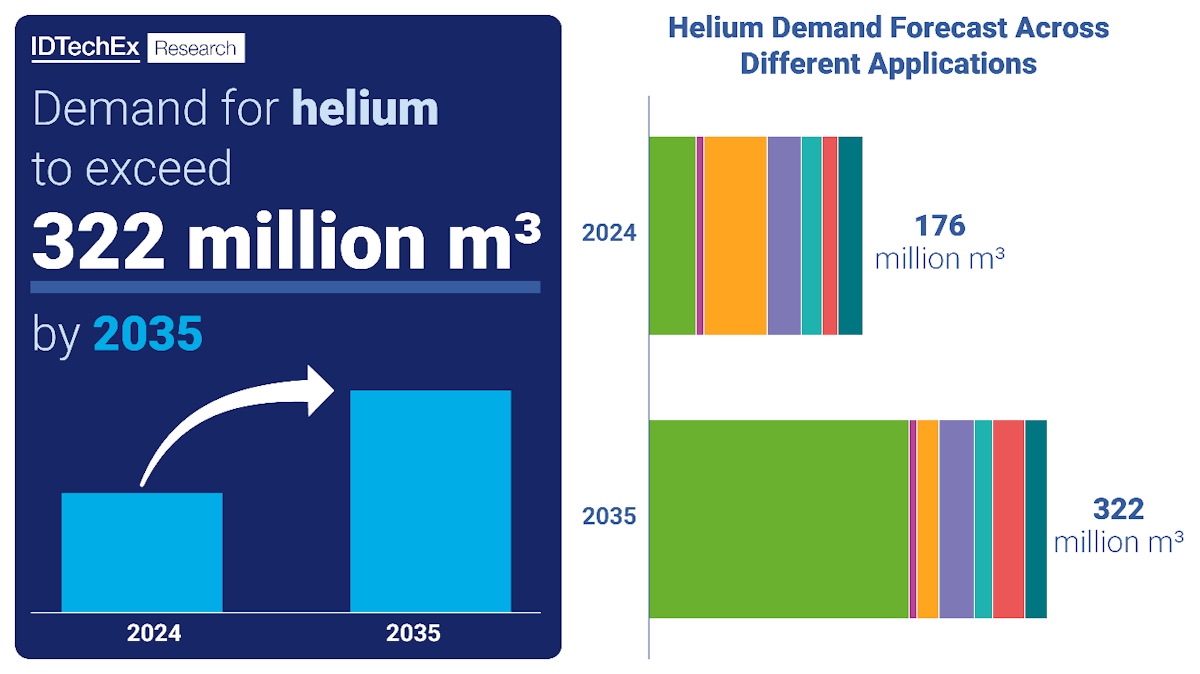
図2:ヘリウム需要の成長予測 出典 IDTechEx
IDTechExの見通し
歴史的に、ヘリウム価格は低水準で推移してきたため、ヘリウム再生技術の革新、探査、採用を推進することは経済的に不可能であった。しかし、ヘリウム供給の安全性は、地政学的な緊張や市場に影響を与える多因子的な要因によって妨げられている。特に、ヘリウムに代わる実行可能な代替物質がない産業では、ヘリウム価格の上昇が、企業に節約戦略の検討や再生技術への投資を促す可能性が高い。
IDTechExの最新レポート「ヘリウム市場 2025-2035年」: ヘリウムの生産と供給、主な用途、見通し、そして産業界が慢性的な供給難に対処するためにヘリウムの節約方法(再生技術など)にどのように適応しているか、あるいは可能であれば代替品を採用しているかという動向に関する主要な市場洞察を提供している。節約戦略と代替品にもかかわらず、IDTechExはヘリウム需要が2024年から2035年にかけてほぼ倍増すると予測している。
主要な側面
本レポートは、ヘリウムの生産と供給、主な用途、見通し、慢性的な供給難に対処するために産業界がどのようにヘリウムの節約方法(再生技術など)に適応しているか、または可能な場合は代替品を採用しているかについての主要な市場洞察を提供しています。
本レポートでは、ヘリウムの世界的な生産能力と供給について、以下の評価とともに考察している:
半導体製造、光ファイバー製造、重要部品のリークテスト、航空宇宙、MRI用冷却超伝導体、NMR、粒子加速器、量子コンピューターなどの主要産業におけるヘリウムの役割について、以下の詳細な評価とともに取り上げる:
本レポートはまた、10年間の市場展望と予測を以下の分析とともに提供している:
目次
Summary
この調査レポートでは、ヘリウム生産の見通し、主要産業におけるヘリウムの役割、ヘリウム代替品の入手可能性と実行可能性、ヘリウム再生技術について批判的に評価しています。
主な掲載内容(目次より抜粋)
Report Summary
Helium is a finite resource that plays a critical role across several industries including medical imaging, thermal management systems for batteries, aerospace engineering, chemicals and pharmaceuticals, semiconductor manufacturing, fiber optics, particle physics, scientific balloons, and many more. Its high thermal conductivity, chemical inertness, and cryogenic properties uniquely lend itself to its applications with limited or no available alternatives in some cases. Owing to helium's key role in the energy transition (e.g. electric vehicles and batteries), digital transformation (electronics, AI, telecoms, etc.), and space exploration, it is classified as a critical mineral by governmental bodies, e.g. the EU and Canada. Despite its importance, due to a lack of production diversification and geopolitical strains, the helium market is renowned for its susceptibility to chronic supply shortages and price volatility.
IDTechEx's report critically assesses the outlook for helium production, the role of helium in key industries, the availability and viability of helium substitutes, and helium reclamation technologies. Market forecasts are given in yearly helium demand segmented by its main applications and yearly production capacity by region.
Figure 1: Key production sources and applications of helium. Source: IDTechEx
Helium in the Manufacturing Industry
Helium is widely used in manufacturing processes due to its cooling and inert properties. It is essential for thermal management during semiconductor production, fiber optics, and is a crucial component for quality control processes such as leak testing of parts including HVAC equipment, fuel tanks, battery packs, aerospace components, etc. It is also key for welding processes to produce numerous parts, including electrical and automotive components. In particular, advancing semiconductor manufacturing processes towards smaller nodes (critical for AI, autonomous vehicles, etc.) will also increase the semiconductor industry's reliance on helium, with no currently viable alternatives.
This report critically examines how these industries are navigating chronic helium supply challenges. Through interviews with key players, e.g. manufacturers of reclamation technologies such as Telstar and Rosendahl Nextrom, the report highlights the trends and market activity in helium conservation (e.g. investing in reclamation technologies) and adoption of helium substitutes where possible.
Helium as a Cryogen
With a normal boiling point of 4.2K, helium is the only liquid at temperatures close to absolute zero (0K). It is therefore critical for operations of superconducting devices such as MRI and NMR machines in medical and chemical industries, particle accelerators such as the Large Hadron Collider, and some nuclear fusion reactors. For quantum computing, several qubit modalities require cooling between 10mK and 4K in some aspects of the initialization, manipulation, and readout chain. To access mK (1mK = 0.001K) temperature, the use of helium within cryostats is currently essential.
In recent decades, MRI scanners have been the leading application of helium by end-use. However, improvements in hardware design (e.g. sealed-for-life designs), software (e.g. AI, deep learning), and material developments (e.g. metamaterials, high-temperature superconductors) are heralding a success story in reducing helium requirements. This report critically analyses the technological advances driving emerging trends in helium demand for MRI, NMR, quantum computing, and more.
Helium in the Aerospace Industry
Helium plays a significant role in many aspects of the aerospace industry. Helium is used as an inert gas to purge hydrogen systems, pressurize ground and flight fluid systems, leak-test components, and as a shielding gas during precision welding. It is also used as a cryogen to cool components. Over the last five years, the frequency of orbital launches has surged, with commercial entities becoming increasingly pivotal to the industry's expansion. This growth underscores the critical role of helium, further cementing its status as an indispensable resource within the sector. IDTechEx's report provides a 10-year forecast detailing the anticipated demand for helium within the aerospace sector.
Trends in Helium Production
Although helium production capacity is expected to increase with Qatar and Russia expected to ramp up production, it does not necessarily guarantee a disruption-free helium supply moving forward when considering geopolitical tensions.
A growing number of small independent players are exploring primary/green helium from geological reserves where it is present in non-hydrocarbon gases. Nonetheless, elucidating the prospects for production capacity in the medium and long term requires extensive data and validation. These projects are leveraging low-capex separation systems, e.g. membrane and PSA technologies to upgrade and purify helium at well sites or local processing facilities. Informed by insights gleaned from providers of helium separation technologies, e.g. UGS and Generon, this report comprehensively compares the merits and challenges of helium separation and purification technologies.
Figure 2: Forecast of growth for helium demand. Source: IDTechEx
IDTechEx Outlook
Historically, helium pricing has been low which rendered it economically unfeasible to drive innovations, explorations, and adoption of helium reclamation technologies. However, helium supply security is encumbered by geopolitical tensions and multifactorial contributions that affect the market. Specifically in industries where there are no viable alternatives to helium, higher helium prices are likely to push companies to consider conservation strategies and invest in reclamation technologies.
IDTechEx's latest report on Helium Market 2025-2035: Applications, Alternatives, and Reclamation provides key market insights into the production and supply of helium, the major applications, outlook, and trends in how industries are adapting to cope with chronic supply challenges with helium conservation methods (e.g. reclamation technologies) or adopting substitutes where possible. Despite conservation strategies and substitutions, IDTechEx forecasts the demand for helium will nearly double from 2024 to 2035.
Key Aspects
The report provides key market insights into the production and supply of helium, the major applications, outlook and trends in how industries are adapting to cope with chronic supply challenges with helium conservation methods (e.g. reclamation technologies) and/or adopting substitutes where possible.
The report considers the global production capacity and supply of helium with an assessment of:
The role of helium in key industries, such as semiconductor manufacturing, fiber optic manufacturing, leak testing of critical components, aerospace, cooling superconductors for MRI, NMR, particle accelerators, quantum computers, and more, are covered with detailed evaluations of:
The report also provides 10 year market outlook and forecasts with analysis on:
Table of Contents
ご注文は、お電話またはWEBから承ります。お見積もりの作成もお気軽にご相談ください。本レポートと同分野(ケミカル)の最新刊レポート
IDTechEx社の 先端材料 - Advanced Materials分野 での最新刊レポート
よくあるご質問IDTechEx社はどのような調査会社ですか?IDTechExはセンサ技術や3D印刷、電気自動車などの先端技術・材料市場を対象に広範かつ詳細な調査を行っています。データリソースはIDTechExの調査レポートおよび委託調査(個別調査)を取り扱う日... もっと見る 調査レポートの納品までの日数はどの程度ですか?在庫のあるものは速納となりますが、平均的には 3-4日と見て下さい。
注文の手続きはどのようになっていますか?1)お客様からの御問い合わせをいただきます。
お支払方法の方法はどのようになっていますか?納品と同時にデータリソース社よりお客様へ請求書(必要に応じて納品書も)を発送いたします。
データリソース社はどのような会社ですか?当社は、世界各国の主要調査会社・レポート出版社と提携し、世界各国の市場調査レポートや技術動向レポートなどを日本国内の企業・公官庁及び教育研究機関に提供しております。
|
|




.png)
.png)